CompTIA Network N10-004 2.1 - Cable Types
-
________ supports up to 10 Mbit/s Ethernet or 4 Mbit/s Token Ring.
-
Cat3
-
Cat5
-
Cat5e
-
Cat6
-
Cat6a
-
This quiz focuses on cable types relevant to the CompTIA Network N10-004 2.1 certification. It assesses knowledge on internal cable twisting, balanced pair operation, and the definitions and characteristics of STP and UTP. It also covers the capabilities of Cat3 and Cat5 cables.
(44).webp)
Quiz Preview
- 2.
________ supports up to 100 Mbit/s Ethernet.
-
Cat3
-
Cat5
-
Cat5e
-
Cat6
-
Cat6a
Correct Answer
A. Cat5Explanation
Cat5 is the correct answer because it supports up to 100 Mbit/s Ethernet. Cat3 supports up to 10 Mbit/s Ethernet, Cat5e supports up to 1000 Mbit/s Ethernet, Cat6 supports up to 10 Gbit/s Ethernet, and Cat6a supports up to 10 Gbit/s Ethernet with improved performance and bandwidth.Rate this question:
-
- 3.
________ supports up to 1 Gbit/s Ethernet.
-
Cat3
-
Cat5
-
Cat5e
-
Cat6
-
Cat6a
Correct Answer
A. Cat5eExplanation
Cat5e supports up to 1 Gbit/s Ethernet. Cat3 and Cat5 have lower data transfer rates, while Cat6 and Cat6a have higher data transfer rates. Therefore, Cat5e is the correct answer as it specifically supports up to 1 Gbit/s Ethernet.Rate this question:
-
- 4.
________ supports up to 10 Gbit/s Ethernet up to 100 meters.
-
Cat3
-
Cat5
-
Cat5e
-
Cat6
-
Cat6a
Correct Answer
A. Cat6aExplanation
Cat6a is the correct answer because it supports up to 10 Gbit/s Ethernet up to 100 meters. Cat3, Cat5, Cat5e, and Cat6 do not support speeds up to 10 Gbit/s. Cat6a is an enhanced version of Cat6, specifically designed to support higher data transfer rates and longer distances. It is capable of handling 10 Gbit/s Ethernet speeds over a distance of 100 meters, making it suitable for high-speed networking applications.Rate this question:
-
- 5.
Modems and direct device connections sometimes use a type of interface that transmit one bit at a time. This interface can directly network devices together via a null-modem connection. This interface can also be used to configure network devices.What is it?
Correct Answer
serial
SerialExplanation
The correct answer is "serial". Serial interfaces are commonly used in modems and direct device connections to transmit data one bit at a time. This type of interface allows devices to be directly networked together via a null-modem connection and can also be used to configure network devices.Rate this question:
- 6.
________ supports up to 10 Gbit/s Ethernet up to 55 meters.
-
Cat3
-
Cat5
-
Cat5e
-
Cat6
-
Cat6a
Correct Answer
A. Cat6Explanation
Cat6 supports up to 10 Gbit/s Ethernet up to 55 meters. Cat6 cables are designed to provide higher bandwidth and faster data transmission compared to previous categories such as Cat3, Cat5, and Cat5e. The improved specifications of Cat6 cables allow for better signal quality and reduced crosstalk, enabling higher data transfer rates over longer distances. Therefore, Cat6 is the correct answer as it meets the given requirements.Rate this question:
-
- 7.
Explain why cabling is twisted internally.
- 8.
Give a general idea of the makeup of balanced pair operation.
- 9.
Define STP and explain the physical makeup and benefits/drawbacks of using it.
- 10.
Define UTP and explain the physical makeup and benefits/drawbacks of using it.
- 11.
What is plenum and why is it important so far as networking is concerned?
- 12.
What is the riser and why is it important so far as networking is concerned?
- 13.
What are PVC and FEP and what are they usually referring to so far as networking is concerned?
- 14.
