CCNA Module2 Pactice Quiz
-
What are two functions of a router? (Choose two.)
-
It connects multiple IP networks.
-
It controls the flow of data via the use of Layer 2 addresses.
-
It determines the best path to send packets.
-
It manages the VLAN database.
-
It increases the size of the broadcast domain
-
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) is a certification which offers a wide range of knowledge on the topic of networking, and as such gives students the opportunity to pursue an equally vast range of careers in the field. Take this CCNA practice quiz to see how your studies are going so far!
(55).webp)
Quiz Preview
- 2.
Which network design feature requires the deployment of a classless routing protocol?
-
Private IP addressing
-
Advertising default routes
-
Variable length subnet masks
-
Summarization on major network boundaries
Correct Answer
A. Variable length subnet masksExplanation
Variable length subnet masks (VLSM) is a network design feature that allows for the creation of subnets with different subnet mask lengths within a single network. This enables more efficient allocation of IP addresses and allows for better utilization of available address space. Classless routing protocols, such as OSPF and EIGRP, support VLSM by allowing routers to advertise subnets with different subnet mask lengths. Therefore, the deployment of a classless routing protocol is required to implement VLSM in a network design.Rate this question:
-
- 3.
A static route has been configured on a router. However, the destination network no longer exists. What should an administrator do to remove the static route from the routing table?
-
Change the routing metric for that route.
-
Nothing. The static route will go away on its own.
-
Change the administrative distance for that route.
-
Remove the route using the no ip route command.
Correct Answer
A. Remove the route using the no ip route command.Explanation
To remove a static route from the routing table, an administrator should use the "no ip route" command. This command is used to remove a specific route by specifying the destination network and subnet mask. By using this command, the administrator can effectively remove the static route that is no longer needed or valid.Rate this question:
-
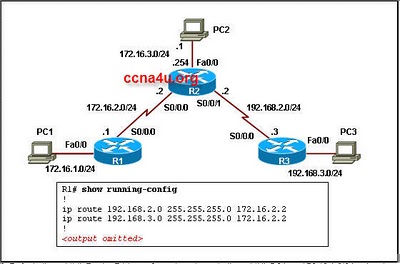
- 4.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is accessing router R1 from the console port. Once the administrator is connected to the router, which password should the administrator enter at the R1> prompt to access the privileged EXEC mode?
-
Cisco001
-
Cisco123
-
Cisco789
-
Cisco901
Correct Answer
A. Cisco789Explanation
The correct password that the administrator should enter at the R1> prompt to access the privileged EXEC mode is Cisco789.Rate this question:
-
- 5.
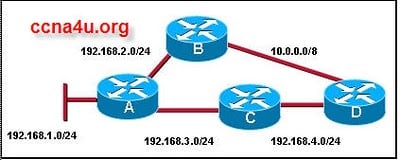
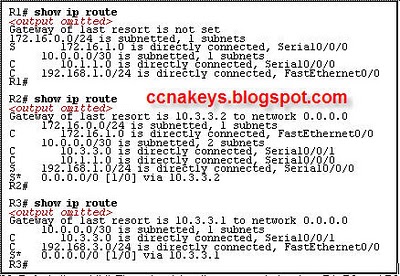
Refer to the exhibit. All router interfaces are configured with an IP address and are operational. If no routing protocols or static routes are configured, what information will be included in the show ip route command output for router A?
-
All of the 192.168.x.0 networks will be in the routing table.
-
Routes to networks 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.2.0/24, and 192.168.3.0/24 will be in the routing table.
-
The routing table will be empty because routes and dynamic routes have not been configured.
-
A default route is automatically installed in the routing table to allow connectivity between the networks.
Correct Answer
A. Routes to networks 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.2.0/24, and 192.168.3.0/24 will be in the routing table.Explanation
The correct answer is that routes to networks 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.2.0/24, and 192.168.3.0/24 will be in the routing table. This is because the router interfaces are configured with IP addresses and are operational, so the router will automatically include these directly connected networks in its routing table. However, since no routing protocols or static routes are configured, there will be no other routes in the routing table.Rate this question:
-
- 6.
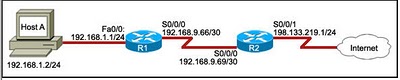
Refer to the exhibit. Host A is unable to access the Internet, and troubleshooting has revealed that this is due to an addressing problem. What is incorrectly configured in this network?the IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of R1 the subnet mask of the S0/0/0 interface of R1 the IP address of the S0/0/0 interface of R1 the subnet mask of the S0/0/0 interface of R2
-
The IP address of the Fa0/0 interface of R1
-
The subnet mask of the S0/0/0 interface of R1
-
The IP address of the S0/0/0 interface of R1
-
The subnet mask of the S0/0/0 interface of R2
Correct Answer
A. The IP address of the S0/0/0 interface of R1Explanation
The IP address of the S0/0/0 interface of R1 is incorrectly configured in this network. This misconfiguration is causing Host A to be unable to access the Internet.Rate this question:
-
- 7.
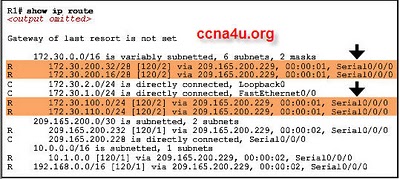
Refer to the exhibit. What information can be determined from the highlighted output?
-
R1 is originating the route 172.30.200.32/28.
-
Automatic summarization is disabled.
-
The 172.30.200.16/28 network is one hop away from R1.
