5/22/19 Population Studies & Interactions Among Living Things Practice For Proprof End Of Units Test
-
If the death rate in a population is greater than the birth rate:
-
The population will generally decrease.
-
The population will remain the same.
-
The population will increase.
-
The birth rate will rise.
-
This quiz titled '5\/22\/19 Population Studies & Interactions Among Living Things Practice' assesses understanding of ecological relationships, including predator-prey dynamics, niches, and limiting factors in ecosystems. It is designed to prepare for the ProProf End of Units Test, focusing on key ecological concepts.

Quiz Preview
- 2.
Ecologists use the birth and death rates to calculate a population's growth rate, the rate the population is changing. The birth rate (b) minus the death rate (d) equals the growth rate (g). So, B-D=G Based on this formula: a population of rabbits with an average of 760 births and 227 deaths has a growth rate of _________ per year:
-
533 rabbits
-
233 rabbits
-
227 rabbits
-
987 rabbits
Correct Answer
A. 533 rabbitsExplanation
The growth rate of the population can be calculated by subtracting the death rate from the birth rate. In this case, the birth rate is 760 and the death rate is 227. Therefore, the growth rate would be 760 - 227 = 533 rabbits per year.Rate this question:
-
- 3.
What does the basic formula for mark and recapture mean?
-
The population sample equals the number marked multiplied by the sum of the unmarked and recaptured divided by the number recaptured
-
The population sample equals the number marked minus the sum of the unmarked and recaptured divided by the number recaptured.
-
The population sample equals the number marked divided by the number recaptured
-
The population sample equals the number unmarked plus the recaptured divided by the number recaptured
Correct Answer
A. The population sample equals the number marked multiplied by the sum of the unmarked and recaptured divided by the number recapturedExplanation
The basic formula for mark and recapture means that the population sample is determined by multiplying the number of marked individuals by the sum of the unmarked and recaptured individuals, and then dividing it by the number of recaptured individuals. This formula allows researchers to estimate the size of a population by marking a sample of individuals, releasing them back into the population, and then recapturing a new sample later on. By comparing the number of marked individuals in the recaptured sample to the total sample, researchers can make inferences about the overall population size.Rate this question:
-
- 4.
The organism that is killed is the:
-
Niche
-
Prey
-
Predator
-
Adaptations
-
Predation
-
Symbiosis
-
Natural selection
-
Commensalism
-
Parasite/parasitism
-
Host
-
Competition
-
Mutualism
Correct Answer
A. PreyExplanation
The correct answer is "Prey". In the context of this question, "prey" refers to the organism that is killed. Prey is the term used to describe an animal that is hunted and killed by another animal for food. In the predator-prey relationship, the predator hunts and kills the prey to fulfill its nutritional needs.Rate this question:
-
- 5.
Identify this method of estimating populations: Red wolves are tagged, released and checked systematically.
-
Direct observation
-
Limiting factor
-
Birth rate
-
Population
-
Indirect observation
-
Death rate
-
Population density
-
Carrying capacity
-
Estimate
-
Emigration
-
Ecology
-
Mark and recapture
-
Immigration
-
Space
-
Food
-
Sample
-
Weather
-
Water
Correct Answer
A. Mark and recaptureExplanation
The method described in the question, tagging and releasing red wolves and then systematically checking them, is known as "mark and recapture." This method involves marking a sample of individuals, releasing them back into the population, and then recapturing a second sample at a later time to estimate the total population size. By comparing the number of marked individuals in the second sample to the total number of individuals in the sample, an estimate of the population size can be calculated.Rate this question:
-
- 6.
All of the following are examples of limiting factors except:
-
Time
-
Food & water
-
Space
-
Weather
Correct Answer
A. TimeExplanation
The question asks for examples of limiting factors, which are factors that restrict the growth or abundance of a population. Time is not typically considered a limiting factor because it does not directly affect the availability of resources or the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce. On the other hand, food and water, space, and weather can all be limiting factors as they can directly impact the survival and growth of populations.Rate this question:
-
- 7.
