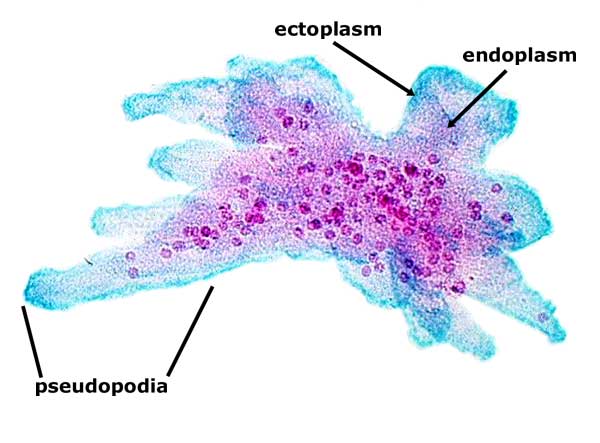
Phylum Rhizopoda |
|
Pseudopods, branch out and move away, retract (ameobas) PROTIST |
| |
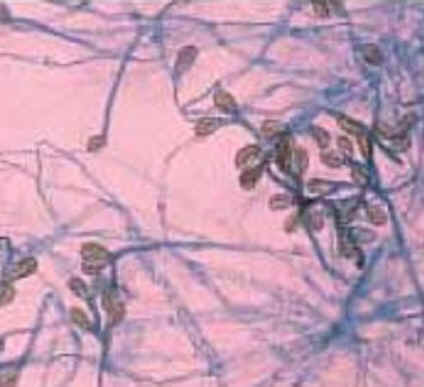
Phylum Myxomycota |
|
Plasmodial slime molds, sporangia, phagocytosisPROTIST |
| |
|
Clade Chromalveolata |
|
Secondary endosymbiosisPROTIST |
| |
|
Clade Alveolata |
|
Alveoli, pellicle can produce armor platesPROTIST |
| |
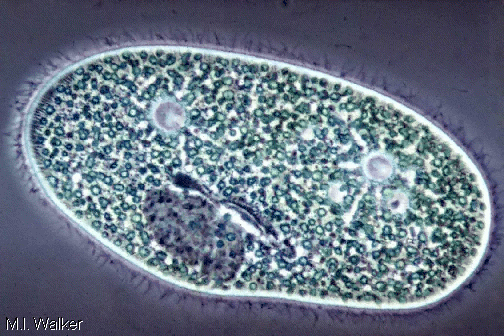
Phylum Cilliophora |
|
Have cilia, micro and macro nuclei, ParameciumPROTIST |
| |

Phylum Dinophyta |
|
Unicellular with flagella, armor look, red tide, endosymbionts called zooanthellaePROTIST |
| |
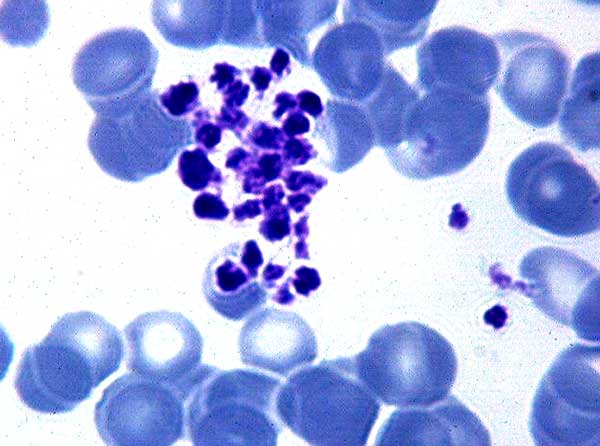
Phylum Apicomplexa |
|
Sporozites, merozites, trophozites --> life cycle of malariaPROTIST |
| |

Phylum Bacillariophyta |
|
Chlorophyll A & C, laminarin --->carbohydrate food, diatomaceous earth --> polishing powder |
| |
|
Phylum Oomycota |
|
Most fungal-like protist, potatoe famine, sporangiophores, flagellated cells called zoospores,PROTIST |
| |

