Everything You Need to Know About Plant Structure and Growth Academic
Lesson Overview
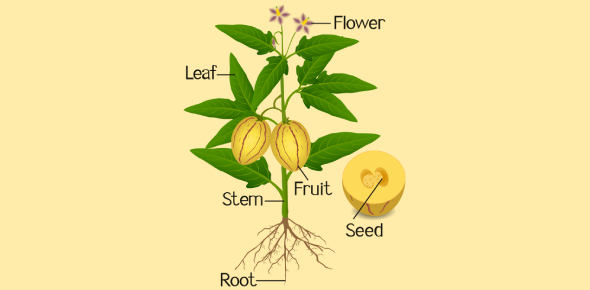
Plants are not just passive organisms-they are dynamic structures with specialized systems that allow them to grow, survive, and adapt. Whether anchoring into soil, photosynthesizing energy, or expanding in height and width, plants rely on internal coordination between cells, tissues, and organs. In this lesson, you'll explore plant tissues, root and shoot systems, growth mechanisms, and monocot vs dicot structural differences. This knowledge is crucial for answering exam and quiz questions confidently.
Plant Life Cycles: Annual, Biennial, and Perennial
Plants are classified based on how long they take to complete their life cycles:
| Plant Type | Life Span | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Annual | 1 growing season (grows, flowers, dies) | Marigold, Wheat |
| Biennial | 2 years (year 1: growth, year 2: reproduction) | Carrot, Foxglove |
| Perennial | Many years (flowers multiple times) | Oak, Rose, Tulip |
Memory Tip:
- Annual = "Once a Year"
- Biennial = "Two-Year Life"
- Perennial = "Perpetual Growth"
Plant Organ Systems: Root vs Shoot
Plants are composed of two major systems:
- Root system: Anchors plant, absorbs water/minerals
- Shoot system: Includes stems, leaves, flowers for support, transport, and photosynthesis
Each organ-root, stem, and leaf-is made of dermal, ground, and vascular tissues (covered later).
Root Systems: Taproot vs Fibrous
Plants have two main types of root systems:
| Root Type | Structure | Typical in | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taproot | One main deep root with smaller offshoots | Dicots | Dandelion, Carrot |
| Fibrous | Dense network of thin roots, shallow | Monocots | Grass, Corn |
- Taproot helps anchor and stores food.
- Fibrous roots quickly absorb water and help prevent soil erosion.
Plant Tissues: Dermal, Ground, Vascular
All plant organs are composed of these three tissue types:
| Tissue | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Dermal | Outer surface | Protection, reduces water loss |
| Ground | Between dermal & vascular | Photosynthesis, support, storage |
| Vascular | Central/internal region | Transport of water and food |
Order in a root: Dermal → Ground → Vascular
Plant Cells Overview
Each tissue is made up of specialized cell types:
| Cell Type | Alive at Maturity? | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Parenchyma | Yes | Photosynthesis, storage |
| Collenchyma | Yes | Flexible support |
| Sclerenchyma | No | Rigid support |
| Xylem vessels | No | Water transport |
| Phloem (sieve-tube) | Yes | Sugar transport |
| Companion cells | Yes | Support sieve tubes |
- Collenchyma gives bendable support for growing parts (e.g. celery stalk).
- Sclerenchyma is dead and lignified-provides rigid structure (e.g. seed coats).
- Xylem = water "pipes"; Phloem = sugar "channels".
Leaf Structure: Mesophyll and Photosynthesis
Mesophyll is the region in the leaf where parenchyma cells carry out photosynthesis. It contains:
- Palisade mesophyll: tightly packed, upper leaf, main site of photosynthesis
- Spongy mesophyll: lower leaf, air spaces for gas exchange
| Leaf Layer | Function |
|---|---|
| Upper Epidermis | Protection |
| Palisade Mesophyll | Absorbs sunlight |
| Spongy Mesophyll | Gas exchange |
| Lower Epidermis | Contains stomata for CO₂/O₂ flow |
Growth Zones in Roots and Shoots
Plants grow from specific zones called meristems:
- Apical Meristems: Tips of roots and shoots; responsible for primary growth (length)
- Lateral Meristems: Cylinders in stems and roots; responsible for secondary growth (width)
Root Primary Growth Zones:
| Zone | Function |
|---|---|
| Zone of Cell Division | Cell creation via mitosis (apical meristem) |
| Zone of Elongation | Cells stretch, causing root/shoot to lengthen |
| Zone of Maturation | Cells differentiate into xylem, phloem, etc. |
Key Point:
Most lengthwise growth happens in the zone of elongation, not at the tip itself.
Meristems: Apical vs Lateral
Apical Meristem (Primary Growth):
- Found at shoot/root tips
- Divides to form new tissues
- Enables lengthening
Lateral Meristems (Secondary Growth):
- Vascular Cambium: Adds secondary xylem (wood) inside and secondary phloem outside
- Cork Cambium: Produces protective outer bark (cork cells)
| Meristem | Produces | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Vascular Cambium | Wood (xylem), inner bark (phloem) | Girth increases |
| Cork Cambium | Cork (outer bark) | Protective covering |
Misconception Alert:
Vascular cambium does NOT make bark-that's the cork cambium's job!
Take This Quiz
Rate this lesson:
 Back to top
Back to top