One type of cable can either be comprised of glass or plastic; features high bandwidths, long distance traversal, and low interference. What is it?
- 15.
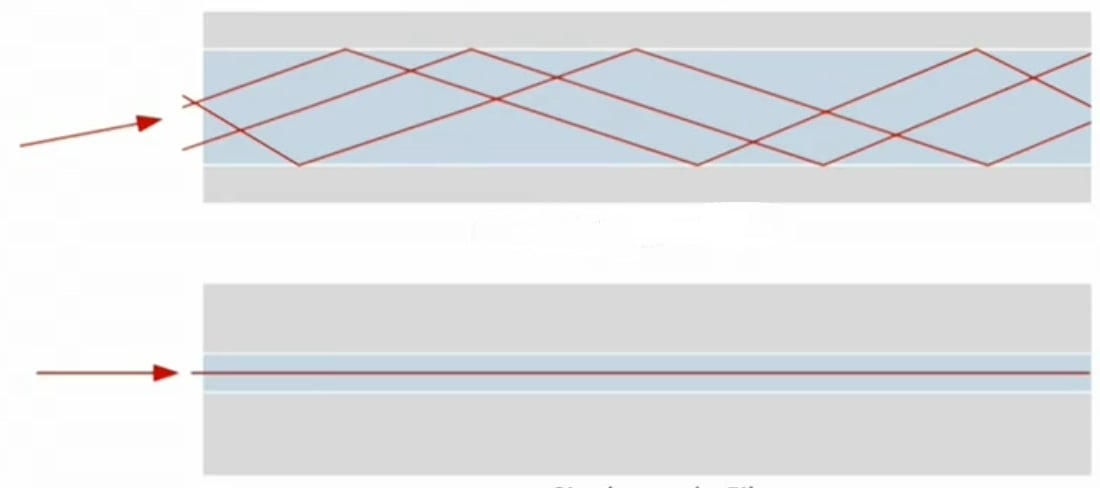
Explain what is being portrayed in this picture and the differences between the two types of transmission.
Quiz Review Timeline (Updated): Dec 5, 2023 +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
-
Current Version
-
Dec 05, 2023Quiz Edited by
ProProfs Editorial Team -
Mar 24, 2011Quiz Created by
Wickedang3l
Network+ Computer Ports Quiz
The Network+ Computer Ports Quiz assesses knowledge of key network port numbers essential for IT professionals. It covers ports for SSH, FTP, HTTPS, Telnet, DHCP, and HTTP,...
Questions:
39 |
Attempts:
588 |
Last updated:
Mar 21, 2023
|
Common Network+ Port / Terms
Acronyms - It'll help you remember what the letters actually mean
Terms - It isn't enough to just know what each acronym means, know the definition
Ports - Have to be...
Questions:
43 |
Attempts:
493 |
Last updated:
Mar 21, 2023
|
Exam Cram 1: CompTIA Network+ N10-005
Exam Cram Part 1
Network+ N10-005
4th edition
by Mike Harwood
Questions:
100 |
Attempts:
261 |
Last updated:
Mar 21, 2023
|
Network+ Chapter 2 Quiz
The Network+ Chapter 2 Quiz assesses knowledge across various networking layers including the application, physical, network, presentation, session, and data link layers. It...
Questions:
30 |
Attempts:
687 |
Last updated:
Mar 22, 2023
|
CompTIA Network Plus Certification Quiz! Trivia
CompTIA Network Plus Certification Practice Quiz. Computer networks are essential in helping computers to share data with each other. By taking up to study CompTIA, one is...
Questions:
20 |
Attempts:
250 |
Last updated:
Mar 21, 2023
|
CompTIA Network+ Certification! Hardest Trivia Quiz
Challenge your knowledge with the 'CompTIA Network+ Certification! Hardest Trivia Quiz.' This quiz tests your understanding of network protocols, security, and troubleshooting,...
Questions:
100 |
Attempts:
381 |
Last updated:
Aug 30, 2024
|
 Back to top
Back to top