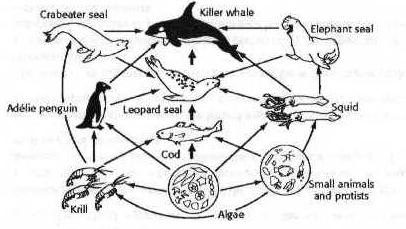
AMONG ALL OF THE FOOD CHAINS, THE ORGANISMS AT THE HIGHEST TROPHIC LEVEL ARE...
A-the crabeater seal
B-the killer whales
C- the krill
D-the algea
|
|
B-the killer whales
|
| |
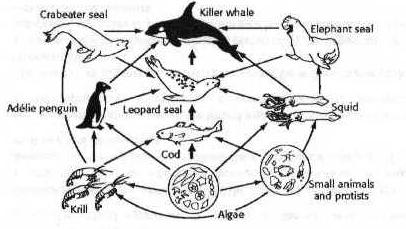
THE DIAGRAM, WHICH SHOWS HOW ENERGY MOVES THROUGH AN ECOSYSTEM, IS CALLED A...
A-habitat net
B-food chain
C-food web
D-trophic level
|
|
C-food web
|
| |
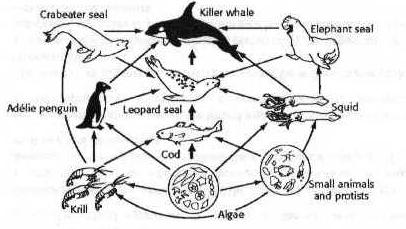
THE LEOPARD SEALS ARE...
A-omnivores
B-producers
C-carnivores
D-herbivores
|
|
C-carnivores
|
| |
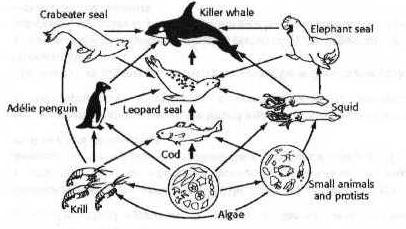
THE PHOTOSYNTHETIC ALGEA ARE
A-decomposers
B-producers
C-parasites
D-consumers
|
|
B-producers
|
| |
A GROUP OF ORGANISMS OF DIFFERENT SPECIES LIVING TOGETHER IN A PARTICULAR PLACE IS CALLED A
A-biome
B-community
C-habitat
D-population
|
|
B-community
|
| |
IN AN ECOLOGICAL ENERGY PYRAMID, ANIMALS THAT FEED ON PLANTS ARE LEAST IN THE...
A-first trophic level
B-second trophic levels
C-third trophic level
D-fourth trophic level
|
|
B-second trophic level
|
| |
IN A FOOD WEB, WHICH TYPE OF ORGANISM RECEIVES ENERGY FROM EVERY OTHER TYPE...
A-carnivore
B-producer
C-decomposer
D-all of the above
|
|
C-decomposer
|
| |
WHEN AN ORGANISM DIES, THE NITROGEN IN ITS BODY...
A-is released by the action of decomposers
B-can never be reused by other living things
C-is immediatley released into the atmosphere
D-all of the above
|
|
A-is released by the action of decomposers
|
| |
HOW MUCH ENERGY IS AVAILABLE TO THE ORGANISMS IN LEVEL 3...
A-all of the energy in level 1 minus the energy in level 2
B-all of the energy in level 1 plus the energy in level2
C-about 10% of the energy in level 2
D-about 90% of the energy in level 2
|
|
C- about 10% of the energy in level2
|
| |
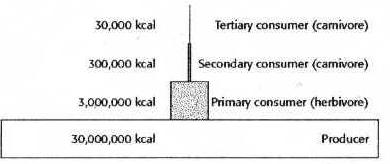
AT EACH TROPHIC LEVEL, THE ENERGY STORED IN THE ORGANISMS IN THAT LEVEL IS...
A-about 10% of the energy in the level below it
B-about 50% of the energy in the level below it
C- about 10% of the energy in the level above it
D-about 50 % of the energy in the level above it
|
|
A-about 10% of the energy in the level below it
|
| |
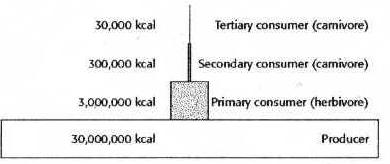
THE DIAGRAM REPRESENTS THE DECREASE IN...
A-the number of organisms between lower and higher trophic levels
B-available energy between lower and higher trophic levels
C-diversity of organisms between lower and higher trophic levels
D-all of the above
|
|
B-available energy between lower and higher trophic levels
|
| |
HUMANS AFFECT THE CARBON CYCLE BY...
A-burning fossil fuels
B-destroying vegetation that absorbs carbon dioxide
C-clearing forests
D-all of the above
|
|
D-all of the above
|
| |
PRECIPITATION AND EVAPORATION ARE IMPORTANT COMPONENTS OF THE...