-
A classful routing protocol is being used
Correct Answer
A. Automatic summarization is disabled.Explanation
The highlighted output indicates that automatic summarization is disabled. This means that the router is not automatically summarizing the routes it learns from its connected networks when advertising them to other routers. This allows for more specific routing information to be shared, which can be beneficial in certain network scenarios.Rate this question:
-
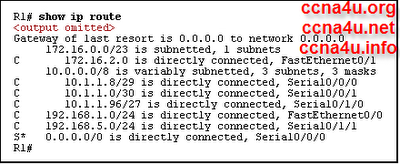
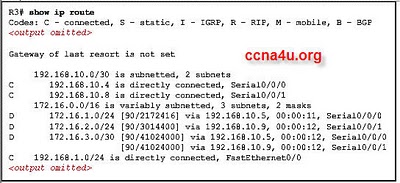
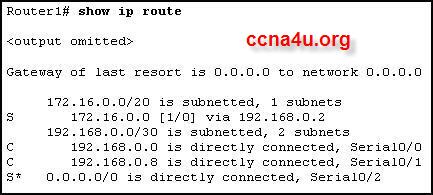
- 8.
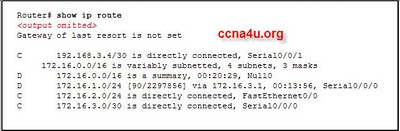
Refer to the exhibit. What happens to a packet that has 172.16.0.0/16 as the best match in the routing table that is shown? .
-
The packet is discarded.
-
The packet is flooded out all interfaces
-
The packet is forwarded via Serial0/0/0.
-
The packet is forwarded via FastEthernet0/0.
Correct Answer
A. The packet is discarded.Explanation
When a packet has 172.16.0.0/16 as the best match in the routing table, it means that this is the most specific match for the destination IP address of the packet. However, the exhibit does not show any corresponding interface or next hop for this route. In such cases, the router does not know how to forward the packet and it is therefore discarded.Rate this question:
-
- 9.
Refer to the exhibit. How many routes are child routes?
-
1
-
3
-
4
-
6
Correct Answer
A. 4Explanation
Based on the exhibit, there are four child routes. This can be determined by counting the number of routes that are connected to a main route or parent route. In this case, there are four routes that are connected to the main route, indicating that they are child routes.Rate this question:
-
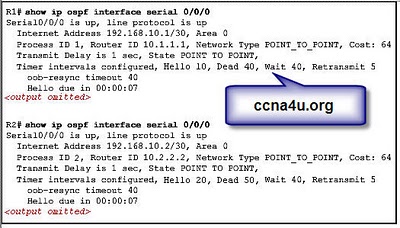
- 10.
Refer to the exhibit. Two routers are unable to establish an adjacency. What is the possible cause for this?
-
The two routers are connected on a multiaccess network.
-
The hello and dead intervals are different on the two routers.
-
They have different OSPF router IDs.
-
They have different process IDs
Correct Answer
A. The hello and dead intervals are different on the two routers.Explanation
The possible cause for the two routers being unable to establish an adjacency is that the hello and dead intervals are different on the two routers. The hello interval is the time interval between the transmission of hello packets, which are used to discover and maintain OSPF neighbor relationships. The dead interval is the time interval after which a neighbor is considered unreachable if no hello packets are received. If the hello and dead intervals are different on the two routers, they will not be able to synchronize their timing for neighbor discovery and maintenance, leading to the failure of adjacency establishment.Rate this question:
-
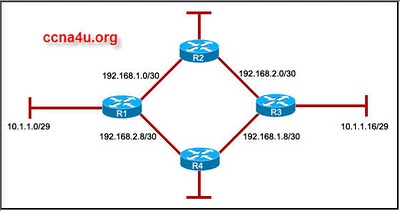
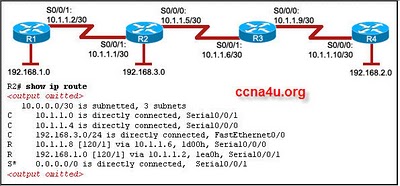
- 11.
Refer to the exhibit. All routers are running RIPv1. The two networks 10.1.1.0/29 and 10.1.1.16/29 are unable to access each other. What can be the cause of this problem?
-
Because RIPv1 is a classless protocol, it does not support this access.
-
RIPv1 does not support discontiguous networks.
-
RIPv1 does not support load balancing.
-
RIPv1 does not support automatic summarization.
Correct Answer
A. RIPv1 does not support discontiguous networks.Explanation
RIPv1 does not support discontiguous networks. This means that if the two networks, 10.1.1.0/29 and 10.1.1.16/29, are not contiguous (not directly connected), RIPv1 will not be able to route between them. Therefore, the lack of support for discontiguous networks in RIPv1 can be the cause of the problem where the two networks are unable to access each other.Rate this question:
-
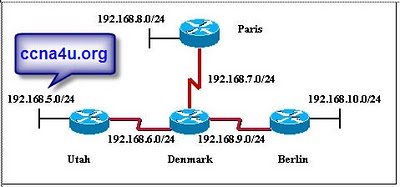
- 12.
Refer to exhibit. Given the topology shown in the exhibit, what three commands are needed to configure EIGRP on the Paris router? (Choose three.)
-
Paris(config)# router eigrp 100
-
Paris(config)# router eigrp Paris(config-router)# network 192.168.6.0
-
Paris(config-router)# network 192.168.7.0
-
Paris(config-router)# network 192.168.8.0
-
Paris(config-router)# network 192.168.9.0
Correct Answer(s)
A. Paris(config)# router eigrp 100
A. Paris(config-router)# network 192.168.7.0
A. Paris(config-router)# network 192.168.8.0Explanation
The three commands needed to configure EIGRP on the Paris router are "Paris(config)# router eigrp 100", "Paris(config-router)# network 192.168.7.0", and "Paris(config-router)# network 192.168.8.0". The first command enables EIGRP routing protocol on the router with an autonomous system number of 100. The second and third commands advertise the network 192.168.7.0 and 192.168.8.0 respectively, allowing EIGRP to form neighbor relationships and exchange routing information with other routers in those networks.Rate this question:
-
- 13.
