Geographical Dispersion Of Network Components
-
Custom Subnet Mask ProblemNetwork Information: Number of needed subnets6Number of needed usable hosts30Network Address210.100.56.0 Adress classdefault subnet maskcustom subnet masktotal number of subnetstotal number of host addressesnumber of usable addressesnumber of bits borrowednumber of host bits
This quiz focuses on the geographical dispersion of network components, exploring various network categories, the concept of converged networks, and the role of IEEE. It assesses understanding of network structures and standards, crucial for students and professionals in IT and computer science.
Quiz Preview
- 2.
A converged network is a network that has the capabilities of transporting multiple types of traffic such as voice, video, and data, which can offer significant cost savings to organizations.
-
True
-
False
Correct Answer
A. TrueExplanation
A converged network refers to a network that can handle various types of traffic, including voice, video, and data. This capability allows organizations to transmit all these types of information over a single network infrastructure, leading to cost savings. By consolidating different types of traffic onto one network, organizations can reduce the need for separate networks for each type of communication. This not only simplifies network management but also reduces hardware and maintenance costs. Therefore, the statement that a converged network can offer significant cost savings to organizations is true.Rate this question:
-
- 3.
When interconnecting multiple sites (for example, multiple corporate locations) via WAN links, a hub-and-spoke topology has a WAN link from each remote site , a spoke site) to the main site , the hub site). The diagram below shows a hub-and-spoke topology.
-
True
-
False
Correct Answer
A. TrueExplanation
The explanation for the given correct answer, which is True, is that in a hub-and-spoke topology, multiple sites are interconnected via WAN links. Each remote site, also known as a spoke site, has a WAN link to the main site, also known as the hub site. This allows for centralized communication and management, as all traffic flows through the hub site. This topology is commonly used in scenarios where there is a central location that needs to communicate with multiple remote locations.Rate this question:
-
- 4.
IEEE stands for the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, and it is an internationally recognized standards body
-
True
-
False
Correct Answer
A. TrueExplanation
IEEE stands for the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, which is a globally recognized organization that sets standards in the field of electrical and electronics engineering. They develop and publish technical standards, organize conferences, and provide resources for professionals in the industry. Being internationally recognized, IEEE plays a crucial role in shaping the development and advancement of technology in various sectors. Therefore, the statement that IEEE is an internationally recognized standards body is true.Rate this question:
-
- 5.
Switching is associated with Layer 2 (data link layer) and Layer 3 (network layer)
-
True
-
False
Correct Answer
A. TrueExplanation
Switching is indeed associated with both Layer 2 (data link layer) and Layer 3 (network layer) in networking. At Layer 2, a switch operates by using MAC addresses to forward data packets within a local network. It learns and stores MAC addresses in its forwarding table to make forwarding decisions. At Layer 3, a switch can also perform routing functions by using IP addresses to forward packets between different networks. This allows the switch to connect multiple local networks and route traffic between them. Therefore, the statement "Switching is associated with Layer 2 and Layer 3" is true.Rate this question:
-
- 6.
At layers above the Physical layer in the OSI Reference Model, bits are grouped together into a Protocol Data Unit (PDU)
-
True
-
False
Correct Answer
A. TrueExplanation
At layers above the Physical layer in the OSI Reference Model, bits are grouped together into a Protocol Data Unit (PDU). This means that the data transmitted at these layers is organized into a specific format or structure, known as the PDU. The PDU contains the necessary information for the layer to function properly and communicate with other layers. This grouping of bits into PDUs allows for more efficient and organized data transmission and processing at higher layers of the OSI model.Rate this question:
-
- 7.
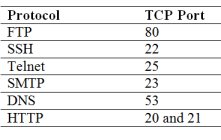
Which of the following protocol to TCP port matching is correct?
