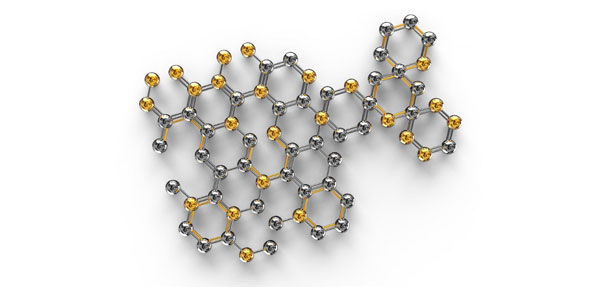
The rigid kinks in _________ fatty acids ______ # of van der waal...
Humans cannot break down what type of glucose?
Give examples of pentose sugars (5 carbon atoms)
Lipids are
Monosachharides and disaccharides differ from polysacharrides and are...
Each amino acid has a different ___________ that makes each protein...
ATP (adenecine triphosphate)is a _______ made up of a nitrogenous base...
State the formula for monosaccharides
Fructose and galactose are examples of _____ of glucose
In DNA, which pair
All of the bases are the same in RNA as DNA except ________ replaces...
Phospholipids have ___ fatty acids and triglycerides have __ fatty...
In phospholipids the phosphate head is ____ and ______ and the 2 fatty...
Phospholipids have __ functional groups, in the head there is ____...
Steroids, being lipids, are ______ and have __ hydrocarbon linked...
Waxes are long chains of _____ ____ that are attached to ________ or a...
Amino acids are called amino acids because they have both ___ groups...
Amino acids are joined together by a _____ ____ to form a __________,...
In a polypeptide there is always one end with a free ________ group...
In tertiary structure the polypeptide chain continues to _____ and...
A nucleotide is made up of a _________ sugar, a ________ group and a...
DNA nucleotides are joined together at the ________ group, attached to...
In addition to phosphodiester bonds, ______ bonds, unite strands of...
State the formula for glucose
In animals, glucose is the main ______ sugar in the blood, _____...
Sucrose is a _______ that is formed when _______ is bonded to _______,...
Lactose is a ______ that is formed when ______ is bonded to...
Polysaccharides are long chains of _____________ joined together by...
Triglycerides are comprised of ______ and ___________
The hydrocarbon chain in a fatty acid can be from __ to __ units long...
DNA and RNA are
Fatty acids are used for ________, ______, and _________, in fatty...
When glycerols _____ group and the fatty acids _______ group react a...
Proteins have an central carbon atom called the ____ ____ and have 3...
At a low pH an amino acid is _________, at a neutral pH there is __...
In secondary structure of proteins, ________ bonds form between the...
The combination of two or more ____________ _______ forms a protein....
___________ direct the growth and development of every living...
DNA and RNA are made up of ______ units called _________. _________...
IN DNA, Purines have ___ ring(s) and include ________ and ______;...
DNA is ____ stranded whereas RNA is ____ stranded. DNA's job is to...
Disaccharides are formed when(state what disachharides are composed...
Starch is broken down into ______ by the enzyme ____________ can be...
Starch is a ______ that is made up of _____ and _____. _____ is an...
Glycogen is formed when excess ____ molecules are linked to form...
Cellulose is a straight chain polymer of ___ _______ molecules held...
If there are no c=c bonds in the hydrocarbon chain that it is a...