A network is configured with the IP, IPX, and AppleTalk protocols. Which routing protocol is recommended for this network?
-
RIPv1
-
RIPv2
-
EIGRP
-
OSPF
Correct Answer
A. EIGRPExplanation
EIGRP is recommended for a network configured with the IP, IPX, and AppleTalk protocols. EIGRP is a routing protocol developed by Cisco that supports multiple protocols and provides fast convergence, scalability, and load balancing. It is compatible with IP, IPX, and AppleTalk, making it suitable for this network configuration. RIPv1 and RIPv2 are older routing protocols that may not support all the required protocols, while OSPF is primarily designed for IP networks.Rate this question:
-
- 14.
12. What two routing protocols use a hierarchal network topology? (Choose two.)
-
IS-IS
-
EIGRP
-
OSPF
-
RIPv1
-
RIPv2
Correct Answer(s)
A. IS-IS
A. OSPFExplanation
IS-IS and OSPF are both routing protocols that use a hierarchical network topology. This means that they organize the network into different levels or areas, with each level having its own routing table. This hierarchy helps to improve scalability and efficiency in large networks. IS-IS and OSPF both use a link-state routing algorithm, which allows for the exchange of routing information between routers in the network. This information is used to build a complete picture of the network topology and determine the best path for forwarding packets.Rate this question:
-
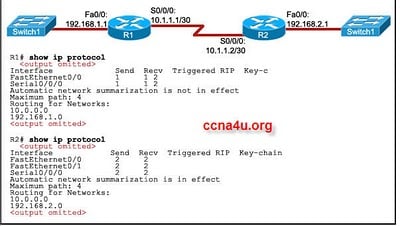
- 15.
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is planning IP addressing of a new network. What part of this addressing scheme must be changed to allow communication between host A and the server?
-
The IP address of the server
-
The default gateway of host A
-
The IP address of host A
-
The default gateway of the server
Correct Answer
A. The IP address of the serverExplanation
To allow communication between host A and the server, the IP address of the server must be changed. The IP address of the server is a crucial component in establishing communication between devices on a network. If the IP address of the server is not properly configured or is incompatible with the addressing scheme of the network, host A will not be able to establish a connection with the server. Therefore, changing the IP address of the server is necessary to enable communication between host A and the server.Rate this question:
-
- 16.
3. Which router component is used to store the routing table?
-
Flash
-
NVRAM
-
ROM
-
SDRAM
Correct Answer
A. SDRAMExplanation
SDRAM stands for Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory. It is a type of computer memory that is used to store data and instructions temporarily while the router is operating. In the case of storing the routing table, SDRAM is used to hold the information about the available routes and their associated metrics. This allows the router to make informed decisions about how to forward packets based on the routing table stored in SDRAM.Rate this question:
-
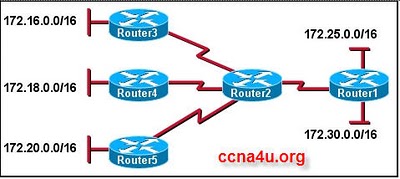
- 17.
Refer to the exhibit. What summary address can Router2 advertise to Router1 to reach the three networks on Routers 3, 4, and 5 without advertising any public address space or overlapping the networks on Router1?
-
172.16.0.0/8
-
172.16.0.0/10
-
172.16.0.0/13
-
172.16.0.0/20
-
172.16.0.0/24
Correct Answer
A. 172.16.0.0/13Explanation
Router2 can advertise the summary address 172.16.0.0/13 to Router1 in order to reach the three networks on Routers 3, 4, and 5 without advertising any public address space or overlapping the networks on Router1. This summary address encompasses the networks 172.16.0.0/24, 172.16.0.0/20, and 172.16.0.0/13, effectively summarizing them into a single address range.Rate this question:
-
- 18.
What command would the network administrator apply to a router that is running OSPF to advertise the entire range of addresses included in 172.16.0.0/19 in area 0?
-
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
-
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
-
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
-
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.31.255 area 0
Correct Answer
A. R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.31.255 area 0Explanation
The correct answer is R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.31.255 area 0. This command is used to advertise the entire range of addresses included in the 172.16.0.0/19 network in area 0 of the OSPF routing protocol. The 0.0.31.255 subnet mask is used to include all addresses from 172.16.0.0 to 172.16.31.255.Rate this question:
-
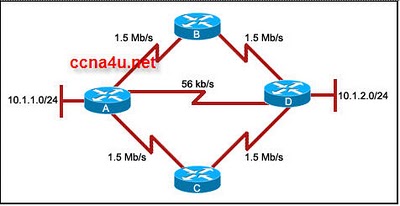
- 19.
Refer to the exhibit. All routers are properly configured to use the EIGRP routing protocol with default settings, and the network is fully converged. Which statement correctly describes the path that the traffic will use from the 10.1.1.0/24 network to the 10.1.2.0/24 network?
-
It will use the A-D path only.
-
It will use the path A-D, and the paths A-C-D and A-B-D will be retained as the backup paths.
-
It will use all the paths equally in a round-robin fashion.
-
The traffic will be load-balanced between A-B-D and A-C-D.