-
ftp 20 and 21, SSH 22, Telnet 23, SMTP 25, DNS 53, HTTP 80
-
Ftp 20 and 23, SSH 22, Telnet 25, SMTP 25, DNS 53, HTTP 80
-
Ftp 20 and 21, SSH 22, Telnet 25, SMTP 23, DNS 53, HTTP 80
-
Ftp 20 and 21, SSH 23, Telnet 25, SMTP 25, DNS 80, HTTP 53
Correct Answer
A. ftp 20 and 21, SSH 22, Telnet 23, SMTP 25, DNS 53, HTTP 80Explanation
The correct answer is ftp 20 and 21, SSH 22, Telnet 23, SMTP 25, DNS 53, HTTP 80. This answer correctly matches the protocols to their respective TCP ports. FTP uses ports 20 and 21, SSH uses port 22, Telnet uses port 23, SMTP uses port 25, DNS uses port 53, and HTTP uses port 80.Rate this question:
-
- 8.
A switch in full-duplex mode does not use CSMA/CD
-
True
-
False
Correct Answer
A. TrueExplanation
A switch in full-duplex mode does not use CSMA/CD because in full-duplex mode, data can be transmitted simultaneously in both directions without the need for collision detection. In CSMA/CD, devices listen for traffic on the network before transmitting, and if a collision is detected, they wait for a random amount of time before retransmitting. However, in full-duplex mode, each device has a dedicated communication path, allowing for simultaneous and uninterrupted transmission in both directions. Therefore, CSMA/CD is not necessary in full-duplex mode.Rate this question:
-
- 9.
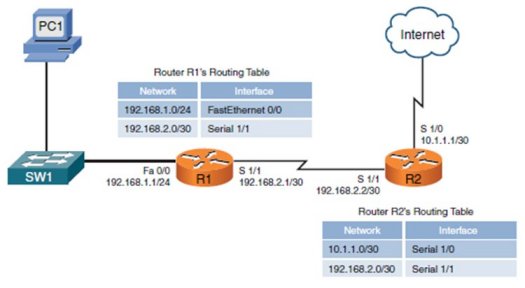
Review the routing tables for Router R1 and Router R2 and evaluate the following statement:True or False: The routes on R1 and R2 are directly connected routes.
-
True
-
False
Correct Answer
A. TrueExplanation
The statement is true because directly connected routes are those that are directly connected to a router's interfaces. By reviewing the routing tables for Router R1 and Router R2, if there are routes listed that have the next hop as one of their own interfaces, then these routes are considered directly connected. Therefore, if the routing tables show such routes on both R1 and R2, the statement is true.Rate this question:
-
- 10.
Which IP address assignment method is easiest for Information Technology professionals to manage for a large network?
-
DHCP
-
Manually
-
BOOTP
-
Statically
Correct Answer
A. DHCPExplanation
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is the easiest IP address assignment method for IT professionals to manage for a large network. DHCP allows for automatic allocation and configuration of IP addresses to devices on the network, eliminating the need for manual assignment. It simplifies the process by centrally managing and distributing IP addresses, reducing the chances of errors and conflicts. Additionally, DHCP provides flexibility by allowing for dynamic IP address allocation, ensuring efficient utilization of available addresses. This makes DHCP the preferred method for managing IP addresses in large networks.Rate this question:
-
- 11.
Custom Subnet Masks ProblemNetwork Information: Number of needed subnets2 Network Address192.168.1.0 Adress classdefault subnet maskcustom subnet masktotal number of subnetstotal number of host addressesnumber of usable addressesnumber of bits borrowednumber of host bits
Correct Answer
C
255.255.255.0
255.255.255.128
2
128
126
1
7Explanation
The given answer provides the correct custom subnet masks for the given network information. The first custom subnet mask, 255.255.255.0, is used when there are 2 subnets needed. The second custom subnet mask, 255.255.255.128, is used when there are 128 host addresses needed. The total number of subnets is 2 and the total number of host addresses is 128. The number of usable addresses is 126, which is calculated by subtracting 2 (network and broadcast addresses) from the total number of host addresses. The number of bits borrowed is 1, which is the number of bits needed to create the desired number of subnets. The number of host bits is 7, which is calculated by subtracting the number of bits borrowed from the default subnet mask.Rate this question:
- 12.
If the bandwidth of an OC-1 link is 51.84 Mbps, what is the bandwidth of an OC-3 link?
