|
Nervous System |
|

Without it, you couldn't exist!
Made up of your brain, your spinal cord, and a network of nerves.
Your brain uses information it receives from your nerves to coordinate all of your actions and reactions. |
| |
|
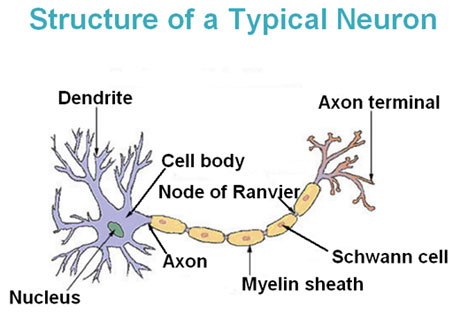
Neuron |
|

A specialized, impulse-conducting cell.
CENTER OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
Consists of the cell body, axon, and dendrites. |
| |
|
Cell Body |
|

Generates energy needed to carry out the work. |
| |
|
Dendrites |
|

Root like structures, attached to the cell body of neuron, that receive impulses form other neurons. |
| |
|
Axon |
|

A long, thin part of a neuron that transmits impulses to other neurons from terminal buttons. |
| |
|
What is a neuron's job? |
|
Carry messages in ONE DIRECTION from dendrites/cell body, through axon, to axon terminals.
Then transmits messages from terminal buttons to other neurons, muscles, or glands |
| |
|
Glial Cells |
|

Remove dead neurons & waste from the nervous system, nourish neurons, and direct their growth. |
| |
|
Myelin |
|

A fatty substance that decreases leakage of electrical current being carried along the axon, allowing messages to conduct regularly. |
| |
|
Afferent Neurons |
|

(Sensory Neurons)
Receive & transmit messages from sensory receptors to the spinal cord and brain.
Ex: The feeling you get in your foot after someone steps on it. |
| |
|
Efferent Neurons |
|
(Motor Neurons)
Transmit messages from the brain or spinal cord to muscles and glands.
Ex: Hopping around after someone steps on your foot. |
| |
|
Luigi Galvani |
|

Discovered that neural impulses are electrochemical.
*Connected lightning rods to dissected frogs. When lightning struct their muscles contracted. |
| |
|
Neural Impulses |
|

Electrochemical messages that travel within neurons at somewhere between 2 and 225 mph.
(neurons & body fluid contain ions in resting state)
Chemical changes happen within neurons which cause them to be transmitted. |
| |
|
Polarize/Resting Potential |
|

An unequal distribution of ions (atoms with a positive or negative charge) on the two sides of the nerve cell membrane.
Expressed as -70 mV, and the minus means that the inside is negative relative to (or compared to) the outside.
It occurs when a membrane is not being stimulated or conducting impulses. |
| |
|
Peripheral part of the nervous system |
|

Everything except the brain & spinal cord |
| |
|
Depolarize |
|
To reduce the resting potential of a cell membrane from about 70 millivolts to -----> 0. positive charge
Permeability of the cell membrane changes again, allowing no more sodium ions to enter. |
| |
|
Action Potential |
|

Very rapid change in membrane potential that occurs when a nerve cell membrane is stimulated.
Potential goes from the resting potential (typically -70 mV) to some positive value (typically about +30 mV) in a very short period of time.
Next section of the cell becomes permeable, positive ions are being pumped out, continuing the cycle.
A L L O R N O N E |
| |
|
How messages travel from neuron to neuron |
|

A neuron fired neurotransmitters out of an axon.
Incoming messages combine to reach a certain threshold. |
| |
|
All-or-none principle |
|
Action potentials occur maximally or not at all. |
| |
|
Refractory Period |
|
A phase following firing during.
A neuron is less sensitive to messages from other neurons and will not fire. |
| |
|
Synapse |
|

Flows info from one neuron to another.
When a nerve impuls reaches a synapse, axon terminals release chemical into the synaptic cleft. |
| |
|
Synaptic Vesicles |
|

Sacs in axon terminals, which contain neurotransmitters. |
| |
|
Neurotransmitters |
|

