There’s a big gap between what people know and what they can actually do. I’ve seen it too many times — learners ace a test, but when it’s time to apply it in real life, they hit a wall.
That’s the problem with traditional exams. They’re good at testing memory but not so great at testing ability.
And that’s where performance-based assessments come in. Instead of asking people to recall facts, you’re asking them to roll up their sleeves and show you what they’ve really learned.
Think presentations, projects, experiments — anything that brings learning out of the textbook and into the real world.
In this guide, I’ll take you through the meaning of performance assessments, how to design them, what types work best, and how to run them in a way that builds real skills — not just scores.
Let’s begin.
What Is Performance-Based Assessment?
A performance-based assessment — also known simply as a performance assessment — is exactly what it sounds like: an assessment where learners show what they can do, not just what they know. It’s about applying knowledge in action, whether that’s building a project, giving a presentation, or solving a real-world problem.
Instead of checking if someone can recall facts, you’re evaluating how well they can use their learning in practical situations. This makes it a powerful tool across classrooms, corporate training rooms, and even hiring processes.
For example, imagine asking students to design a small community garden plan instead of listing the steps of sustainable farming. They’d have to think through soil types, weather, plant compatibility, and layout — applying knowledge to create a real-world solution.
It’s this hands-on relevance that makes performance-based assessments so effective. They push learners to think deeper, apply their knowledge creatively, and build genuine confidence in their abilities.
Watch: How to Create an Assessment Online
Why Is Performance Assessment Important?
Here’s why performance assessments are indispensable for businesses and other organizations:
- Real-World Application
Performance assessments reflect an individual’s abilities by evaluating their performance in practical tasks rather than theoretical knowledge alone. This ensures individuals are ready to tackle real-world challenges effectively.
A great example of this in action is St. Ronan’s College in Lurgan. Glenn Wilkinson, Head of Media Studies, brought his film analysis classes to life using ProProfs Quiz Maker.
With embedded clips and interactive questions, students didn’t just study directing styles — they actively critiqued and responded through text and video, bridging the gap between theory and creative practice.
Watch: How Glenn Wilkinson Creates Effective Video Exams With ProProfs
- Helps in Skill Development
These assessments help analyze skill gaps, enabling targeted training and development. By identifying areas of weakness, educators and trainers can provide focused support to enhance these skills.
- Aids in Better Learning
Performance assessments focus on practical application and promote deeper understanding and retention. When individuals apply their learning in realistic scenarios, they are more likely to grasp and remember the material.
- Enables Motivation & Engagement
Real-world tasks can be more motivating and engaging for learners, leading to better outcomes. When assessments are relevant and practical, individuals are more likely to be invested in their success.
5. Fosters Lifelong Learning and Reflection
Performance assessments encourage learners to think critically about their progress. The real-world feedback they receive doesn’t just improve immediate outcomes — it builds habits of reflection and continuous improvement that serve them far beyond the classroom or training environment.
Types of Performance Assessments
There isn’t just one way to design a performance assessment — and that’s the beauty of it. Depending on your learning goals, you can pick formats that spark curiosity and draw out real understanding. Let’s go through the most common ones educators are using today.
1. Project-Based Assessments
These are hands-on, immersive, and highly versatile. Think designing a marketing campaign, creating a science model, or producing a short documentary. Students tackle a complex problem or task over time, pulling together research, creativity, and critical thinking. It’s not just busy work — it helps learners connect theory with real-world application while building self-management along the way.
2. Portfolio Assessments
Rather than a one-off assignment, portfolios collect a range of student work over time. Essays, reports, videos, even reflections — all bundled into one place.
This format gives both educators and learners a fuller view of growth, strengths, and areas to work on. Plus, it builds a genuine sense of progress that’s hard to capture with traditional tests.
3. Simulation-Based Assessments
Here, students step into real-world scenarios and make decisions on the fly. Picture role-playing a customer service rep handling a tough client or using a video response quiz to answer job-style questions in real time. With ProProfs Quiz Maker, for example, educators can create these video interview quizzes easily — where students record video responses to questions that simulate real workplace scenarios. It’s a fantastic way to test not just what students know, but how they communicate under pressure, think critically, and apply knowledge in dynamic situations.