-
155 mbps
-
155.52 mbps
-
1.54 mbps
-
51.84 mbps
Correct Answer
A. 155.52 mbpsExplanation
An OC-3 link has a bandwidth of 155.52 Mbps. This is because an OC-3 link is three times faster than an OC-1 link. Since the bandwidth of an OC-1 link is given as 51.84 Mbps, multiplying it by three gives us the bandwidth of an OC-3 link, which is 155.52 Mbps.Rate this question:
-
- 13.
Which OSI reference model layer is responsible for?(a) Setting up a session(b) Maintaining a session(c) Tearing down a session
-
Session Layer (Layer 5)
-
Data-Link Layer (Layer 2)
-
Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
-
Transport Layer (Layer 4)
Correct Answer
A. Session Layer (Layer 5)Explanation
The Session Layer (Layer 5) in the OSI reference model is responsible for setting up, maintaining, and tearing down a session. It establishes and manages the connection between two communicating devices, allowing them to exchange data. This layer handles session establishment, synchronization, and termination, ensuring that the communication between the devices remains reliable and error-free. It also manages session checkpoints, allowing for the recovery of data in case of interruptions or failures.Rate this question:
-
- 14.
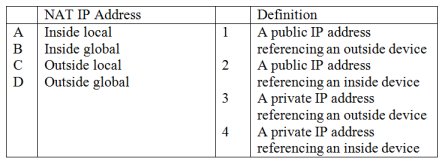
Match the Type of NAT on the left with the correct definition on the right.
-
A4, B2, C3, D1
-
A1, B2, C3, D4
-
A2, B1, C4, D3
-
A3, B2, C4, D1
Correct Answer
A. A4, B2, C3, D1 -
- 15.
The data portion of an Ethernet frame may contain ____ bytes of information
-
46
-
46 to 1500
-
1500
-
More then 1500
Correct Answer
A. 46 to 1500Explanation
The data portion of an Ethernet frame may contain anywhere from 46 to 1500 bytes of information. This range allows for flexibility in the amount of data that can be transmitted in a single frame, accommodating for different network and application requirements. The minimum of 46 bytes ensures that even small amounts of data can be transmitted efficiently, while the maximum of 1500 bytes allows for larger data transfers without exceeding the maximum frame size.Rate this question:
-
- 16.
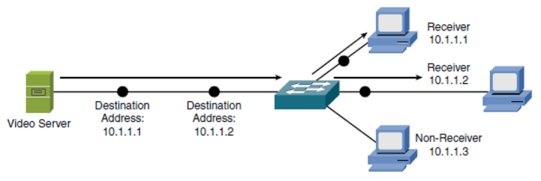
The diagram below shows an example of what kind of transmission?
-
Unicast
-
Anycast
-
Broadcast
-
Multicast ITS ME BLACKSMITH
Correct Answer
A. UnicastExplanation
The diagram shows a single source transmitting data to a single destination. This type of transmission is known as unicast, where information is sent from one sender to one receiver. Unicast is commonly used in point-to-point communication, such as a phone call or a private message.Rate this question:
-
- 17.
How fast can category 5e transfer data?
-
1000 mbps
-
10 mbps
-
100 mbps
-
10 gbps
Correct Answer
A. 1000 mbpsExplanation
Category 5e cables are capable of transferring data at a speed of 1000 Mbps. Mbps stands for megabits per second, which is a unit of data transfer rate. This means that category 5e cables can transmit data at a rate of 1000 million bits per second, making it suitable for high-speed internet connections and data-intensive applications.Rate this question:
-
- 18.
Modern LANs use ____ or higher wiring.
-
Cat 3
-
Cat 5
-
Rg-6
-
Rg-59
Correct Answer
A. Cat 5Explanation
Modern LANs use cat 5 or higher wiring. Cat 5 is a type of Ethernet cable that is commonly used for local area networks (LANs). It supports data transfer speeds of up to 1000 Mbps and is capable of transmitting signals over longer distances compared to older cable types like cat 3. Cat 5 wiring is more reliable and efficient, making it the preferred choice for modern LAN installations.Rate this question:
-
- 19.
The IP address range of 172.16.0.0 -172.31.255.255 is what address class?
