|
What is a hydrocarbon? |
|
A compund composed of only carbon and hydrogen. |
| |
|
What are the 4 different types of hydrocarbons? |
|
Alkanes (Chapter 11) - Only carbon-carbon single bonds
Alkenes (Chapter 12) - One or more carbon-carbon double bond
Alkynes (Chapter 12) - one or more carbon-carbon triple bond
Arenes (Chapter 13) - One or more benzene-like rings |
| |
|
What is an alkane? |
|
Hydrocarbons containing only carbon-carbon single bones. |
| |
|
What is a line-angle formula? |
|
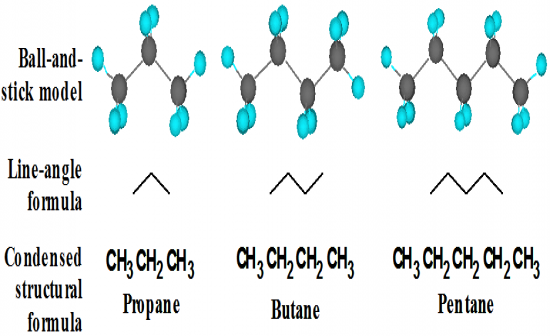
A line represents a carbon-carbon bond and a vertex and a line terminus represent a carbon atom.
Hydrogen atoms are not shown in line-angle formulas. |
| |
|
What are the first 10 alkanes? |
|
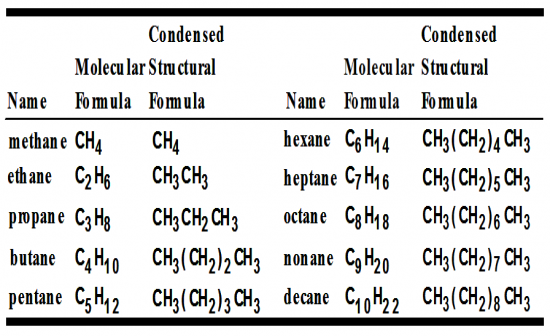
|
| |
|
What is a constitutional isomer? |
|
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas (different connectivity) |
| |
|
What are the three molecular formulas where there is only one structural formula? |
|
CH4, C2H6, C3H8 |
| |
|
What are the two structural formulas and names of the molecular formula C4H10. |
|
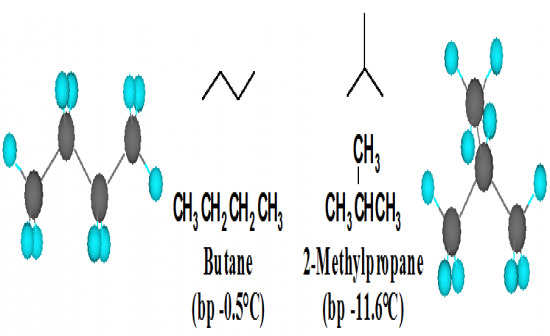
|
| |
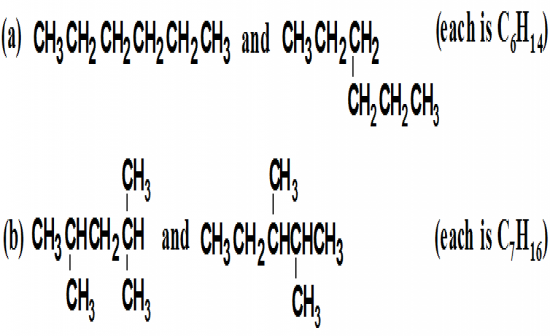
Do the structural formulas in each set represtent the same compound or constitional isomers? |
|
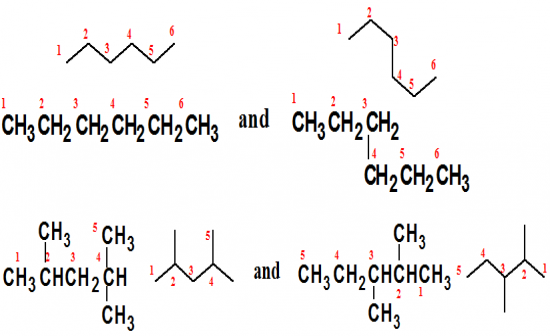
(a) represents the same compound
(b) represents constitutional isomers
|
| |
|
What is a parent chain? |
|
The chain that has the most most carbon atoms |
| |
|
What is a substituent? |
|
the groups bonded to the parent chain |
| |
|
How do you name an organic compound? |
|
1. Find the longest chain and number it so that the substituate has the smallest number.
a) if the same substituent occurs number the times the substituent occurs by a prefix, di-, tri-, terta-, penta-, hexa-, etc. Use a comma to sperate position numbers
b)If there are different substituents at the same poition number so that one that comes first alphabetely has the lower number.