Correct Answer
A. The traffic will be load-balanced between A-B-D and A-C-D.Explanation
The correct answer is that the traffic will be load-balanced between paths A-B-D and A-C-D. This means that the traffic will be divided between these two paths, allowing for better utilization of network resources and potentially improving overall network performance.Rate this question:
-
- 20.
Which two statements are true regarding link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
-
They are aware of the complete network topology.
-
They offer rapid convergence times in large networks.
-
They do not include subnet masks in their routing updates.
-
They rely on decreasing hop counts to determine the best path.
-
They do not work well in networks that require special hierarchical designs.
Correct Answer(s)
A. They are aware of the complete network topology.
A. They offer rapid convergence times in large networks.Explanation
Link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF and IS-IS, maintain a complete view of the network topology by exchanging link-state advertisements (LSAs) with neighboring routers. This allows them to have accurate and up-to-date information about the network, including the state of each link and the shortest path to each destination. As a result, they can make more informed routing decisions. Additionally, link-state protocols have faster convergence times compared to distance-vector protocols, as they only need to update the affected routers with the changes in the network rather than propagating the entire routing table.Rate this question:
-
- 21.
A network administrator needs to assign the very last usable IP address in the 172.24.64.0/18 network range to the router interface that serves this LAN. Which IP address should the administrator configure on the interface?
-
172.16.128.154/18
-
172.16.255.254/18
-
172.24.64.254/18
-
172.24.127.254/18
Correct Answer
A. 172.24.127.254/18Explanation
The given IP address 172.24.127.254/18 falls within the 172.24.64.0/18 network range. The /18 subnet mask indicates that the first 18 bits of the IP address are used to identify the network, leaving the remaining 14 bits for host addresses. Since the network administrator needs to assign the last usable IP address, the host portion should be set to its maximum value, which is 11111111 in binary or 127 in decimal. Therefore, the correct IP address for the router interface is 172.24.127.254.Rate this question:
-
- 22.
Which two components are used to determine the router ID in the configuration of the OSPF routing process? (Choose two.)
-
The IP address of the first FastEthernet interface
-
The highest IP address of any logical interface
-
The highest IP address of any physical interface
-
The default gateway IP address
-
The priority value of 1 on any physical interface
Correct Answer(s)
A. The highest IP address of any logical interface
A. The highest IP address of any physical interfaceExplanation
The router ID in the configuration of the OSPF routing process is determined by the highest IP address of any logical interface and the highest IP address of any physical interface. These two components are used to uniquely identify the router within the OSPF network. The router ID is important for OSPF to establish adjacencies and calculate the shortest path to destination networks. The highest IP address of any logical interface and physical interface are used to ensure that the router ID remains stable even if interface configurations change.Rate this question:
-
- 23.
Refer to the exhibit. The show cdp neighbors command was run at R1. Which two facts about the newly detected device can be determined from the output? (Choose two.)
-
ABCD is a router that is connected to R1.
-
ABCD is a non-CISCO device that is connected to R1.
-
The device is connected at the Serial0/0/1 interface of R1.
-
R1 is connected at the S0/0/1 interface of device ABCD.
-
ABCD does not support switching capability.
Correct Answer(s)
A. ABCD is a router that is connected to R1.
A. The device is connected at the Serial0/0/1 interface of R1.Explanation
From the output of the "show cdp neighbors" command, it can be determined that ABCD is a router that is connected to R1. This is indicated by the fact that ABCD is listed as a neighbor device. Additionally, it can be determined that the device is connected at the Serial0/0/1 interface of R1. This is indicated by the interface information provided in the output.Rate this question:
-
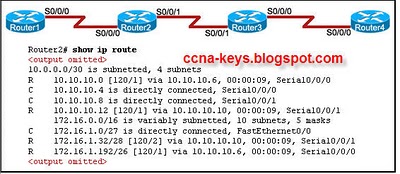
- 24.
Refer to the exhibit. Which router is advertising subnet 172.16.1.32/28?
-
Router1
-
Router2
-
Router3
-
Router4
Correct Answer
A. Router4Explanation
Based on the given exhibit, it can be inferred that router4 is advertising subnet 172.16.1.32/28.Rate this question:
-
- 25.
Refer to the exhibit. A ping between host A and host B is successful, but pings from host A to operational hosts on the Internet fail. What is the reason for this problem?
-
The FastEthernet interface of R1 is disabled.
-
One of the default routes is configured incorrectly.
-
A routing protocol is not configured on both routers.
-
The default gateway has not been configured on host A.
Correct Answer
A. One of the default routes is configured incorrectly.Explanation
The reason for the problem is that one of the default routes is configured incorrectly. This means that the router is not able to properly route traffic to hosts on the Internet. The successful ping between host A and host B indicates that the local network connectivity is fine, but the issue lies in the routing of traffic beyond the local network.Rate this question:
-
- 26.
Refer to the exhibit. The network has three connected routers: R1, R2, and R3. The routes of all three routers are displayed. All routers are operational and pings are not blocked on this network. Which ping will fail?
-
From R1 to 172.16.1.1
-
From R1 to 192.168.3.1
-
From R2 to 192.168.1.1
-
From R2 to 192.168.3.1
Correct Answer
A. From R1 to 192.168.3.1Explanation
The ping from R1 to 192.168.3.1 will fail because there is no route to that destination network in the routing table of R1.Rate this question:
-
- 27.
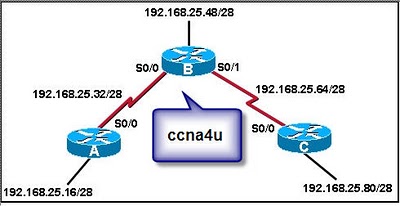
A network administrator has enabled RIP on routers B and C in the network diagram. Which of the following commands will prevent RIP updates from being sent to Router A?