The largest population that an area can support is called:
-
Direct observation
-
Limiting factor
-
Birth rate
-
Population
-
Indirect observation
-
Death rate
-
Population density
-
Carrying capacity
-
Estimate
-
Emigration
-
Ecology
-
Mark and recapture
-
Immigration
-
Space
-
Food
-
Sample
-
Weather
-
Water
Correct Answer
A. Carrying capacityExplanation
Carrying capacity refers to the maximum population size that an environment can sustainably support. It is determined by factors such as the availability of resources, space, and other limiting factors. Once the population reaches the carrying capacity, further growth may be limited due to resource scarcity or increased competition for resources. This term is commonly used in ecology to study population dynamics and understand the relationship between organisms and their environment.Rate this question:
-
- 8.
All of the following are examples of limiting factors for populations except:
-
Space
-
Food
-
Emigration
-
Weather
Correct Answer
A. EmigrationExplanation
Emigration is not a limiting factor for populations because it refers to individuals leaving a population, which actually helps to reduce population density and can alleviate limiting factors such as competition for resources. Limiting factors are typically factors that restrict population growth, such as limited space, food availability, and adverse weather conditions.Rate this question:
-
- 9.
A mouse, raccoon and hawk are all members of the same:
-
Species
-
Niche
-
Community
-
Population
Correct Answer
A. CommunityExplanation
A community refers to a group of different species living in the same area and interacting with each other. In this case, the mouse, raccoon, and hawk are all different species, but they can be found living together in the same environment and potentially interacting with each other. Therefore, they can be considered as members of the same community.Rate this question:
-
- 10.
An organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms is:
-
A decomposer.
-
A consumer.
-
A herbivore.
-
A producer.
Correct Answer
A. A consumer.Explanation
A consumer is an organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms. This means that it consumes other living organisms as a source of food in order to obtain the energy it needs to survive and carry out its life processes. Consumers can be further classified into different categories based on their specific feeding habits, such as herbivores (which eat only plants), carnivores (which eat other animals), and omnivores (which eat both plants and animals). Therefore, a consumer is the correct answer in this case.Rate this question:
-
- 11.
The organism that does the killing of another is the:
-
Commensalism
-
Parasite/parasitism
-
Host
-
Competition
-
Mutualism
-
Niche
-
Prey
-
Predator
-
Adaptations
-
Predation
-
Symbiosis
-
Natural selection
Correct Answer
A. PredatorExplanation
A predator is an organism that hunts, kills, and feeds on other organisms. It is the one that does the killing in a predator-prey relationship. Predators have adaptations that allow them to effectively capture and consume their prey. They play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling the population of prey species.Rate this question:
-
- 12.
Why are there fewer organisms at the top of the food chain?
-
There are usually few organisms at the top because there is a limited amount of energy available at that level of a food web.
-
There are usually few organisms at the top because the organisms at the top of the food chain care for their young longer than organisms lower on the food chain.
-
There are usually few organisms at the top because the organisms at the top of the food chain consume are omnivores that consume diverse kinds of organisms that are lower on the food chain.
-
There are usually few organisms at the top because the organisms at the top of the food chain are scavengers consuming what other organisms have left behind.
Correct Answer
A. There are usually few organisms at the top because there is a limited amount of energy available at that level of a food web.Explanation
The correct answer is that there are usually few organisms at the top of the food chain because there is a limited amount of energy available at that level of a food web. As energy is transferred from one organism to another through consumption, only a fraction of the energy is passed on, resulting in less energy being available at each trophic level. This means that as you move up the food chain, there is less energy available to support a large number of organisms, leading to fewer organisms at the top.Rate this question:
-
- 13.
Changes in population may occur when a group moves into a population. This is called:
-
Direct observation
-
Limiting factor
-
Birth rate
-
Population
-
Indirect observation
-
Death rate
-
Population density
-
Carrying capacity
-
Estimate
-
Emigration
-
Ecology
-
Mark and recapture
-
Immigration
-
Space
-
Food
-
Sample
-
Weather
-
Water
Correct Answer
A. ImmigrationExplanation
Immigration refers to the movement of individuals into a population. It is a factor that can cause changes in population size. When individuals from one group move into a population, it can increase the population size. Immigration can have various effects on a population, such as introducing new genetic variation or changing the dynamics of competition for resources.Rate this question:
-
- 14.