-
A
-
B
-
D
-
C
Correct Answer
A. BExplanation
The IP address range of 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 is classified as Class B. In Classful addressing, the first octet of a Class B address ranges from 128 to 191. The range specified falls within this range, making it a Class B address.Rate this question:
-
- 20.
The term packet is used fairly generically to refer to a protocol data unit (PDU). However, a PDU might have additional names based on its OSI layer. What is the name of the PDU in the physical layer of the OSI reference Model?
-
Segmen
-
Packet
-
Bits
-
Frames
Correct Answer
A. BitsExplanation
In the physical layer of the OSI reference model, the PDU is called "Bits". The physical layer deals with the actual transmission of data over a physical medium, such as cables or wireless signals. At this layer, the data is represented as individual bits, which are the smallest unit of data. Therefore, "Bits" is the correct answer for the PDU in the physical layer.Rate this question:
-
- 21.
What is the purpose of a DNS server?
-
Routing packets to the Internet
-
Connecting devices at Layer 2 of the OSI
-
Providing an IP address for an Fully Qualified Domain Name
-
Blocking packets from the Internet
Correct Answer
A. Providing an IP address for an Fully Qualified Domain NameExplanation
The purpose of a DNS server is to provide an IP address for a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). DNS servers act as a directory that translates human-readable domain names (e.g., www.example.com) into the corresponding IP addresses (e.g., 192.168.1.1) that computers use to communicate with each other over the internet. By resolving domain names to IP addresses, DNS servers enable devices to locate and connect to the correct destination on the internet.Rate this question:
-
- 22.
A more efficient design which involves the logical separation of switch ports into different broadcast domains is known as a ________.
-
LAN
-
Virtual Area Network (VLAN)
-
Subnet
-
Collision domain
Correct Answer
A. Virtual Area Network (VLAN)Explanation
A more efficient design which involves the logical separation of switch ports into different broadcast domains is known as a Virtual Area Network (VLAN). VLANs allow for better network management and security by dividing a physical network into smaller, isolated networks. This allows for better control over network traffic and improves overall network performance.Rate this question:
-
- 23.
What is the binary version of the decimal number 49?
-
00111010
-
00110001
-
00110010
-
10110001
Correct Answer
A. 00110001Explanation
The binary version of the decimal number 49 is 00110001. In binary, each digit represents a power of 2, starting from the rightmost digit as 2^0. By converting 49 to binary, we can break it down into powers of 2 that add up to 49. In this case, 49 can be represented as 32 + 16 + 1, which translates to 00110001 in binary.Rate this question:
-
- 24.
What is the purpose of ARP?
-
ARP resolves an IP address to a Hostname.
-
ARP resolves the MAC address to a NetBIOS name.
-
ARP resolves the IP address of a Host to its MAC address.
-
ARP locates the default gateway of the network.
Correct Answer
A. ARP resolves the IP address of a Host to its MAC address.Explanation
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a network protocol used to resolve the IP address of a host to its corresponding MAC address. When a device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it needs to know the MAC address of the destination device. ARP helps in this process by sending out a broadcast message asking for the MAC address of the device with a specific IP address. The device with the corresponding IP address then responds with its MAC address, allowing the requesting device to establish communication. Therefore, the purpose of ARP is to resolve the IP address of a host to its MAC address.Rate this question:
-
- 25.
A ____ occurs when two transmissions interfere with each other.
-
Jam
-
Collision
-
Carrier sense
-
Multiple access event
Correct Answer
A. CollisionExplanation
A collision occurs when two transmissions interfere with each other. This happens when two devices attempt to transmit data simultaneously on a shared network medium, causing their signals to collide and become corrupted. Collisions can occur in networks that use the carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) protocol, where devices listen for a clear channel before transmitting. If multiple devices detect a clear channel at the same time and start transmitting, a collision can occur.Rate this question:
-
- 26.
What is the network address for APIPA?
-
192.168.0.0/24
-
10.0.0.0/8
-
169.254.0.0/16
-
172.16.0.0/16
Correct Answer
A. 169.254.0.0/16Explanation
The network address for APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) is 169.254.0.0/16. APIPA is a feature in Windows operating systems that allows devices to automatically assign themselves an IP address in the absence of a DHCP server. The range of IP addresses reserved for APIPA is 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255, with a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 (/16). This range ensures that devices using APIPA will not conflict with manually assigned IP addresses or addresses obtained from a DHCP server.Rate this question:
-
- 27.