-
A(config)# router rip A(config-router)# passive-interface S0/0
-
B(config)# router rip B(config-router)# network 192.168.25.48 B(config-router)# network 192.168.25.64
-
A(config)# router rip A(config-router)# no network 192.168.25.32
-
B(config)# router rip B(config-router)# passive-interface S0/0
-
A(config)# no router rip
Correct Answer
A. B(config)# router rip B(config-router)# passive-interface S0/0Explanation
The command "B(config)# router rip B(config-router)# passive-interface S0/0" will prevent RIP updates from being sent to Router A. By configuring the interface S0/0 as passive, Router B will not send RIP updates out of that interface, effectively preventing Router A from receiving any RIP updates.Rate this question:
-
- 28.
2. When a router boots, what is the default order to locate the Cisco IOS if there is no boot system command?
-
ROM, TFTP server, flash
-
Flash, TFTP server, ROM
-
Flash, NVRAM, TFTP server
-
NVRAM, TFTP server, flash
Correct Answer
A. Flash, TFTP server, ROMExplanation
When a router boots, it first checks the flash memory for the Cisco IOS. If it is not found in the flash memory, the router then attempts to locate the IOS image from a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server. If the IOS image is still not found, the router will finally look for it in the ROM (Read-Only Memory). Therefore, the default order to locate the Cisco IOS if there is no boot system command is flash, TFTP server, ROM.Rate this question:
-
- 29.
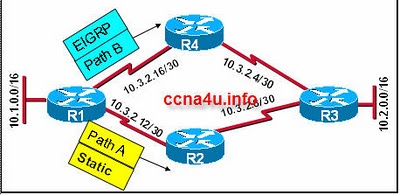
Refer to the exhibit. R1 knows two routes, Path A and Path B, to the Ethernet network attached to R3. R1 learned Path A to network 10.2.0.0/16 from a static route and Path B to network 10.2.0.0/16 from EIGRP. Which route will R1 install in its routing table?
-
Both routes are installed and load balancing occurs across both paths.
-
The route via Path B is installed because the EIGRP route has the best metric to network 10.2.0.0/16.
-
The route via Path A is installed because the static route has the best metric to network 10.2.0.0/16.
-
The route via Path B is installed because the EIGRP route has the lowest administrative distance to network 10.2.0.0/16.
-
The route via Path A is installed because the static route has the lowest administrative distance to network 10.2.0.0/16.
Correct Answer
A. The route via Path A is installed because the static route has the lowest administrative distance to network 10.2.0.0/16.Explanation
The route via Path A is installed because the static route has the lowest administrative distance to network 10.2.0.0/16. Administrative distance is a value assigned to different routing protocols to determine their reliability or trustworthiness. In this case, the static route has a lower administrative distance than the EIGRP route, so it is considered more reliable and is chosen as the preferred route.Rate this question:
-
- 30.
What is the function of the OSPF LSR packet? .
-
It is used to confirm the receipt of LSUs.
-
It is used to establish and maintain adjacency with other OSPF routers.
-
It is used by the receiving routers to request more information about any entry in the DBD.
-
It is used to check the database synchronization between routers
Correct Answer
A. It is used by the receiving routers to request more information about any entry in the DBD.Explanation
The OSPF LSR packet is used by the receiving routers to request more information about any entry in the DBD (Database Description). This packet allows the receiving router to obtain additional details or updates from the sending router regarding the entries in the database. It helps in ensuring that the routers have the most up-to-date information about the network topology and can make informed routing decisions.Rate this question:
-
- 31.
What does RIP use to reduce convergence time in a larger network?
-
It uses multicast instead of broadcast to send routing updates.
-
It reduces the update timer to 15 seconds if there are more than 10 routes.
-
It uses triggered updates to announce network changes if they happen in between the periodic updates.
-
It uses random pings to detect if a pathway is down and therefore is preemptive on finding networks that are down
Correct Answer
A. It uses triggered updates to announce network changes if they happen in between the periodic updates.Explanation
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) uses triggered updates to announce network changes if they happen in between the periodic updates. This means that when a network change occurs, such as a link failure or a new route becoming available, RIP immediately sends an update to inform other routers about the change. This helps to reduce the convergence time in a larger network, as routers can quickly adjust their routing tables based on the updated information.Rate this question:
-
- 32.
What should be considered when troubleshooting a problem with the establishment of neighbor relationships between OSPF routers? (Choose two.)
-
OSPF interval timers mismatch
-
Administrative distance mismatch
-
Interface network type mismatch
-
No loopback interface configured
-
Gateway of last resort not redistributed
Correct Answer(s)
A. OSPF interval timers mismatch
A. Interface network type mismatchExplanation
When troubleshooting a problem with the establishment of neighbor relationships between OSPF routers, two factors should be considered. First, OSPF interval timers mismatch can cause issues as the routers may not be able to synchronize their timing, leading to failed neighbor relationships. Second, interface network type mismatch can also cause problems as OSPF requires that all routers on a network segment have the same network type configured. If there is a mismatch, the routers may not be able to form neighbor relationships.Rate this question:
-
- 33.