A-carbon cycle
B-water cycle
C-nitrogen cycle
D-all of the above
|
|
B-water cycle
|
| |
WATER AND MINERALS NEEDED BY ALL ORGANISMS ON EARTH PASS BACK AND FORTH BETWEEN THE BIOTIC AND ABIOTIC PORTIONS OF THE ENVIROMENT IN A PROCESS CALLED
A-a biochemical pathway
B-a throphic cycle
C-a biogeochemical cycle
D-a trophic pathway
|
|
C-a biogeochemical cycle
|
| |
THE ORGANIC MATERIAL IN AN ECOSYSTEM IS CALLED...
A-biomass
B-trophic level
C-productivity
D-energy
|
|
A-biomass
|
| |
WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A WAY THAT ORGANISMS DEAL WITH UNFAVORABLE ENVIROMENTAL CONDITIONS...
A-interdependence
B-dormancy
C-body temperature regulation
D-migration
|
|
A-interdependence
|
| |
THE NUMBER OF TROPHIC LEVELS IN AN ECOLOGICAL ENERGY PYRAMID...
A-never exceeds three
B-is limitless
C-is limited by the amount of energy that is lost at each trophic level
D-is impossible to count because energy is lost at each trophic level
|
|
C-is limited by the amount of energy that is lost at each trophic level
|
| |
SPECIES WITH NARROW NICHES...
A-are called specialists
B-use a wide variety of resources
C-can tolerate a range of enviromental conditions
D-all of the above
|
|
A-are called specialists
|
| |
THE PRIMARY PRODUCERS IN A GRASSLAND ECOSYSTEM WOULD MOST LIKELY BE...
A-algae
B-insects
C-grasses
D-bacteria
|
|
C-grasses
|
| |
COAL, OIL, AND NATURAL GAS...
A-are formed from decayed plants
B-are fossil fuels
C-release carbon dioxide when they are burned
D-all of the above
|
|
D-all of the above
|
| |
ORGANISMS THAT MANUFACTURE ORGANIC NUTRIENTS FOR AN ECOSYSTEM ARE CALLED...
A-omnivores
B-consumers
C-producers
D-predators
|
|
C-producers
|
| |
THE STUDY OF THE INTERACTION OF LIVING ORGANISMS WITH EACH OTHER AND WITH THEIR PHYSICAL ENVIROMENT IS CALLED...
A-health
B-economy
C-geology
D-ecology
|
|
D-ecology
|
| |
IN GOING FROM ONE TROPHIC LEVEL TO THE NEXT HIGHER LEVEL...
A-the amount of usable energy decreases
B-the number of organisms increases
C-the amount of usable energy increases
D-none of the above
|
|
A-the amount of usable energy decreases
|
| |
THE SPECIFIC PHYSICAL LOCATION IN WHICH A GIVEN SPECIES LIVES IS CALLED ITS...
A-community
B-climate
C-abiotic factor
D-habitat
|
|
D-habitat
|
| |
AN ECOSYSTEM CONSISTS OF...
A-a community of organisms
B-energy
C-the soil, water and weather
D-all of the above
|
|
D-all of the above
|
| |
ECOLOGICAL MODELS ARE USEFUL FOR ALL OF THE FOLLOWING PURPOSES EXCEPT...
A-evaluating proposed solutions to enviromental problems
B-making predictions about future ecological changes
C-testing predictions about future ecological changes
D-accounting for all the variables that exist in a real enviroment
|
|
D-accounting for all the variables that exist in a real enviroment
|
| |
ALL ORGANISMS IN AN ECOSYSTEM ARE LINKED TOGETHER IN ANETWORK OF INTERACTIONS. THIS QUALITY IS CALLED...
A-interdependence
B-isolation
C-communication
D-geochemical processes
|
|
A-interdependence
|
| |
THE AREAS OF AN ORGANISM'S TOLERANCE CURVE THAT LIE AT THE EXTREME HIGH OR LOW FOR AN ENVIROMENTAL VARIABLE REPRESNT THE...
A-range of the enviromental variable preferred by the organism
B-zones of efficent performance by the organism
C-zones of poorest performance by the organism
D-optimal range of the enviromental variable for the organism
|
|
C-zones of poorest performance by the organism
|
| |
WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS COMMON TO THE CARBON CYCLE, THE NITROGEN CYCLE, AND THE WATER CYCLE...
A-the largest reserves of the substance are always in organisms
B-the substance is rearranged into different types of molecules as it moves through its cycle
C-the substance must pass through decomposers in order to complete its cycle
D-the substance is required by all living things and its involved in many processes that occur in living things
|
|
D-the substance is required by all living things and is involved in many processes that occur in living things.
|
| |
WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT PART OF THE NITROGEN CYCLE...
A-nitrogen fixation
B-conversion of nitrogen from decaying organisms into ammonia
C-conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into usable organic compounds by bacteria
D-nitrogen evaporation
|
|
D-nitrogen evaporation
|
| |
WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING WOULD NOT BE INCLUDED IN A DESCRIPTION OF AN ORGANISMS NICHE...
A-its trophic level
B-the humidity and temperature it prefers
C-when it reproduces
D-its number of chromosomes
|
|
D-its number of chromosomes
|
| |