Which two types of media are twisted-pair cable?
-
RJ-11 and RJ-45
-
STP and UTP
-
RG-59 and RG-58
-
MMF and SMF
Correct Answer
A. STP and UTPExplanation
STP and UTP are the correct answers because they both refer to types of twisted-pair cables. STP stands for Shielded Twisted Pair, which has an additional layer of shielding to protect against electromagnetic interference. UTP stands for Unshielded Twisted Pair, which does not have the extra shielding. Both STP and UTP cables are commonly used in Ethernet networks for transmitting data. RJ-11 and RJ-45 are types of connectors used with twisted-pair cables, while RG-59 and RG-58 are types of coaxial cables, and MMF and SMF are types of fiber optic cables.Rate this question:
-
- 28.
What is the result of the binary conversion in the example below? 128643216842110000000
-
256
-
127
-
32
-
128
Correct Answer
A. 128Explanation
The binary conversion of the given number, 128643216842110000000, is 128.Rate this question:
-
- 29.
Which one do you like?
-
Option 1
-
Option 2
-
Option 3
-
Option 4
Correct Answer
A. Option 1 -
- 30.
Which of the following is NOT a layer of the Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) reference model?
-
Physical Layer
-
Data Link Layer
-
Presentation Layer
-
Internet Access Layer
Correct Answer
A. Internet Access LayerExplanation
The Internet Access Layer is not a layer of the OSI reference model. The OSI model consists of seven layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. The Internet Access Layer is not part of this model and is not recognized as a standard layer in the OSI reference model.Rate this question:
-
- 31.
What are the steps a DHCP client goes through when requesting an IP address? Make sure they are in the correct order.
-
DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK
-
DHCPOFFER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
-
DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
-
DHCPACK, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOFFER
Correct Answer
A. DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACKExplanation
The correct order of steps that a DHCP client goes through when requesting an IP address is DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK. The client first sends a DHCPDISCOVER message to discover available DHCP servers. Then, the server responds with a DHCPOFFER message, offering an IP address to the client. The client then sends a DHCPREQUEST message to request the offered IP address. Finally, the server acknowledges the request with a DHCPACK message, assigning the IP address to the client.Rate this question:
-
- 32.
What is the actual distance of 10Base 2?
-
185 meters
-
2 meters
-
10 meters
-
200 meters
Correct Answer
A. 185 metersExplanation
The actual distance of 10Base 2 is 185 meters. This refers to the maximum length of the coaxial cable that can be used in a 10Base 2 Ethernet network. It is important to adhere to this distance limit in order to maintain the integrity and quality of the network signal.Rate this question:
-
- 33.
How many subnets do you get with a subnet of 192.168.1.0/28?
-
12
-
20
-
13
-
16
Correct Answer
A. 16Explanation
With a subnet of 192.168.1.0/28, the network address is 192.168.1.0 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.240. This means that the subnet mask has 4 bits turned on, allowing for 2^4 or 16 possible subnets. Therefore, the correct answer is 16.Rate this question:
-
- 34.
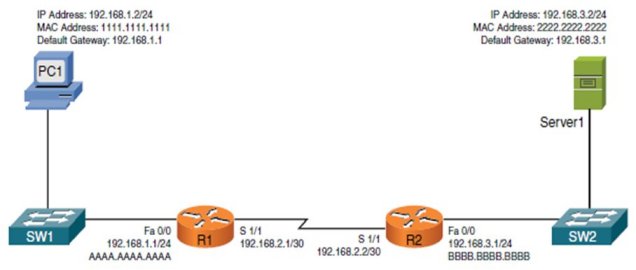
Both PC1 and Server 1 have a default gateway, what is the purpose of a default gateway?
-
Forward Frames
-
Block packets
-
Route packets to the same subnet
-
Route packets to a different subnet
Correct Answer
A. Route packets to a different subnetExplanation
The purpose of a default gateway is to route packets to a different subnet. When a device wants to communicate with a destination that is not on its own subnet, it sends the packet to the default gateway. The default gateway then forwards the packet to the appropriate subnet, allowing communication between different subnets on a network.Rate this question:
-
- 35.
