|
Cardiac and skeletal muscle are _____ |
|
striated |
| |
|
Cardiac and smooth muscle are also _______ |
|
involuntary |
| |
|
smooth muscle is typically found within the walls of hollow visceral organs, blood vessels, and ____ |
|
airways |
| |
|
A skeletal muscle cell is called a _____ fiber |
|
muscle |
| |
|
epimysium |
|
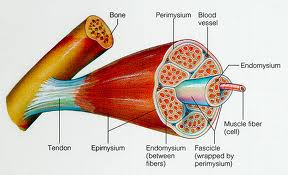
epimysium |
| |
|
perimysium |
|
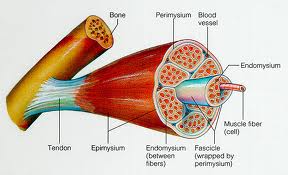
perimysium |
| |
|
fasicicles and endomysium and muscle fibers. |
|
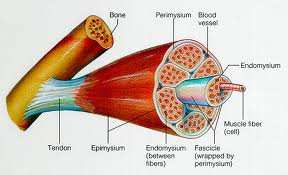
fascicles |
| |
|
Functional unit of muscle contraction is the sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum, and _____ |
|
sarcoplasm |
| |
|
Thin myofilaments are composed of myosin, actin, and light chain _____ |
|
myokinase |
| |
|
The sarcoplasmic reticulum of muscle fibers is a storage site for calcium ions and releases the calcium when stimulated. |
|
by action potential |
| |
|
_ tubules are continuous with the sarcolemma |
|
T |
| |
|
An action potential is a rapid up and down shift in the voltage across a membrane from the negative resting to a positive ____ |
|
value |
| |
|
resting membrane potential is maintaned by |
|
sodium potasium ATP pump |
| |
|
Acetyl choline is the neurotransmitter released from vesicles in the synaptic knob of the ____ |
|
neuron |
| |
|
Excitation-Contraction Coupling |
|
1.) Nerve signal
2.) Calcium is released
3.) ACh diffuses across synaptic cleft
4.) Binding causes a comformational change
5.) K+ gates open
6.) Depolarization spreads along sarcolemme
7.) depolar runs through T Tubules
8.) Ca2+ diffuses out of SR and binds to troponin
9.) Active sites exposed
10.) ATP causes release of G-Actin |
| |
|
A ___ unit consists of a motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates. |
|
motor |
| |
|
The amount of tension generated by a muscle and the force of its contraction depends on how relaxed or contracted it was prior to ________. |
|
stimulation |
| |
Concentric muscle contraction
ecentric |
|
muscle curling up
weight going down |
| |