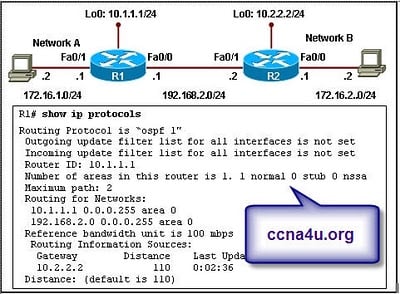
Refer to the exhibit. All interfaces are configured with the correct IP addresses and subnet masks. OSPF has been configured as the routing protocol. During troubleshooting, it is determined that hosts on network B can ping the Lo0 interface on R1 but are unable to reach hosts on network A. What is the cause of the problem?
-
Routers R1 and R2 have incorrect router IDs configured.
-
Router R1 is unable to form a neighbor relationship with router R2.
-
Routers R1 and R2 have been configured in different OSPF areas.
-
The configuration of router R1 fails to include network A in the OSPF routing process
Correct Answer
A. The configuration of router R1 fails to include network A in the OSPF routing processExplanation
The cause of the problem is that the configuration of router R1 fails to include network A in the OSPF routing process. This means that router R1 is not advertising network A to the OSPF neighbors, including router R2. As a result, hosts on network B can ping the Lo0 interface on R1 because it is directly connected, but they cannot reach hosts on network A because the OSPF routing table does not have the necessary information to route traffic to that network.Rate this question:
-
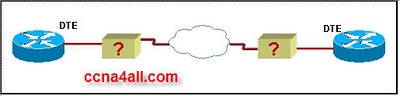
- 34.
Which of the following could describe the devices labeled "?" in the graphic? (Choose three.)
-
DCE
-
CSU/DSU
-
LAN switch
-
Modem
-
Hub
Correct Answer(s)
A. DCE
A. CSU/DSU
A. ModemExplanation
The devices labeled "?" in the graphic could be a DCE (Data Communications Equipment), a CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit), and a modem. A DCE is responsible for establishing and maintaining communication between data terminal equipment (DTE) and a network. A CSU/DSU is a device used to connect a digital circuit to a higher-speed line, such as a T1 line. A modem is a device that modulates and demodulates signals to transmit data over telephone lines. These devices are commonly used in networking to establish connections and facilitate data transmission.Rate this question:
-
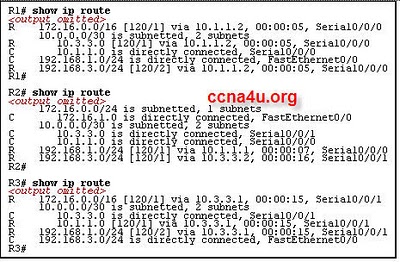
- 35.
Refer to the exhibit. The network has three connected routers: R1, R2 and R3. The routes of all three routers are displayed. What can be verified from the output?
-
R1 and R3 are connected to each other via the S0/0/0 interface.
-
The IP address of the S0/0/0 interface of R1 is 10.1.1.2.
-
The IP address of the S0/0/1 interface of R2 is 10.3.3.2.
-
R2 is connected to the S0/0/1 interface of R3.
Correct Answer
A. R2 is connected to the S0/0/1 interface of R3.Explanation
The output from the routes of all three routers indicates that R2 is connected to the S0/0/1 interface of R3.Rate this question:
-
- 36.
Refer to the exhibit. Both routers are using the RIP protocol. Devices on the 192.168.1.1 network can ping the S0/0/0 interface on R2 but cannot ping devices on the 192.168.2.1 network. What is a possible cause of this problem?
-
The routers are configured with different versions of RIP.
-
R2 is not forwarding the routing updates.
-
The R1 configuration should include the no auto-summary command.
-
The maximum path number has been exceeded.
Correct Answer
A. The routers are configured with different versions of RIP.Explanation
The possible cause of the problem is that the routers are configured with different versions of RIP. This can lead to incompatibility between the routers, causing devices on the 192.168.1.1 network to be able to ping the S0/0/0 interface on R2 but not devices on the 192.168.2.1 network.Rate this question:
-
- 37.
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true based on the exhibited output? (Choose two.)
-
Automatic summarization is disabled.
-
The EIGRP routing protocol is being used.
-
There is one feasible successor in the routing table.
-
The serial interface S0/0/0 is administratively down.
-
The router is originating the route to 172.16.1.0/24 via the S0/0/0 interface
Correct Answer(s)
A. Automatic summarization is disabled.
A. The EIGRP routing protocol is being used.Explanation
Based on the exhibited output, we can determine that automatic summarization is disabled because the output does not display any summarized routes. Additionally, we can conclude that the EIGRP routing protocol is being used because the output shows the prefix "D" which stands for EIGRP.Rate this question:
-
- 38.
6. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator issues the command no ip classless on Router1. What forwarding action will take place on a packet that is received by Router1 and is destined for host 192.168.0.26?
-
The packet will be dropped.
-
The packet will be forwarded to the gateway of last resort.
-
The packet will match the 192.168.0.0 network and be forwarded out Serial 0/0.
-
The packet will most closely match the 192.168.0.8 subnet and be forwarded out Serial 0/1
Correct Answer
A. The packet will be dropped.Explanation
When the command "no ip classless" is issued on Router1, it means that the router will not perform classless routing. In this scenario, the packet received by Router1 and destined for host 192.168.0.26 will not be forwarded to any specific network or interface. Instead, it will be dropped, as the router does not have the capability to determine the appropriate forwarding action for the packet.Rate this question:
-
- 39.
Which two statements are correct about the split horizon with poison reverse method of routing loop prevention? (Choose two.)
-
It is enabled by default on all Cisco IOS implementations
-
It assigns a value that represents an infinite metric to the poisoned route.
-
It instructs routers to hold all changes that might affect routes, for a specified period of time.
-
It sends back the poisoned route update to the same interface from where it was received.