An environmental factor that causes a population to decrease is a ____________.
-
Direct observation
-
Limiting factor
-
Birth rate
-
Population
-
Indirect observation
-
Death rate
-
Population density
-
Carrying capacity
-
Estimate
-
Emigration
-
Ecology
-
Mark and recapture
-
Immigration
-
Space
-
Food
-
Sample
-
Weather
-
Water
Correct Answer
A. Limiting factorExplanation
A limiting factor is an environmental factor that restricts the growth or size of a population. It can include factors such as availability of food, space, or water, as well as competition for resources and predation. When these limiting factors become insufficient or unfavorable, they can cause a decrease in the population size.Rate this question:
-
- 15.
The living parts of a habitat are:
-
Ecosystem
-
Niche
-
Abiotic factors
-
Population
-
Organisms
-
Biotic factors
-
Ecology
-
Habitat
-
Ecotone
-
Community
-
Species
-
Photosynthesis
Correct Answer
A. Biotic factorsExplanation
Biotic factors refer to the living components of a habitat, such as plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. These organisms interact with each other and with the non-living components of the habitat, known as abiotic factors, to form a complex ecosystem. Biotic factors play a crucial role in shaping the structure and function of an ecosystem, as they are involved in processes like predation, competition, and symbiosis. Understanding the biotic factors in a habitat is essential for studying the relationships and dynamics within an ecosystem.Rate this question:
-
- 16.
When might an ecologist use indirect observation to estimate a population?
-
Indirect observation may be used when a population is small or difficult to find.
-
Indirect observation may be used when a population is located in a remote area that the scientist cannot get to.
-
Indirect observation may be used to mark and recapture organisms.
-
Indirect observation may be used for sampling.
Correct Answer
A. Indirect observation may be used when a population is small or difficult to find.Explanation
Indirect observation may be used when a population is small or difficult to find. This method allows the ecologist to gather information about the population without directly observing the individuals. It can be challenging to locate and monitor small or elusive populations, so indirect observation techniques such as analyzing tracks, nests, or droppings can provide valuable data. Additionally, indirect observation can be less invasive and disruptive to the population, making it a preferred method in certain situations.Rate this question:
-
- 17.
The role of an organism in its habitat:
-
Niche
-
Prey
-
Predator
-
Adaptations
-
Predation
-
Symbiosis
-
Natural selection
-
Commensalism
-
Parasite/parasitism
-
Host
-
Competition
-
Mutualism
Correct Answer
A. NicheExplanation
The term "niche" refers to the specific role or position that an organism has within its habitat. It includes the way the organism interacts with other species, the resources it uses, and how it responds to environmental conditions. The niche of an organism determines its place in the ecosystem and its impact on other organisms.Rate this question:
-
- 18.
What is a sampling estimate?
-
A sampling estimate is an approximation of a number based on reasonable assumptions.
-
The practice of mark and recapture.
-
Uses mathematical formulas to estimate the total population.
-
A direct count of the organisms in a population.
Correct Answer
A. A sampling estimate is an approximation of a number based on reasonable assumptions.Explanation
A sampling estimate is an approximation of a number based on reasonable assumptions. This means that it is not an exact measurement, but rather a calculated estimation that takes into account certain assumptions. It is commonly used in statistics and research when it is not feasible or practical to measure an entire population. By taking a sample from the population and making reasonable assumptions about the characteristics of the entire population, a sampling estimate can be obtained. This allows researchers to make inferences and draw conclusions about the population as a whole based on the sample.Rate this question:
-
- 19.
An environmental factor that causes a population to decrease is a ____________.