Watch: How to Create a Video Response Quiz
How Are Performance Assessments Used?
Performance assessments are widely used across various industries, each leveraging the unique benefits:
- Education
Teachers use performance assessments to evaluate students’ understanding and application of the curriculum. For instance, a science teacher might ask students to conduct an experiment and report their findings, demonstrating their grasp of scientific principles.
- Corporate Training
Businesses use training assessments to gauge employees’ competency and readiness for specific roles or tasks. For example, a customer service team might be assessed on their ability to handle difficult customer interactions through simulated scenarios.
- Creative Fields
Artists and designers are evaluated based on their ability to create and present their work. This might involve submitting portfolios or participating in live demonstrations, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of their creative abilities.
- Healthcare
Medical professionals are assessed on their practical skills, such as patient care and surgical procedures. Performance assessments ensure that healthcare providers can deliver high-quality care, directly impacting patient outcomes.
Real-Life Success Story
How to Conduct a Performance-Based Assessment: Step-by-Step Process
Designing a performance-based assessment isn’t just about ticking boxes — it’s about creating an experience where learners genuinely apply their skills to real-world situations. Here’s how to approach it thoughtfully.
1. Define What Success Looks Like
Before you think of tasks or tools, get clear on the outcomes.
Ask yourself: What should learners be able to do by the end of this assessment?
This isn’t just about recalling facts — it’s about applying knowledge, making decisions, and demonstrating understanding in practical scenarios.
For example, if you’re teaching environmental science, success could mean students designing a sustainable solution for waste management in their community.
2. Design Meaningful, Real-World Tasks
Now that you have clarity on outcomes, design tasks that mirror real-world challenges. The goal is to move away from theoretical tests and into practical demonstrations of skill. Tasks could include:
- Prototyping a product or solution
- Writing and presenting a business case
- Conducting a live demonstration
- Solving a complex, scenario-based problem
Whatever you choose, make sure the task feels relevant and purposeful — this boosts both engagement and learning retention.
3. Create a Transparent Evaluation System
Here’s where structure really matters. Learners should know exactly how they’ll be evaluated before they begin.
Rather than vague goals, provide clear scoring criteria that assess both the process and the final output.
A well-crafted rubric can go a long way here, detailing expectations for creativity, accuracy, application of knowledge, and critical thinking. Sharing this upfront helps students take ownership of their work.
4. Equip Learners With the Right Tools and Resources
No matter how well-designed your task is, if learners lack access to proper tools or materials, the experience falls short.
Prepare essential resources in advance:
- Reference materials or guidelines
- Templates or frameworks for structuring their work
- Access to required technology or tools
These supports don’t hand them the answers but provide the scaffolding they need to succeed.
5. Build in Feedback Along the Way
Performance-based assessments are not “one and done.” Regular feedback checkpoints are crucial.
Rather than waiting until the end, create natural pauses where you can:
- Offer formative feedback
- Encourage peer reviews
- Allow learners to reflect and revise their work
This approach turns the assessment into an ongoing learning journey rather than a final hurdle.
6. Facilitate, Don’t Dictate
When learners are deep in the assessment task, your role shifts to that of a guide.
Clarify expectations at the start, but once they begin, step back and let them take charge. Encourage creative solutions, even if they don’t follow a linear path. Resist the urge to over-correct — this is their opportunity to explore and problem-solve.
7. Evaluate Holistically
Finally, assess not just the final result but also the learner’s approach, adaptability, and reasoning.
A great performance-based assessment values both the journey and the destination. Consider:
- How effectively did they apply their knowledge?
- Did they demonstrate critical thinking and creativity?
- Were they able to self-assess and iterate on their work?
By evaluating both product and process, you’ll capture a true picture of their abilities.
Designing strong performance-based assessments isn’t complicated, but it does require intention. When you focus on real-world relevance, transparent expectations, and meaningful feedback, you create an environment where learners thrive and showcase their best work.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
Tips to Conduct a Performance Assessment
Conducting a successful performance assessment involves several practical steps. Here are ten tips to guide you:
- Plan Thoroughly
Outline the tasks or activities and gather all necessary resources in advance. Define the scope, objectives, and timeline for the assessment. Make sure all materials and tools needed are available and in working order. This preparation minimizes confusion and ensures a smooth assessment process.