3. DO NOT include the prefixes when alphabetizing
|
| |
|
What is a cyclic hydrocarbon? |
|
A hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms joined to form a ring |
| |
|
What is a cycloalkane? |
|
A cyclic hudrocarbon in which all the carbons are saturated (no double or triple bonds)
Cycloalkanes with ring sizes ranging from 3 - over 30 carbon atoms are known in nature.
Rings with 5 and 6 carbons are the most stable and six five varbonds (cyclohexanes and cyclopentanes) are common in nature. |
| |
|
How do you name a cycloalkane? |
|
Prefix the name of the corresponding open-chain alkane with cyclo-, and name each substituent on the ring.
If there is only one substituent on the rinf, there is no need to give it a location number
If there are more than one substituent, number the rinf beginning with the substituent of lower alphabetical order.
|
| |
|
What is an isomer? |
|
Two molecules with exaclty the same number of atoms of each element but in two different arrangements. |
| |
|
What are cis and trans isomers? |
|
Cis = on the same side
Trans = across from.
|
| |
|
What are examples of a cyclopentane with 2 methyl substituents. (from the side) |
|
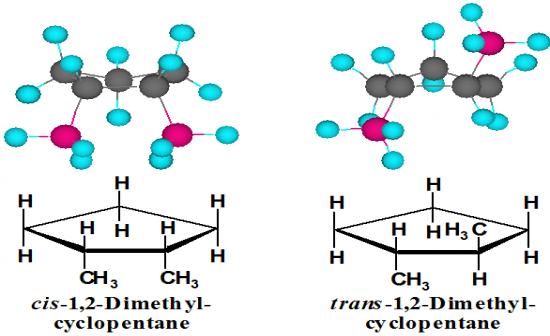
|
| |
|
What are examples of a cyclopentane with 2 methyl substituents. (from the top) |
|
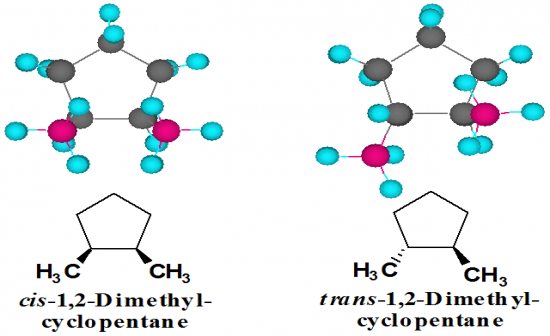
|
| |
Practice naming.
/educmat/chm19104/nomenclature/quizes.html |
|
/educmat/chm19104/nomenclature/quizes.html |
| |
|
What is it called when an isomer has a different orientation of atoms in space? |
|
sterioisomer
cis-trans isomer is one type
enantiomers is another |
| |
|
What are the physical properties of alkanes and cycloalkanes? |
|
almost all have a lack of polarity.
The electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is 2.5 - 2.1 = 0.4 on the Pauling scale
Given this small difference, we classify a C-H bond as nonpolar covalent.
Alkanes are nonpolar compounds and the only interaction between their molecules are the very weak London dispersion forces.
Melting point and boiling points
- boiling points of alkanes are lower than those of almost any other type of compound of the same molecular weight.
In general, both boiling and melting points of alkanes increase with increasing molecular weight. |
| |
|
What are the similarities and differences of an isomer? |
|
Same molecular weight and formula, different structural formaula. They have different physical and chemical properties. |
| |
|
Describe the solubility of alkanes? |
|
Alkanes are not soluble in water; they are unable to form hydrogen bonds with water
Alkanes are soluble in each other
Alkanes are also soluble in other nonpolar organic compounds, e.g. toluene and diethylether.
|
| |
|
Describe the density of alkanes. |
|
The average density of the liquid alkanes listed in Table 11.4 is about 0.7 g/mL; that of higher-molecular-weight alkanes is about 0.8 g /mL.