Which of the following is an Exterior Gateway Protocol? Choose only one.
-
RIP
-
OSPF
-
BGP
-
EIGRP
Correct Answer
A. BGPExplanation
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is an Exterior Gateway Protocol used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems (AS) on the internet. It is designed to provide scalability and support for complex network topologies. BGP is commonly used by internet service providers (ISPs) to connect their networks and exchange routing information with other ISPs. It allows for efficient and reliable routing decisions based on factors such as network policies, path attributes, and performance metrics.Rate this question:
-
- 36.
Which of the following is NOT an example of an application that can travel over a network's connections?
-
Voice over IP (VoiceIP)
-
Email
-
Instant Messaging (IM) between computers with IM software installed
-
File sharing between computers
-
Local Area Network
Correct Answer
A. Local Area NetworkExplanation
A Local Area Network (LAN) is not an example of an application that can travel over a network's connections. A LAN is a network that connects computers and devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or building. It is a network infrastructure rather than an application itself. Voice over IP (VoiceIP), email, instant messaging, and file sharing are all examples of applications that can utilize a network's connections to transmit data or communicate between devices.Rate this question:
-
- 37.
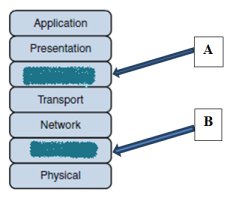
What layers of the OSI correspond to labels A and B?
-
A is session layer and B is application.
-
A is session layer and B is Physical.
-
A is Host-to-Host layer and B is Internet access layer.
-
A is session layer and B is data-link layer.
Correct Answer
A. A is session layer and B is data-link layer. -
- 38.
Which of the following layers of the OSI reference model is primarily concerned with forwarding data based on logical addresses?
-
Data Link Layer
-
Physical Layer
-
Network Layer
-
Presentation Layer
Correct Answer
A. Network LayerExplanation
The Network Layer of the OSI reference model is primarily concerned with forwarding data based on logical addresses. This layer is responsible for routing and addressing, ensuring that data packets are properly directed to their destination based on logical addresses, such as IP addresses. The Network Layer also handles congestion control, error handling, and fragmentation of data packets.Rate this question:
-
- 39.
The more twists per foot in a pair of wires, the more resistant the pair will be to ____.
-
Throughput
-
Attenuation
-
Cross talk
-
Latency
Correct Answer
A. Cross talkExplanation
The more twists per foot in a pair of wires, the more resistant the pair will be to cross talk. Cross talk refers to the interference caused by electromagnetic signals from one wire affecting the signals in an adjacent wire. By increasing the number of twists per foot, the wires become less susceptible to cross talk, as the twists help to cancel out the electromagnetic interference.Rate this question:
-
- 40.
____ describes wiring that connects workstations to the closest telecommunications closet
-
Backbone wiring
-
Horizontal wiring
-
Work area
-
Simple wiring
Correct Answer
A. Horizontal wiringExplanation
Horizontal wiring refers to the cabling that connects individual workstations or devices to the nearest telecommunications closet or distribution point. It is responsible for carrying data and voice signals from the work area to the main network infrastructure. This type of wiring is typically installed within the same floor or building, and it serves as a crucial link between end-user devices and the network backbone. Horizontal wiring is essential for establishing reliable and efficient connectivity within a local area network (LAN) environment.Rate this question:
-
- 41.
Which of the following is an advantage of fiber-optic cable?
-
Protect Networks from hackers and crackers
-
Immunity from electromagnetic interference
-
High bandwidth capacity
-
Use in dial-up analog modem
-
Prevent Network problems
-
Prevent Network problems
Correct Answer(s)
A. Immunity from electromagnetic interference
A. High bandwidth capacityExplanation
Fiber-optic cables have the advantage of being immune to electromagnetic interference, which means that they are not affected by nearby electrical devices or power lines. This makes them more reliable and less prone to signal loss or degradation. Additionally, fiber-optic cables have a high bandwidth capacity, meaning they can transmit large amounts of data quickly and efficiently. This makes them ideal for high-speed internet connections and other applications that require fast data transfer.Rate this question:
-
- 42.