-
Direct observation
-
Limiting factor
-
Birth rate
-
Population
-
Indirect observation
-
Death rate
-
Population density
-
Carrying capacity
-
Estimate
-
Emigration
-
Ecology
-
Mark and recapture
-
Immigration
-
Space
-
Food
-
Sample
-
Weather
-
Water
Correct Answer
A. Limiting factorExplanation
A limiting factor is an environmental factor that restricts the growth or size of a population. It can be a scarcity of resources such as food, water, or space, or it can be a presence of unfavorable conditions such as extreme weather or limited access to suitable habitats. When a limiting factor becomes too severe, it can cause a decrease in the population size as individuals struggle to survive and reproduce. Therefore, a limiting factor can be an explanation for a population decrease.Rate this question:
-
- 20.
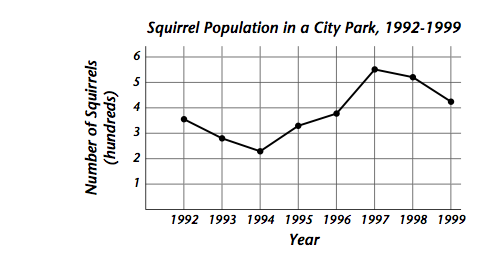
Use the graph to answer the questions about the changes in squirrel population. Which year did the squirrel population decrease the most?
-
1994
-
1996
-
1999
-
1997
Correct Answer
A. 1999Explanation
The squirrel population decreased the most in 1999. This can be determined by analyzing the graph and observing the trend of the population over the years. In 1999, there is a significant drop in the population compared to the previous years, indicating a decrease.Rate this question:
-
- 21.
One method of estimating population size is to count the number of organisms in a small _________ area and then apply multiples of that area to the larger area.
-
Direct observation
-
Limiting factor
-
Birth rate
-
Population
-
Indirect observation
-
Death rate
-
Population density
-
Carrying capacity
-
Estimate
-
Emigration
-
Ecology
-
Mark and recapture
-
Immigration
-
Space
-
Food
-
Sample
-
Weather
-
Water
Correct Answer
A. SampleExplanation
One method of estimating population size is to count the number of organisms in a small sample area and then apply multiples of that area to the larger area. This allows for a representative estimate of the population size without having to count every single organism in the entire area. By accurately sampling a smaller area and extrapolating the results, researchers can estimate the population size in a larger area.Rate this question:
-
Quiz Review Timeline (Updated): Mar 21, 2023 +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
-
Current Version
-
Mar 21, 2023Quiz Edited by
ProProfs Editorial Team -
May 21, 2019Quiz Created by
Rhaveno
Science Baseline Quiz Exam!
The 'Science Baseline Quiz Exam!' assesses understanding of ecological relationships and biological interactions. Questions cover topics such as parasitism, mutualism, and energy...
Questions:
30 |
Attempts:
222 |
Last updated:
Mar 19, 2023
|
Life Sciences 11E
The 'Life Sciences 11E' quiz explores ecological relationships and adaptations in living organisms. It assesses understanding of species interactions, competition, symbiosis, and...
Questions:
10 |
Attempts:
264 |
Last updated:
Apr 29, 2024
|
Animal And Plant Orientation
Explore the fascinating dynamics of animal and plant interactions, including behavioral responses, hormonal influences, and ecological relationships like commensalism.
Questions:
11 |
Attempts:
154 |
Last updated:
Jun 05, 2024
|
Is My Ex Flirting With Me Quiz
Talking to an EX can be emotionally & mentally draining. Take this interesting " is my ex flirting with me quiz." This fantastic quiz is specially curated to give...
Questions:
10 |
Attempts:
887 |
Last updated:
Apr 21, 2022
|
What Is Your Attachment Style?
Do you know about the different attachment styles? To know what is your attachment style, take this quiz. Your attachment style will reflect your personality as well as your...
Questions:
10 |
Attempts:
660 |
Last updated:
Jun 05, 2025
|
12A - Natural Relationships
B.12(A) interpret relationships, including predation, parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, and competition among organisms
Questions:
5 |
Attempts:
259 |
Last updated:
Mar 21, 2023
|
 Back to top
Back to top