Chemical substances involved in the transmission of neural impulses from one neuron to another.
Work only at matching sites. -Exite: cause others to fire -Inhibit: prevent others to fire
Excess or Deficiencies lead to depression & schizophrenia
|
| |
|
Receptor Site |
|
A location on a dendrite of a receiving neuron tailored to receive a neurotransmitter. |
| |
|
Parts of the nervous system |
|
Brain, spinal cord, and nerves linking them to sensory organ, muscles, and glands. |
| |
|
Central part of the nervous system |
|
The brain & spinal cord |
| |
|
Somatic Nervous System |
|
Transmits messages about sight, sound, ect.Afferent (Sensory) & Efferent (Motor) |
| |
|
Automatic Nervous System |
|

Regulate glands & muscles of internal organs. -Sympathetic: prepares body for emergency -Parasympathetic: becomes active during relaxation. |
| |
|
Spinal Cord |
|

A long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain |
| |
|
Spinal Reflex |
|
A simple, unlearned response to a stimulus that may involve only 2 neurons (sensory & motor neuron) |
| |
|
Gray Matter |
|

Nonmyelinated neurons. Grayish neurons and neural segments that are involved in spinal reflex/or send axons to brain. |
| |
|
White Matter |
|
Longer myelinated axons that carry messages to and from the brain. |
| |
|
Episonic Memory |
|
remember what, where, and when you at dinner? |
| |
|
Amygdala |
|
Fear, emotion, and anxiety. Discovered by Delgado
Triggers stereotypical aggressive responses. |
| |
|
Down Syndrome results from |
|
when you have an extra chromosome on the 21st pair
Characterized by mental deficiency, a broad face, and slanting eyes. Death by middle age. |
| |
|
Wilder Penfield |
|
Stimulated parts of the brain with electrical probes |
| |
|
The Electroencephalograph (EEG) |
|
Record natural electricity in the brain (brain waves) passed between electrodes.
Associated with feeling of relaxation, sleep stages, and epilepsy. |
| |
|
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT Scan) |
|
Brain imaging that passes a narrow x-ray beam through the head & measures structures that reflect the rays from various angles, enabling a computer to generate a 3D image. |
| |
|
Position Emission Tomography (PET Scan) |
|
Brain imaging that injects a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream and assesses activity of parts of the brain according to the amount of glucose they metabolize. |
| |
|
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) |
|
Brain imaging that places a person in a magnetic field and uses radio waves to cause the brain to emit signals that reveal shifts in the floe of blood, which, in turn, indicate brain activity. |
| |
|
Functional MRI |
|
A form of MRI that enables researchers to observe the brain "while it works" by taking repeated scans. |
| |
|
Prefrontal Cortex |
|
EXECUTIVE CENTER where decisions are made to keep information in memory and solve problems |
| |
|
Hindbrain |
|
Where the spinal cord rises to meet the brain. |
| |
|
Pons(bridge) |
|
A structure of the hindbrain involved in respiration, attention, sleep, and dreaming.
In front of medulla. Transmits info about body movement. |
| |
|
Medulla |
|
An oblong area of the hindbrain involved in regulating heartbeat and respiration. |
| |
|
Cerebellum |
|
A part of the hindbrain involved in maintaining balance and controlling motor behavior. |
| |
|
Reticular Activating System (RAS) |
|
A part of the brain involved in attention, sleep, and arousal.
Vital in attention, sleep, and arousal.
Injury may result in a coma. |
| |
|
Forebrain |
|
Most forward part of the brain. |
| |
|
Thalamus |
|
Near the center of the brain involved in the relay of sensory information to the cortex and in the functions of sleep and attention. |
| |
|
Hypothalamus |
|
A bundle of nuclei below the thalamus involved in body temperature, motivation, and emotion. |
| |
|
James Olds & Peter Milner |
|
Discovered an animal's hypothalamus on accident.
PLEASURE CENTER
Humans are stimulated by higher functions. Choices & Values. |
| |
|
Limbic System |
|
A group of structures involved in memory, motivation, and emotion that forms a fringe along the inner edge of the cerebrum. |
| |
|
Cerebrum |
|