Which of the following correctly explains the parts of the term 100Base-T
-
100 years, baseband, technology
-
100 Mbps, baseball, technology
-
100 meters, baseband, twisted pair
-
100 Mbps, baseband, twisted pair
-
100 Mbps, baseband, technology
Correct Answer
A. 100 Mbps, baseband, twisted pairExplanation
The term "100Base-T" refers to a type of Ethernet network standard. The correct answer, "100 Mbps, baseband, twisted pair," explains the different components of this term. "100 Mbps" indicates the data transfer rate of the network, which is 100 megabits per second. "Baseband" refers to the type of signaling used in the network, where the entire bandwidth is dedicated to a single channel. "Twisted pair" refers to the type of cable used to transmit the signals, which consists of pairs of wires twisted together to reduce interference.Rate this question:
-
- 43.
At the moment PC1 can't reach the Internet. You add a static default route to R1 that sends all traffic to an unknown destination out s1/1. Can a user on PC1 access the Internet?
-
No, packets will stop at R2
-
Yes, PC1 has internet access.
-
No, packets can make it to the internet but they will never make it back to PC1.
-
No, packets won't make it past R1.
Correct Answer
A. No, packets will stop at R2Explanation
Adding a static default route to R1 that sends all traffic to an unknown destination out s1/1 means that R1 will forward all packets to R2. However, since R2 does not have a route back to PC1, the packets will not be able to reach PC1. Therefore, PC1 will not be able to access the Internet.Rate this question:
-
- 44.
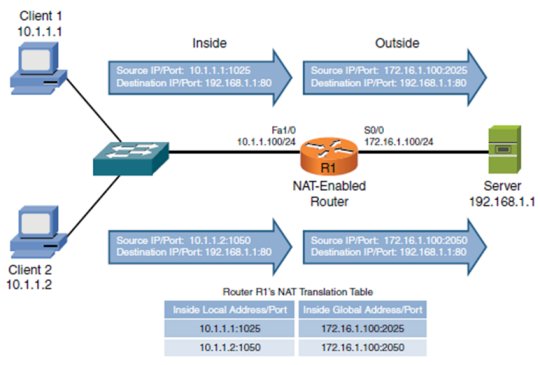
For static NAT to work, how many inside global addresses are needed for inside local addresses?
-
10 inside global addresses for unlimited inside local addresses
-
1 inside global address for every inside local address
-
1 inside global addresses for unlimited inside local addresses
-
2 inside global addresses for every inside local address
Correct Answer
A. 1 inside global address for every inside local addressExplanation
For static NAT to work, 1 inside global address is needed for every inside local address. This means that each inside local address will be mapped to a unique inside global address. This allows for one-to-one correspondence between the inside local and inside global addresses, ensuring that each device on the inside network can be uniquely identified and accessed from the outside network.Rate this question:
-
- 45.
Which two media types can be used with 1000Base-T (Gigabit Ethernet)?
-
Cat 5e
-
Cat 5
-
10base2
-
Option 4
Correct Answer(s)
A. Cat 5e
A. Cat 5Explanation
Cat 5e and Cat 5 are the two media types that can be used with 1000Base-T (Gigabit Ethernet). These are Ethernet cable standards that support data transmission at gigabit speeds. 10base2 is not compatible with 1000Base-T as it is an older Ethernet standard that supports lower speeds. Option 4 is not a valid media type and does not provide any information.Rate this question:
-
- 46.
R1 is using both NAT and PAT, what is the purpose of the port numbers in the translation table
-
The port numbers are not used.
-
PAT only uses the destination port to track separate communication flows.
-
Basic NAT uses the port numbers to track separate communication flows.
-
PAT uses the port numbers to track separate communication flows.
Correct Answer
A. PAT uses the port numbers to track separate communication flows.Explanation
The purpose of the port numbers in the translation table is to track separate communication flows in PAT (Port Address Translation). PAT uses both the source and destination port numbers to differentiate between multiple connections from the same IP address. This allows PAT to map multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address by using different port numbers for each connection. By tracking the port numbers, PAT can correctly route incoming packets to the appropriate private IP address and maintain the integrity of the communication flows.Rate this question:
-
- 47.