- Communicate Clearly
Explain the assessment process and expectations to participants. Provide detailed instructions and clarify any doubts beforehand. Use simple, clear language to ensure everyone understands what is required. Clear communication helps set the right expectations and reduce anxiety among participants.
- Use Diverse Methods
Combine different types of assessments for a comprehensive view of performance. For example, mix practical tasks, quizzes, written reflections, and peer reviews to evaluate various competencies. This approach caters to learning and performance styles, providing a more rounded evaluation.
Watch: How to Create an Online Quiz
- Create Realistic Scenarios
Design tasks that mimic real-world challenges. For example, in performance assessments for sales training, simulate real customer interactions to evaluate how well participants apply their skills in realistic settings. This makes the assessment more relevant and engaging and better prepares participants for job tasks.
- Offer Immediate Feedback
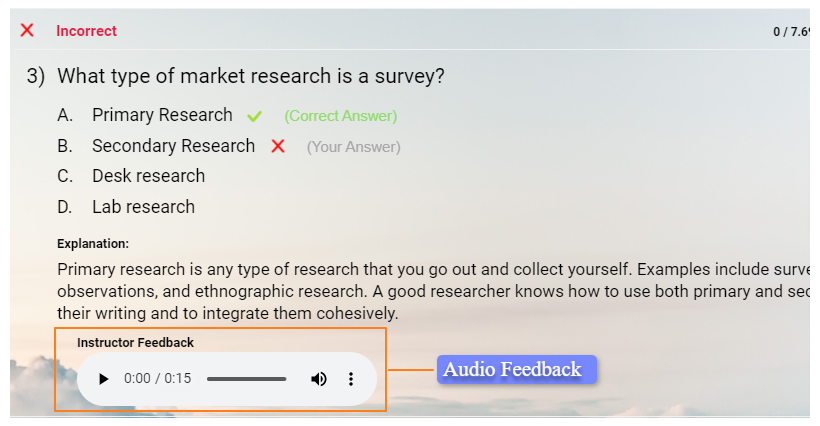
Provide specific, actionable feedback right after a performance-based assessment. This helps individuals understand their strengths and areas for improvement while the experience is still fresh.
Use a feedback sandwich approach—start with positive feedback, provide constructive criticism, and end with positive reinforcement.
Immediate feedback helps participants make timely adjustments and improvements.
- Document Everything
Keep detailed records of assessment results. Documentation helps track progress, identify trends, and make informed decisions about future assessments. Use digital tools to store and organize this information efficiently. Proper documentation & reporting also aid in accountability and transparency in the assessment process.
Watch: How to Review Quiz Reports & Statistics
- Engage Participants
Involve participants in the performance assessment process. Encourage self-assessments and peer assessments to provide a well-rounded evaluation. This fosters a sense of ownership and promotes self-reflection and peer learning. Engagement can lead to more accurate and comprehensive assessments.
- Use Technology
Use cutting-edge technology to elevate the efficiency and effectiveness of performance evaluation tests.
Performance assessment tools such as online quiz makers, video recording software, and digital submission platforms can greatly enhance both the administration and evaluation stages.
You can create more engaging and comprehensive performance assessments by leveraging diverse question formats supported by an online quiz maker.
- Audio Responses: Let assessment takers record audio to assess communication abilities, capturing nuances in tone and articulation.
- Video Responses: Request video submissions to gauge interaction skills, particularly how participants engage with customers or prospects.
- Interactive Video Tasks: Encourage learners to watch a demonstration video, pause to replicate the activity while recording themselves, and then upload their video response. This method is especially effective for practical skill and psychometric assessments.
- Image Uploads: Enable graphic designers and other visual artists to upload their creations, assessing both their creativity and technical skills.
- Document Uploads: Allow participants to submit written works, such as research papers or articles, to thoroughly evaluate their research and writing capabilities.
Moreover, online quiz platforms support remote assessments, broadening access and making it easier for participants to engage from any location.
- Simulate High-Stakes Environments
For roles that involve high pressure, create assessments that simulate these conditions. This could include timed tasks or multi-step challenges that require quick thinking and problem-solving.
Simulating high-stakes environments helps prepare participants for real-world pressures and assesses their performance under stress.
