The number of phenotypes produced in the F2 generation of a trihybrid...
The number of genotypes produced in the F2 generation of a trihybrid...
The number of different types of gametes produced in the F2 generation...
If you can't figure out the progeny of a cross in genetics, it is best...
The dominance relationship between the red-flower allele and the...
The dominance relationship between the A allele and the B allele in in...
An example of a human trait that shows incomplete penetrance...
Assume that plant height in a certain plant is determined by three...
If a trait has a heretability (h2) = 0.15, then the trait is...
In mice, the allele for agouti color (A) is dominant to the allele for...
In mice, the allele for agouti color (A) is dominant to the allele for...
In the type of gene interaction called gene suppression, an individual...
Among the viable progeny of the cross of two yellow-furred...
The expression of a gene can be altered by moving it to a new...
Himalayan coat in rabbits, where fur can be white or dark, is due to a...
If a single mutation has more that one phenotypic expression, it is...
If the phenotype is determined by the genotype of the mother, the...
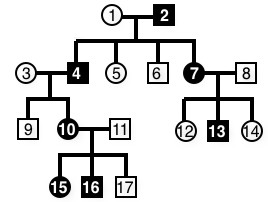
The trait (dark circles or squares) illustrated by the...
The trait (dark circles or squares) illustrated by the pedigree above...
This pedigree shows a trait (dark circles or squares) caused by an...
One of the most significant exceptions to Mendel's concepts of...
A woman with blood type AB has a child with blood type AB. Which...
The trait (dark circles or squares) illustrated by the...
A mother who is blood type A has a child who is also blood type A....
In Drosophila, one recessive mutation is found that causes the fly to...