All liquid and solid alkanes are less dense than water (1.0 g/mL) and, because they are insoluble i water, they float on water. |
| |
|
What are the different types of reactions of alkanes? |
|
Oxidation (combustion)
Halogenation (reaction with halogens)
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
|
| |
|
Describe Oxidation reaction of alkanes. |
|
aka combustion - oxidation of hydroarbons, including alkanes and cycloalkanes, is the basis for their use as energy sources for heat [natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and fuel oil] and power (gasoline, diesel fuel, and aviation fuel).
e.g. CH4 + 2O2 --> CO2 + 2H2O + energy (887 kJ/mol)
CH3CH2CH3 + 5O2 --> 3CO2 + 4H2O + energy (2218 kJ/mol) |
| |
|
Describe a reaction of alkanes and halogens. |
|
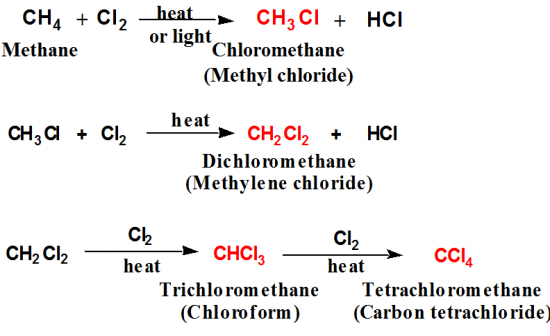
Halogentation is a substitution reaction.
|
| |
|
What are chlorfluorocarbons? |
|
Chloroflurocarbons (CFCs)
Manufactured under the trade name Freon
CFCs are nontoxic, nonflammable, odorless, and noncorrosive.
Amoung the CFCs most widely used were CCl3F (freon-11) and CCl2F2 (Freon-12) |
| |
|
Where are CFCs used? |
|
Heat-transfer agents in refrigeration systems.
Industrial cleaning solvents to prepare surfaces for coating and to remove cutting oils from millings.
Propellants for aerosol sprays. |
| |
|
What is the structural formula and the use of Freon 12. |
|
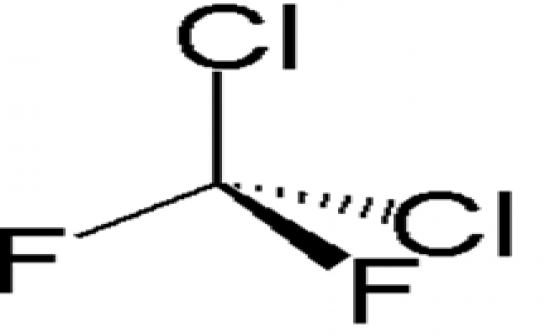
Freon 12 was used for aerosols. It is non-toxic and non flammable so very "safe" |
| |
|
What is the structural formula of Halon 1211 and the use. |
|
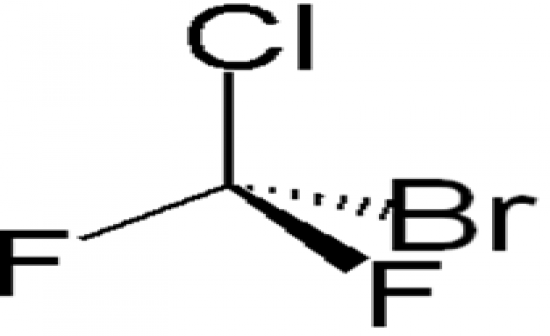
Halon 1211 was used for fire extingushing systems in aircraft, subarines and computer facilities. Very effective and non-toxic - you can breath it. |
| |
|
What are the replacements of CFC and why? What are the two compounds? |
|
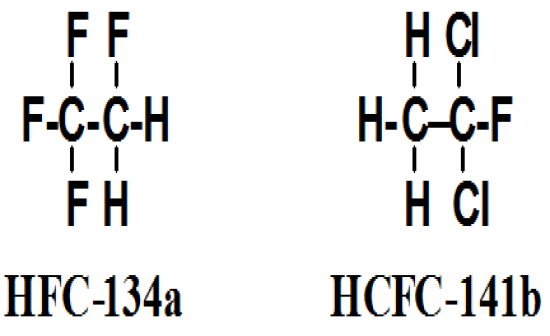
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) cause destruction of the Earth's stratoshperic ozone layer/
The most prominent replacements are the hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrochloroflurocarbons (HCFCs)
- These compounds are chemically more reactive than CFCs and are destroyed before they reach the stratosphere.
Natural gas
- 90 to 95 percent methane
5 - to 10 percent ethane and
- a mixture of other relatively low-boiling alkanes, chiefly propane, butane and 2 methylpropane
Petroleum - A thick, viscous liquid mixture of thousands of compounds, most of them hydrocarbons formed from the decomposition of maine plants and animals |
| |
|
What are the main natural gases and what percentage? |
|
90 - 95 percent methane
5 - 10 percent ethane
the rest is a mixture of other relatively low-boiling alkanes, chiefly propane, butane, and 2-methylpropane. |
| |
|
What is petroleum? |
|
A thick, viscous liquid mixture of thousdands of compounds, most of them hydrocarbons formed from the decompostion of marine plants and animals. |
| |
Practice naming.
/APchemistry/APtaters/alkanes.htm |
|
/APchemistry/APtaters/alkanes.htm |
| |