-
It limits the number of hops a packet can traverse through the network before it is discarded
Correct Answer(s)
A. It assigns a value that represents an infinite metric to the poisoned route.
A. It sends back the poisoned route update to the same interface from where it was received.Explanation
The split horizon with poison reverse method of routing loop prevention assigns an infinite metric to the poisoned route, indicating that the route is unreachable. This helps prevent routing loops by making the route undesirable for selection. Additionally, this method sends back the poisoned route update to the same interface from where it was received. This ensures that the routers are aware of the poisoned route and can update their routing tables accordingly.Rate this question:
-
- 40.
Which three statements describe the operation of routing with EIGRP? (Choose three.)
-
As new neighbors are discovered, entries are placed in a neighbor table.
-
If the feasible successor has a higher advertised cost than the current successor route, then it becomes the primary route.
-
If hello packets are not received within the hold time, DUAL must recalculate the topology.
-
The reported distance is the distance to a destination as advertised by a neighbor.
-
EIGRP maintains full knowledge of the network topology in the topology table and exchanges full routing information with neighboring routers in every update.
Correct Answer(s)
A. As new neighbors are discovered, entries are placed in a neighbor table.
A. If hello packets are not received within the hold time, DUAL must recalculate the topology.
A. The reported distance is the distance to a destination as advertised by a neighbor.Explanation
EIGRP uses a neighbor table to keep track of newly discovered neighbors. If hello packets are not received within the hold time, the DUAL (Diffusing Update Algorithm) must recalculate the network topology. The reported distance is the distance to a destination as advertised by a neighboring router.Rate this question:
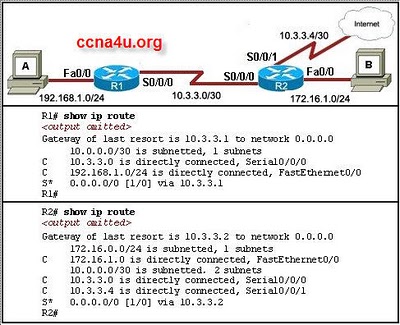
-
- 41.
Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 is configured as shown in the exhibit. PC1 on 172.16.1.0/24 network can reach the default gateway on R1. The rest of the routers are configured with the correct IP addresses on the interfaces. Routers R2 and R3 do not have static or dynamic routing enabled. How far will PC1 be able to successfully ping?
-
Router R1 Fa0/0 interface
-
Router R1 S0/0/0 interface
-
Router R2 S0/0/0 interface
-
Router R2 Fa0/0 and S0/0/1 interfaces
-
Router R3 Fa0/0 and S0/0/0 interfaces
Correct Answer
A. Router R1 S0/0/0 interfaceExplanation
PC1 will be able to successfully ping up to the interface connected to router R1 S0/0/0. Since routers R2 and R3 do not have static or dynamic routing enabled, they will not be able to forward the ping packets beyond their own interfaces. Therefore, PC1 will not be able to reach any devices connected to routers R2 and R3.Rate this question:
-
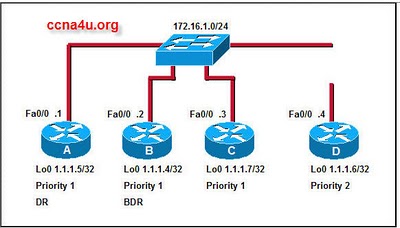
- 42.
Refer to the exhibit. The interface addresses and OSPF priorities are configured as shown. Because of the boot order of the routers, router A is currently the DR and router B is the BDR. If router A fails and is replaced the next day by a new router, router D, what OSPF protocol action or actions will happen?
-
Router D will be elected DR, and router C will become the BDR.
-
Router D will be elected DR, and router B will remain the BDR.
-
Router C will become the DR, and router B will become the BDR.
-
Router B will remain the BDR, and OSPF will function on the segment via the use of only the
Correct Answer
A. Router D will be elected DR, and router C will become the BDR.Explanation
In OSPF, the DR (Designated Router) is responsible for maintaining neighbor relationships with all routers on a multiaccess network, while the BDR (Backup Designated Router) acts as a backup in case the DR fails. When router A fails and is replaced by router D, the election process for the DR and BDR will occur. Since router D has the highest OSPF priority among the routers, it will be elected as the new DR. Router C, which has the second-highest OSPF priority, will become the new BDR. Therefore, the correct answer is "Router D will be elected DR, and router C will become the BDR."Rate this question:
-
- 43.
Refer to the exhibit. What action will R2 take for a packet that is destined for 192.168.2.0?
-
It will forward the packet via the S0/0/0 interface.
-
It will forward the packet via the Fa0/0 interface.
-
It will forward the packet to R1
-
It will drop the packet.
Correct Answer
A. It will forward the packet to R1Explanation
R2 will forward the packet to R1 because the destination IP address 192.168.2.0 is not directly connected to R2. R2 does not have a directly connected network with that IP address, so it will send the packet to its default gateway, which is R1, for further routing.Rate this question:
-
- 44.
5. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true concerning the routing configuration?
-
Using dynamic routing instead of static routing would have required fewer configuration steps.
-
The 10.1.1.0/24 and 10.1.2.0/24 routes have adjacent boundaries and should be summarized.
-
Packets routed to the R2 Fast Ethernet interface require two routing table lookups.
-
The static route will not work correctly
Correct Answer
A. Packets routed to the R2 Fast Ethernet interface require two routing table lookups.Explanation
The correct answer is "Packets routed to the R2 Fast Ethernet interface require two routing table lookups." This means that when packets are sent to the R2 Fast Ethernet interface, the router needs to perform two lookups in the routing table to determine the appropriate path for forwarding the packets. This could potentially slow down the routing process compared to other options, such as using dynamic routing protocols, which may require fewer steps and provide more efficient routing.Rate this question:
-
- 45.