The data rates for T3 link is ________.
-
40 Mbps, 50 Mbps
-
44.736 MBPS
-
45.736 Mbps, 51.84 Mbps
-
44.736 Mbps, 52.84
Correct Answer
A. 44.736 MBPSExplanation
The correct answer is 44.736 Mbps. This is the standard data rate for a T3 link, which is a high-speed telecommunications line capable of transmitting data at approximately 44.736 Mbps.Rate this question:
-
- 48.
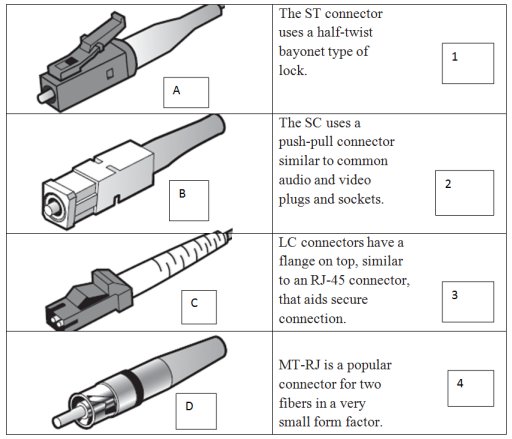
In the diagram below match the fiber connector on the left with the correct description on the right
-
A2, B1, C3, D4
-
A3, B2, C4, D3
-
A1, B2, C3, D4
-
A3, B2, C4, D1
Correct Answer
A. A3, B2, C4, D1 -
- 49.
How many usable hosts can you have with a subnet of 192.168.1.0/28?
-
16
-
6
-
30
-
14
Correct Answer
A. 14Explanation
A subnet of 192.168.1.0/28 means that the network portion of the IP address is 192.168.1.0 and the subnet mask is 28 bits long. The subnet mask of 28 bits allows for 4 bits to be used for the host portion of the IP address. With 4 bits, we can have 2^4 or 16 different combinations. However, the first and last combinations are reserved for the network address and broadcast address respectively, leaving us with 14 usable hosts.Rate this question:
-
Quiz Review Timeline (Updated): Mar 21, 2023 +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
-
Current Version
-
Mar 21, 2023Quiz Edited by
ProProfs Editorial Team -
Mar 05, 2015Quiz Created by
Edin86
Do You Know Routing Paths And Subnets?
Immerse yourself in the dynamic world of computer networking with our intriguing quiz! Explore the intricacies of routing paths and subnets as you put your networking expertise to...
Questions:
10 |
Attempts:
149 |
Last updated:
Nov 16, 2023
|
CCT Exam Practice Test Questions And Answers
Are you preparing for the CCT (Cisco Certified Technician) test? Then, take this CCT Exam practice test and answer the questions related to Cisco networking. This test is...
Questions:
116 |
Attempts:
1773 |
Last updated:
Mar 22, 2023
|
This Is A Quiz About Internet Network And Connections
A network is a collection of computers, servers, mainframes, network devices, peripherals, or other devices connected to one another to allow the sharing of...
Questions:
10 |
Attempts:
828 |
Last updated:
Apr 02, 2025
|
Quiz To Learn Computer Networking Basics
How well do you understand computer networking? Do you know what are its types? Take our online quiz and learn useful information along the way.
Questions:
15 |
Attempts:
1238 |
Last updated:
Apr 18, 2023
|
The Ultimate Computer Network Quiz
Ever wondered how much do you know about computer networks? Why do we need a network? What are its types? Check out our online quiz to test your knowledge and learn interesting...
Questions:
12 |
Attempts:
495 |
Last updated:
May 08, 2025
|
TLE 10 - Reinforcement Examination
The 'TLE 10 - Reinforcement Examination' assesses knowledge in networking protocols and internet technologies. It covers internetworking, TCP\/IP, SMTP, FTP, and HTTP,...
Questions:
27 |
Attempts:
197 |
Last updated:
Mar 21, 2023
|
 Back to top
Back to top