Sheep Brain Anatomy Explained: Meaning, Importance & Applications
Lesson Overview
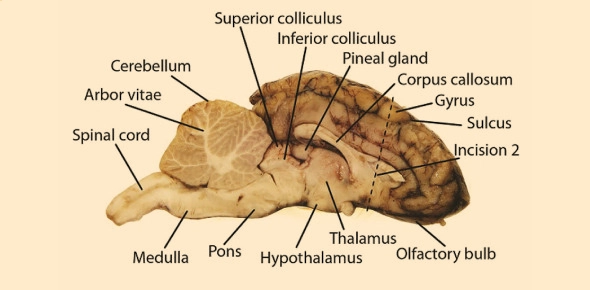
Sheep brain anatomy helps us understand the human brain due to structural similarities. This lesson introduces key parts of the sheep brain, covering external and internal anatomy, using quiz-based breakdowns, helpful visuals, and retention tips. It's structured for easy learning, review, and high quiz performance.

Major Brain Structures (With Table)
The sheep brain has 3 main regions: Cerebrum, Cerebellum, and Brainstem. Let's summarize:
| Structure | Location | Function |
| Cerebrum | Top/front; largest part | Thinking, memory, voluntary movement |
| Cerebellum | Back/bottom | Balance, coordination |
| Brainstem | Bottom center | Vital functions: breathing, heartbeat |
| Olfactory Bulbs | Front, underside | Sense of smell |
| Corpus Callosum | Deep middle | Connects left and right brain hemispheres |
Brain Coverings – Meninges
The brain is protected by three layers:
| Layer | Description |
| Dura Mater | Tough outer layer |
| Arachnoid Mater | Web-like middle layer |
| Pia Mater | Thin layer clinging to brain |
Teacher Tip: Use "DAP" (Dura-Arachnoid-Pia) to remember the order.
Surface Folds – Gyri, Sulci & Fissures
- Gyri = ridges (e.g., brain folds)
- Sulci = shallow grooves
- Fissures = deeper grooves (e.g., between hemispheres)
These folds increase surface area for more neurons.
Directional Terms in Brain Anatomy
| Term | Meaning |
| Rostral | Toward the nose |
| Caudal | Toward the tail |
| Dorsal | Toward the back |
| Ventral | Toward the belly |
Memory Aid: Rostral rhymes with nostril!
Some Concept Breakdown & Explanations
Outer Covering
Question: What's the outermost layer of the brain?
Answer: Dura Mater
Why: It's the thick, durable outer protection.
Largest Structure (Dorsal View)
Answer: Cerebral Cortex
Why: The cerebrum dominates the top view.
Folds on Cerebrum
Answer: Gyri
Why: These are the ridged folds.
What's Caudal to the Infundibulum?
Answer: Mammillary Bodies
Why: Located just behind the pituitary stalk.
Boundary Between Piriform Cortex & Temporal Lobe
Answer: Rhinal Fissure
Why: This deep groove separates olfactory and temporal regions.
Connects Hemispheres
Answer: Corpus Callosum
Why: Major bridge of communication between left and right hemispheres.
Dorsal Surface of Medulla Forms Floor of…
Answer: Fourth Ventricle
Why: Located between the cerebellum and medulla.
Structure Lateral to Peduncles
Answer: Piriform Cortex
Why: Found on the sides near the cerebral stalks.
Deeper Sulci Are Called…
Answer: Fissures
Why: Deeper grooves than sulci, such as the longitudinal fissure.
Round Structure Under Optic Chiasm
Answer: Pituitary Gland
Why: The major endocrine gland hanging under the hypothalamus.
Quick Review Table
| Quiz Topic | Correct Answer | Key Point |
| Outer covering | Dura Mater | Thick outer layer of meninges |
| Largest dorsal structure | Cerebral Cortex | Top view dominated by cerebrum |
| Surface folds | Gyri | Brain's ridges |
| Caudal to infundibulum | Mammillary Bodies | Located behind pituitary stalk |
| Boundary between cortex/lobe | Rhinal Fissure | Separates olfactory from temporal lobe |
| Hemispheres connector | Corpus Callosum | Allows L-R brain communication |
| Floor of 4th ventricle | Medulla (dorsal) | Dorsal medulla forms ventricle's base |
| Lateral to peduncles | Piriform Cortex | Found beside the brain's stalks |
| Deeper sulci | Fissures | Large grooves dividing lobes/regions |
| Under optic chiasm | Pituitary Gland | Endocrine gland under brain base |
Memory Tricks for Retention
| Concept | Trick |
| Meninges | DAP: Dura, Arachnoid, Pia |
| Rhinal fissure | "Rhino = Nose" → Olfactory separation |
| Corpus callosum | "Call someone" → connects hemispheres |
| Infundibulum | Latin for "funnel" → connects pituitary |
| Arbor Vitae | "Tree of life" in cerebellum |
| Gyrus vs Sulcus | Gyrus = ridge, Sulcus = sunken groove |
Key Takeaway
Understanding sheep brain anatomy is a window into how all mammalian brains work. From identifying key structures like the corpus callosum and pituitary gland, to using directional terms like rostral and caudal, this lesson has walked you through every quiz concept with clarity. With diagrams, tables, and memory aids, you're now well-prepared to ace your quiz and build a foundation in brain science.
Take This Quiz
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top