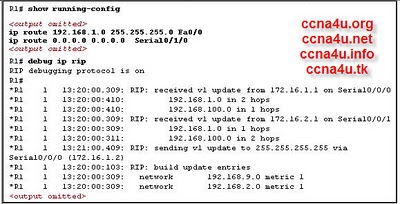
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output from the show running-config and debug ip rip commands, what are two of the routes that are added to the routing table of R1? (Choose two.)
-
R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.2.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/1
-
R 192.168.100.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.1.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
-
S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via FastEthernet0/0
-
R 192.168.9.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.2.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
-
R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.1.2, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
Correct Answer(s)
A. R 192.168.100.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.1.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
A. S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via FastEthernet0/0Explanation
Based on the output, the two routes that are added to the routing table of R1 are:
1. R 192.168.100.0/24 [120/1] via 172.16.1.1, 00:00:24, Serial0/0/0
2. S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via FastEthernet0/0
The first route is learned through RIP (Routing Information Protocol) and has a metric of 120/1. It is reachable via the next hop 172.16.1.1 and the outgoing interface is Serial0/0/0.
The second route is a static route (indicated by the "S" in the output) and has a metric of 1/0. It is reachable via the next hop FastEthernet0/0.
These routes are added to the routing table of R1 based on the information received from the RIP protocol and the static route configuration.Rate this question:
-
- 46.
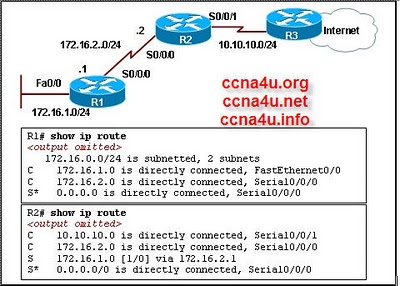
Refer to the exhibit. The users on the local network 172.16.1.0/24 complain that they are unable to connect to the Internet. What step should be taken to remedy the problem?
-
A new static route must be configured on R1 with the R3 serial interface as the next hop.
-
A new default route must be configured on R1 with the R3 serial interface as the next hop.
-
The default route on R2 should be configured with the R3 serial interface as the next hop.
-
The default route on R2 must be replaced with a new static route and the next hop should be the R1 FastEthernet interface
Correct Answer
A. The default route on R2 must be replaced with a new static route and the next hop should be the R1 FastEthernet interfaceExplanation
The correct answer suggests that the default route on R2 should be replaced with a new static route, with the next hop being the R1 FastEthernet interface. This means that R2 should be configured to send all traffic to R1's FastEthernet interface, which will then route the traffic to the Internet. This is the most appropriate solution as it ensures that all traffic from the local network is directed towards R1 for further routing.Rate this question:
-
- 47.
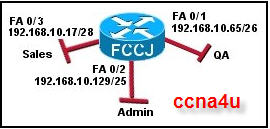
Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network properly. What is the cause?
-
The default gateway is incorrect.
-
The address is in the wrong subnet.
-
The host address and default gateway are swapped.
-
192.168.10.31 is the broadcast address for this subnet
Correct Answer(s)
A. The address is in the wrong subnet.
A. The host address and default gateway are swapped.
A. 192.168.10.31 is the broadcast address for this subnetExplanation
The cause for the PC not communicating properly with the network is that the address is in the wrong subnet. Additionally, the host address and default gateway are swapped, which further hinders communication. Furthermore, 192.168.10.31 is the broadcast address for this subnet.Rate this question:
-
Quiz Review Timeline (Updated): May 27, 2024 +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
-
Current Version
-
May 27, 2024Quiz Edited by
ProProfs Editorial Team -
Aug 06, 2010Quiz Created by
Kapper59
CCNA 2 - Chapitre 10
This quiz focuses on advanced networking topics under CCNA 2, assessing knowledge in Syslog severity levels, Cisco IOS licensing, Syslog server capabilities, VoIP implementation,...
Questions:
40 |
Attempts:
376 |
Last updated:
Mar 22, 2023
|
CCNA Routing & Switching 200-125: New Questions - Part 3
CCNA Routing & Switching 200-125: New Questions - Part 3 of 3.
Questions:
49 |
Attempts:
711 |
Last updated:
Mar 22, 2023
|
CCNA Routing & Switching 200-125: New Questions - Part 1
CCNA Routing & Switching 200-125: New Questions - Part 1 of 3.
Questions:
50 |
Attempts:
456 |
Last updated:
Mar 16, 2023
|
CCNA 4 Final Exam
The 'CCNA 4 Final Exam' assesses knowledge on WAN technologies, network design, and related policies. It covers topics such as WAN characteristics, privacy issues, network...
Questions:
145 |
Attempts:
271 |
Last updated:
Mar 18, 2023
|
CCNA 4 V6.0 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS 100% OPTION C
This CCNA 4 V6.0 Final Exam assesses key networking skills, focusing on differences between LAN and WAN, WAN technologies, and WAN solutions like MPLS and VSAT. It is crucial for...
Questions:
55 |
Attempts:
414 |
Last updated:
Mar 22, 2023
|
CCNA 4 V6.0 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS 100% OPTION B
This CCNA 4 V6.0 FINAL EXAM covers essential topics for corporate WAN implementation, WAN providers, WAN-specific devices, DWDM technology, and MPLS paths. It assesses skills...
Questions:
55 |
Attempts:
413 |
Last updated:
Mar 21, 2023
|
 Back to top
Back to top