What Is Structures and Functions of the Endocrine System? Explore Its Types, Uses & More
Lesson Overview
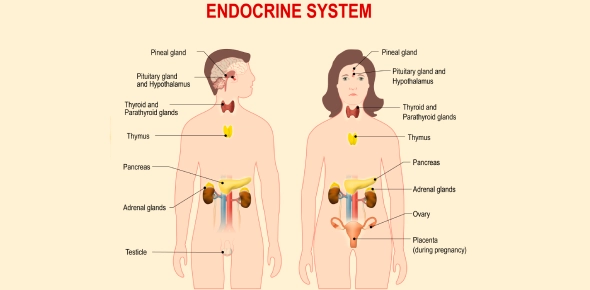
- What Is the Endocrine System and Why Does It Matter?
- How Do Endocrine and Exocrine Glands Differ?
- Why Is the Pituitary Called the "Master Gland"?
- How Do the Hypothalamus and Pituitary Work Together?
- What Roles Do the Pineal and Thymus Glands Play?
- Why Are Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Essential for Metabolism and Calcium?
- How Do Adrenal Glands Respond to Stress?
- What Role Does the Pancreas Play in Blood Sugar Regulation?
- How Do Ovaries and Testes Control Reproduction and Sexual Development?
- How Can You Study the Endocrine System Effectively?
When Sarah couldn't understand her fatigue, her doctor explained the issue involved the structures and functions of the endocrine system. Like Sarah, many overlook the system regulating our energy, growth, and stress responses. This lesson explores these vital glands and hormones, empowering you to grasp their importance clearly and effectively.
What Is the Endocrine System and Why Does It Matter?
In this section, we'll introduce the endocrine system. You'll learn how hormones work as chemical messengers and why they're essential for keeping your body stable and responsive.
The endocrine system consists of glands that release hormones directly into the bloodstream. Hormones regulate metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood. Unlike the nervous system, the endocrine system sends slower, lasting signals that affect many parts of your body simultaneously.
Take This Quiz
How Do Endocrine and Exocrine Glands Differ?
Next, we'll distinguish endocrine glands from exocrine glands. This will help you understand how hormones are released differently compared to substances like sweat or saliva.
Endocrine glands are ductless and release hormones directly into the bloodstream (e.g., pituitary and thyroid glands). Exocrine glands release substances through ducts onto body surfaces or into organs (e.g., sweat and salivary glands).
Why Is the Pituitary Called the "Master Gland"?
Here, we explore why the pituitary gland is central to the endocrine system. You'll understand its two lobes and the hormones each secretes.
Located at the base of the brain, the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands. It consists of two lobes:
- Anterior Pituitary: Produces hormones like Growth Hormone (GH), Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
- Posterior Pituitary: Stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus like Oxytocin and Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH).
Pituitary hormones control growth, metabolism, stress response, and reproductive processes.
How Do the Hypothalamus and Pituitary Work Together?
This section covers the critical relationship between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, highlighting how they coordinate endocrine functions.
The hypothalamus, part of the brain, controls the pituitary gland by releasing hormones. It tells the pituitary when to stimulate other glands like the thyroid and adrenals. This ensures that hormones are balanced in response to bodily needs.
What Roles Do the Pineal and Thymus Glands Play?
Here, we focus on two lesser-known glands: the pineal gland, controlling sleep cycles, and the thymus, critical for immune development.
- Pineal Gland: Produces melatonin, regulating your sleep-wake cycle based on light exposure.
- Thymus Gland: Located behind the sternum, helps develop the immune system during childhood by producing thymosin, which matures immune cells called T-cells.
Why Are Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Essential for Metabolism and Calcium?
You'll discover why maintaining metabolic rate and calcium balance relies on the thyroid and parathyroid glands.
- Thyroid Gland: Located in your neck, it produces hormones T3 and T4, controlling metabolism, energy levels, and growth.
- Parathyroid Glands: Four small glands behind the thyroid regulate blood calcium by releasing Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), which increases blood calcium levels.
Calcium regulation is crucial for bone strength, muscle contraction, and nerve function.
How Do Adrenal Glands Respond to Stress?
We'll explain how your adrenal glands help you cope with short-term and long-term stress by producing different hormones.
Located above the kidneys, the adrenal glands consist of two parts:
- Adrenal Medulla: Releases adrenaline for quick fight-or-flight responses, increasing heart rate and energy.
- Adrenal Cortex: Produces cortisol for sustained stress responses, regulating blood sugar, immune responses, and metabolism over time.
This dual-system allows your body to manage immediate threats and prolonged stress effectively.
What Role Does the Pancreas Play in Blood Sugar Regulation?
We'll discuss how the pancreas controls your blood sugar through insulin and glucagon and why this balance is vital.
The pancreas releases two key hormones from cell clusters called Islets of Langerhans:
- Insulin: Lowers blood glucose levels by allowing cells to absorb glucose from the blood.
- Glucagon: Raises blood glucose levels by signaling the liver to release stored glucose when sugar is low.
This precise control prevents hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, conditions that could severely disrupt bodily functions.
How Do Ovaries and Testes Control Reproduction and Sexual Development?
You'll learn how the reproductive glands, ovaries in females and testes in males, produce hormones essential for reproductive health and sexual characteristics.
- Ovaries: Produces estrogen and progesterone, regulating menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and female characteristics.
- Testes: Produce testosterone, controlling male characteristics, libido, and sperm production.
Both are regulated by pituitary hormones FSH and LH, maintaining reproductive health and fertility.
How Can You Study the Endocrine System Effectively?
Finally, we'll share proven tips to help you remember endocrine glands and hormones efficiently.
- Mnemonic aids: Use acronyms like "FLAT PEG" for pituitary hormones.
- Visual learning: Draw diagrams and flowcharts to understand gland locations and hormone pathways.
- Tables and charts: Organize the presentation of glands, hormones, functions, and target organs clearly.
- Practice scenarios: Solve quiz questions explaining the reasons behind the correct answers.
- Feedback loops: Understand hormonal negative feedback to master regulation concepts.
- Real-life connections: Link hormones to real-world issues (e.g., diabetes, stress responses).
Applying these techniques will significantly enhance your learning and retention.
Take This Quiz
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top
.webp)