Phylum Phaeophyta |
|
brown algae, kelps, stipe (stems) and blades (leaves), laminarinPROTIST
|
| |

Phylum Chlorophyta |
|
Green algae, chlorphyll a & b, methyl cellulose, conjugation, PROTIST |
| |

Phylum Rhodophyta |
|
red algae, chlorphyll a, starch for carbs, calcium carbonate in cell wallsPROTIST |
| |
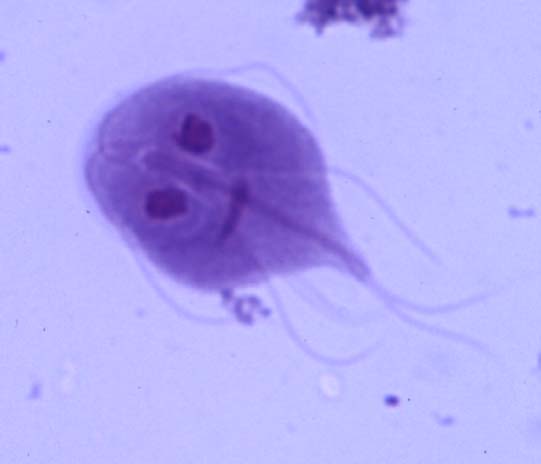
Phylum Euglenophyta |
|
eyespot (stigma), flexible pellicle, energy as the carb paramylon, heterotophicPROTIST |
| |
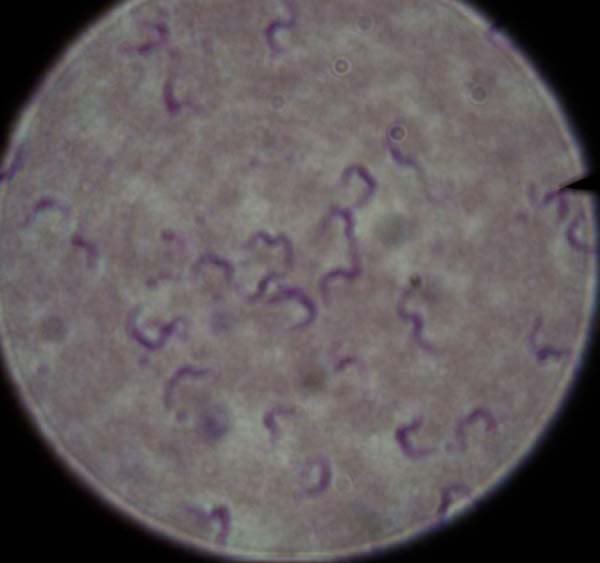
Phylum Kinetoplasta |
|
African Sleeping Sickness (trypanosoma)PROTIST |
| |
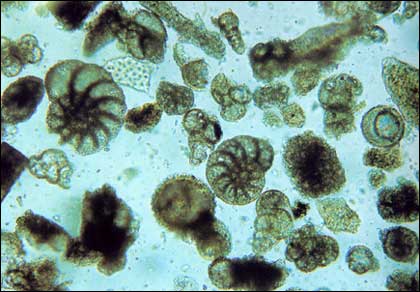
Phylum Formanifera |
|
shell of calcium carbonate, white cliffs of DoverPROTIST |
| |

Phylum Radiolaria |
|
shell of silicon dioxidePROTIST |
| |

Phylum Bryophyta |
|
lack vascular tissue, two generations, sporophyte and gametophyte, gametangia, branching structure called protonema, antheridium and archegonia, meispores, |
| |

Phylum Hepatophyta |
|
Liverworts, produce asexually by gemmae |
| |

Phylum Psilophyta |
|
stem branches dichotomously, homosporous |
| |
|
Phylum Lycophyta |
|
adf |
| |
|
adf |
|
adf |
| |
|