The large mass of the forebrain, which consists of 2 hemispheres |
| |
|
Cerebral Cortex |
|
The wrinkled surface area(gray matter) of the cerebrum. |
| |
|
Fissure |
|
Valley in the cortex. |
| |
|
Somatosensory Cortex |
|
The section of cortex in which sensory stimulation is projected. It lies behind the central fissure in the parietal lobe. |
| |
|
Prefrontal region |
|
Involved in thinking & language. |
| |
|
Aphasia |
|
A disruption in the ability to understand or produce language. |
| |
|
Wernicke's Aphasia |
|
A language disorder characterized by difficulty comprehending the meaning of spoken language. |
| |
|
Broca's Aphasia |
|
A language disorder characterized by slow difficult speech. |
| |
|
Left Brain |
|
Logical & Intellectual |
| |
|
Right Brain |
|
Intuitive, creative, and emotional. |
| |
|
Left Handedness |
|
Used to be considered a deficiency.
Tend to have language problems, yet gifted in music & math.
1 parent left handed = 80% probability for child |
| |
|
Epilepsy |
|
Temporary disturbances of brain function that involve sudden neural discharges. |
| |
|
Glands |
|
Organs that secrete one or more chemical substances such as hormones, saliva, milk.
2 Types: with & without ducts |
| |
|
Ducts |
|
A passageway that carries substances to specific locations. |
| |
|
Endocrine System |
|
System of ductless glands that secrete hormones and release them directly into the blood stream. |
| |
|
Hormone |
|
A substance secreted by an endocrine gland that regulates body functions.
Ex: growth,metabolism, and some behavior |
| |
|
Pituitary Gland |
|
MASTER GLAND -growth hormone(muscles, bones, glands) -prolactin (maternal behavior) -Vasopressin (paternal behavior for animals) -Oxytocin (stimulates labor) |
| |
|
Hypothalamus |
|
COMMANDER GLAND |
| |
|
Pineal Gland |
|
Secretes melatonin: regulates sleep-wake cycle |
| |
|
Thyroid Gland |
|
Produces thyroxin, which affects the body's metabolism. |
| |
|
Hypothyroidism |
|
A condition that results from too little thyroxin.
Too much or too little causes overweight & sluggishness. |
| |
|
Cretinism |
|
A condition characterized by stunned growth & mental retardation. |
| |
|
Adrenal Glands |
|
(located above the kidneys)Secretes hormones called corticosteroids: increase resistance to stress, promote muscle development, cause liver to release sugar, making more energy available for emergencies. |
| |
|
Darwin |
|
Believed in evolution & contradicted the Bible |
| |
|
Batural Selection |
|
Species that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. |
| |
|
Mutation |
|
Small, random genetic variations. |
| |
|
Evolutionary Psychology |
|
Studies ways in which adaptation and natural selection are connected with mental processes and behavior. |
| |
|
Instincts |
|
Stereotyped pattern of behavior that is triggered by a particular stimulus. |
| |
|
Heredity |
|
Defines Nature
Traits from parents to offspring by means of genes. |
| |
|
Genetics |
|
Defines Nurture
The area of biology that focuses on heredity. |
| |
|
Genes |
|
MOST BASIC unit of heredity, found on a specific point on chromosome |
| |
|
Chromosomes |
|
A microscopic rod-shaped body in the cell nucleus carrying genes that transmit heredity traits from generation to generation. |
| |
|
DNA |
|
Forms the basic material of chromosomes; form of a double helix and contains genetic code.
James Watson & Francis Crick |
| |
|
Polygenetic |
|
Traits influenced by gene combos.
Ex: intelligence. |
| |
|
Genotype |
|
Genetic makeup based on nucleotide sequencing.
NATURE |
| |
|
Phenotype |
|
Outer appearance based off life experiences.
NURTURE |
| |
|
Sex Chromosomes |
|
23rd pair, which determines sex
X from father =femaleY from father=male |
| |
|
Kinship Studies |
|
*identical twins share 100% genes**parents & children have 50%**aunts & uncles share 25% with nieces/nephews**1st cousins share 12.5%* |
| |
|
Zygote |
|
The fertilized egg cell (ovum) that carries genetic messages from both parents |
| |
|
Monozygotic Twins (MZ) |
|
Develop from a single fertilized ovum that divides into 2 early in development; share the same genetic code. (IDENTICAL) |
| |
|
Dizygotic Twins |
|
Develop from 2 fertilized ova who are closest relates as brother & sister in general (FRATERNAL) |
| |
