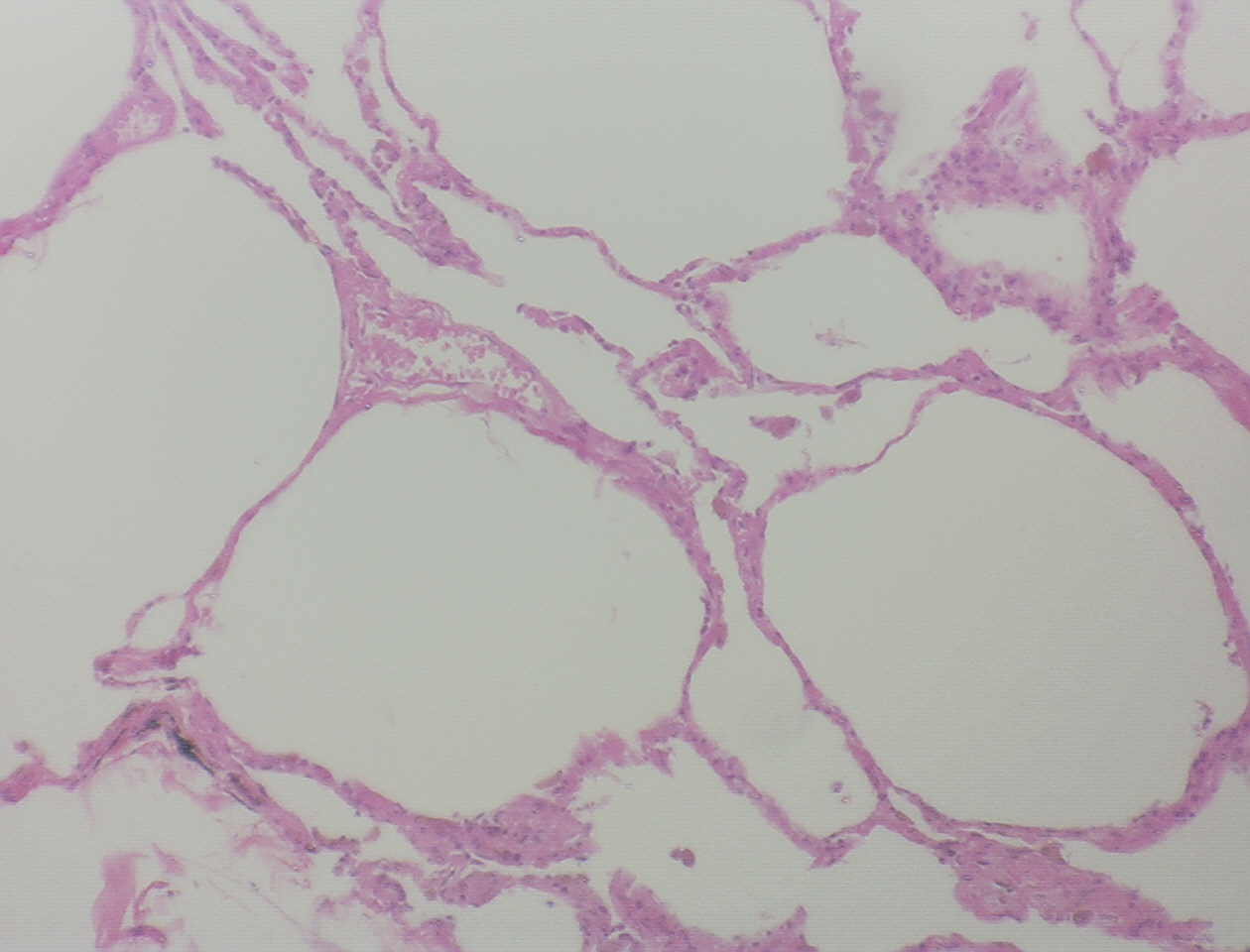
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
|
DESCRIPTION: Single layer of flattened cells, disc shaped nuclei.
FUNCTION: Allows passage by diffusion and filtration. LOCATION: Located in Kidney, glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels.
|
| |
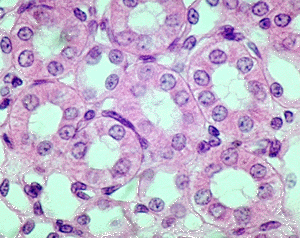
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
|
DESCRIPTION: Single layer of cube like cells, large spherical central nuclei.
FUNCTION: Secretion and absorbtion
LOCATION: Kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface.
|
| |
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
|
DESCRIPTION: Single layer of tall cells with rounded nuclei.
FUNCTION: Absorption, secretion of mucus, ciliated type propels mucus.
LOCATION: non-ciliated types lines most of digestive tract; ciliated types lines small bronchi, uterine tubes.
|
| |
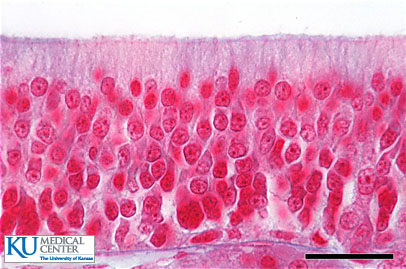
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
|
DESCRIPTION: Single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface; nuclei seen at different levels. May contain goblet cells and cilia.
FUNCTION: Secretion of mucus, propulsion of mucus bu cilia.
LOCATION:Non-ciliated type in male's sperm carrying ducts. Ciliated types lines trachea and most of upper respiratory tract.
|
| |
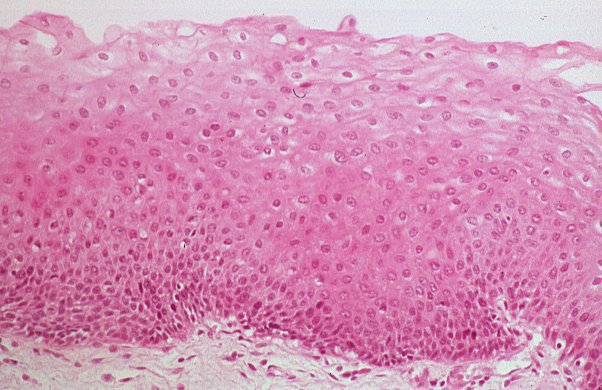
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
|
DESCRIPTION: Thick membrane composed of several cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or columnar. Surface cells are flattened / squamous. KERATINIZED TYPE surface cells are full of keratin and dead: basal cells are active in mitosis.
FUNCTION: Protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion.
LOCATION: NONKERATINIZED TYPE form the moist linings of the esophagus, mouth and vagina. KERATINIZED forms the epidermis of the skin, a DRY membrane.
|
| |
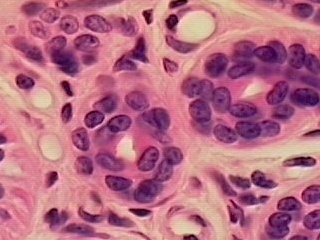
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
|
|
DESCRIPTION: Two layers of cube like cells
FUNCTION: Protection
LOCATION:Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands and salivary glands.
|
| |

Transitional Epithelium
|
|
DESCRIPTION: Resembles both stratified squamous AND stratified cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or columnar; surface cells DOME SHAPED or squamous (depending on degree of organ stretch, like full bladder).
FUNCTION: Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine.
LOCATION: Lines ureters, bladder and part of urethra.
|
| |