For example, you could create a timed online test in which customer support executives need to respond to customer complaints quickly and effectively.
Watch: How to Create a Timed Quiz
- Review & Revise
Regularly review and revise your assessment methods based on feedback and outcomes. Continuous improvement ensures that your assessments remain relevant and effective. Gathering feedback from both assessors and participants can highlight areas for enhancement, leading to more effective assessments over time.
Examples of Performance-Based Assessment Tasks
Here are some examples that illustrate the range and depth of performance assessments:
Short Tasks
- In-Class Writing Exercises: Quick prompts that require students to organize and express their thoughts on a topic within a class period.
- Short-Answer Tests: These tests evaluate students’ recall and understanding of key concepts through concise questions.
Extended Projects
- Real-World Problem Solving: Students tackle current issues by analyzing data and proposing viable solutions.
- Example: Developing a community plan to reduce plastic waste.
- Document Analysis Essays: Students examine and interpret literary or historical documents, crafting detailed essays showcasing critical thinking.
- Example: Analyzing the significance of the Declaration of Independence.
- Prototype Development: Students design and build models or devices to solve specific problems, demonstrating creativity and technical skills.
- Example: Constructing a bridge model to test engineering principles.
Creative & Technical Skills
- Art Projects: Creating original artworks allows students to demonstrate their artistic abilities and conceptual understanding.
- Example: Producing a painting on environmental themes.
- Technique Demonstrations: Students perform specific skills, such as in culinary arts or lab procedures, to show their proficiency.
- Example: Demonstrating precision knife skills in cooking.
Interactive & Collaborative Tasks
- Multimedia Presentations: Students use various media to create and present projects, enhancing their research and technical skills.
- Example: Presenting the impacts of World War II using slides, videos, and interactive elements.
- Software Development: Writing and debugging programs that meet specific requirements to showcase problem-solving and coding skills.
- Example: Developing a simple educational game or application.
- Physical Education Assessments: Engaging in sports or physical activities to demonstrate fitness and teamwork.
- Example: Playing a basketball game to exhibit skills and strategy.
- Debates: Structured debates where students articulate and defend their positions on controversial topics.
- Example: Arguing for and against renewable energy solutions.
Build Smarter, Stronger Assessments That Drive Real Learning
Performance-based assessment isn’t just a nice-to-have — it’s how you bridge classroom learning with real-world readiness. By focusing on how students apply their knowledge in authentic scenarios, you’re not just testing memory; you’re unlocking deeper understanding and critical skills.
Of course, building these kinds of assessments takes thoughtful planning. From choosing the right formats to designing meaningful tasks, every choice shapes the learning experience. And this is where the right tools can make a real difference.
With ProProfs Quiz Maker, you can design interactive, multimedia-rich assessments that bring real-world scenarios to life. Use video responses, scenario-based questions, and auto-graded formats to streamline your process. Get clear insights into student progress and create experiences that go beyond simple recall.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a performance-based approach in learning and assessment?
A performance-based approach focuses on applying knowledge to real-world tasks instead of just recalling facts. Learners demonstrate their understanding through projects, presentations, or practical exercises. This method encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and deeper learning, making assessments more meaningful and reflective of actual skills.
What are the pros of performance-based assessments?
They encourage practical skill application, boost engagement, and help learners retain knowledge better. By focusing on real-world tasks, these assessments promote critical thinking and problem-solving while providing a more accurate measure of ability than traditional tests.
What is the difference between performance-based assessment and authentic assessment?
Performance-based assessments test skills through tasks like presentations or experiments. Authentic assessments take it further, mirroring real-life situations closely. In short: all authentic assessments are performance-based, but not all performance-based assessments fully replicate real-world contexts.
What are some examples of performance-based assessments?
Examples include role-plays, presentations, portfolio submissions, and real-world simulations. For instance, a science student might design an experiment, while a marketing trainee could create a campaign pitch. These tasks test applied knowledge and critical thinking beyond written exams.
When should you use performance-based assessments?
Use them when you want to assess applied skills, problem-solving, or critical thinking. They’re especially effective for project-based learning, training simulations, or skill certifications, where demonstrating ability matters more than memorizing facts.

 We'd love your feedback!
We'd love your feedback! Thanks for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback!