|
Magna Carta |
|
(1215) Limited the king's power.
-Based on the feudal contract. Kings & leaders are held accountable for their actions.
-Became the basis for English Law & the US Bill of Rights |
| |
|
1215 |
|
Magna Carta was signed & limited the King's power |
| |
|
1607 |
|
Establishment of the first English colony in North America at Jamestown |
| |
Bill of Rights |
|
Amendments #1-10 of the U.S. Constitution.
- They protect personal freedoms and property. |
| |
|
establishment |
|
Creation |
| |

colony &
colonists |
|

the creation of a community of one group of people outside of their homeland or what these people are called |
| |
|
Jamestown |
|
The first colony from England in North America |
| |
|
Virginia House of Burgesses |
|
(1619) The 1st representative assembly in the American colonies |
| |
Representative Assembly |
|
a meeting of people who represent (stand for) citizens to make political decisions |
| |

Mayflower Compact |
|

(1620) Written by the Pilgrims who came to America, it said that they would follow the laws they would write |
| |

consent |
|

approval |
| |

English Bill of Rights |
|

(1689) In England, it says the Parliment will make the laws & the king and people will follow the laws.
- It was the basis for the U.S. Bill of Rights |
| |
Parliament (in England)
Congress (in the United States) |
|
These groups are made up of the representatives of the people
- they make decisions in government for the people (this is known as representative democracy)
- these representatives are voted for by the common people |
| |
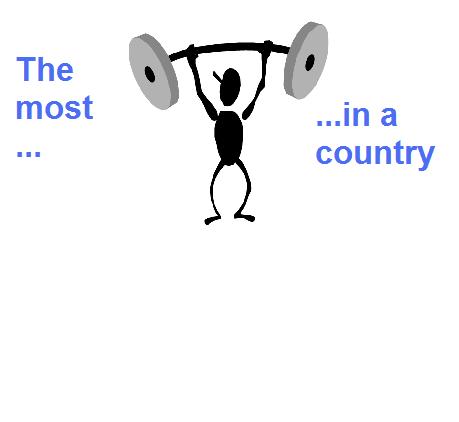
sovereign |
|
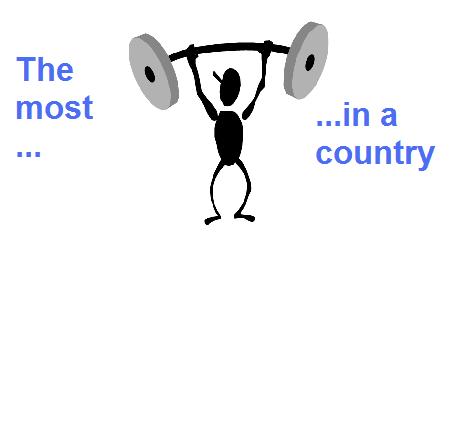
the most powerful politican in a country |
| |

sovereignty |
|

a nation or states supreme power inside its borders |
| |

monarchy |
|

rule by a king or queen |
| |
|
absolute monarchy |
|
when a king or queen hold all the power in a country (and does not share it) |
| |

limited monarchy |
|

when a king or queen shares power with the people (or with Parliament or Congress) |
| |

nationalism |
|

the feeling of loyalty and attachment to a country |
| |

common law |
|

laws that applies to everyone in a country
(the United States has a common set of laws) |
| |
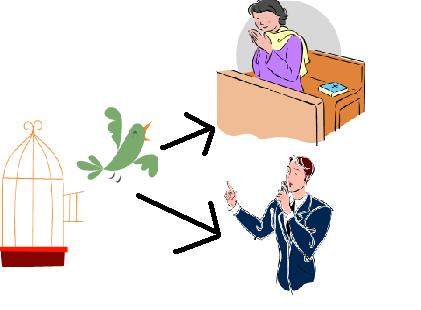
individual rights |
|
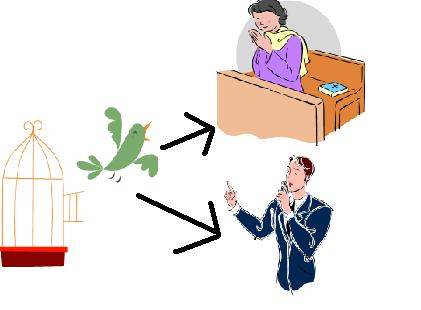
rights that belong to a person, such as:
freedom of speech
freedom of religion
right to a jury trial
innocent until proven guilty |
| |
republic |
|
a type of government in which the leader is not a monarch and some citizens have the right to vote
|
| |
popular sovereignty |
|
power belongs to the people |
| |
|
Articles of Confederation |
|
the 1st form of government in the United States
- it was made to bring the states together to end the Revolutionary War
- had a weak central government |
| |
|
federalism |
|
a type of government in which power (sovereignty) is divided between the national and state governments |
| |

Judiciary branch |
|

one of the 3 branches of government
- this is the courts and judges
- interprets the law |
| |

Executive branch |
|

one of the 3 branches of government
- this is the president, governors, mayors
- carries out the laws |
| |

Legislative branch |
|

one of the 3 branches of government
- this is made up of the officials people vote for to represent them (at the city council, and state and national Senates & House of Representatives)
- makes laws |
| |
Separation of Powers |
|
power is divided between the 3 branches of government (Judicial, Executive, and Legislative) |
| |
checks and balances |
|
no one branch of government can get too much power, because the other two branches will check on it and balance it out |
| |
|
represent |
|
to stand for |
| |
Declaration of Independence |
|
- written by Thomas Jefferson in 1776 in America
- told King George III what he was doing wrong and why the colonists were breaking from England
- expressed desires for a democratic, representative government |
| |
|
Revolutionary War |
|
the war fought between the American colonists and England from 1775 - 1781 |
| |

Treaty of Paris (1783) |
|

Ended the Revolutionary War
- Colonies were recognized (seen as) independent
- the United States are officially formed!!! |
| |

grievance |
|

complaint
(such as the ones listed by the colonists about King George III in the Declaration of Independence) |
| |

ratified |
|

officially approve or pass
(the states had to each ratify, or approve, of the Constitution before it became official) |
| |
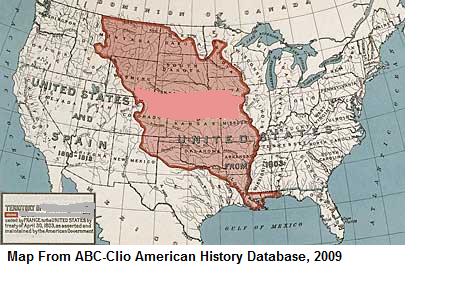
Louisiana Purchase (1803) |
|
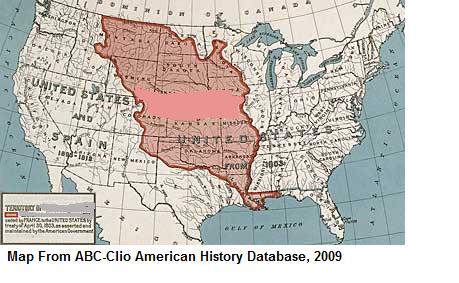
Bought from France in 1803
- it doubled the size of the United States |
| |
surrender |
|
to give up
(especially in war) |
| |
|
alliance |
|
a group (of people or countries) who all want the same thing
- those people or countries are each others allies |
| |
|
restrict |
|
prevent |
| |

Samuel Adams |
|

Leader of the Boston Tea Party
- Anti-British
- Signed the Declaration of Independence |
| |

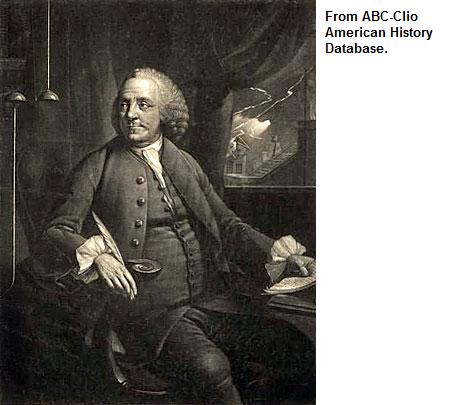
Benjamin Franklin |
|
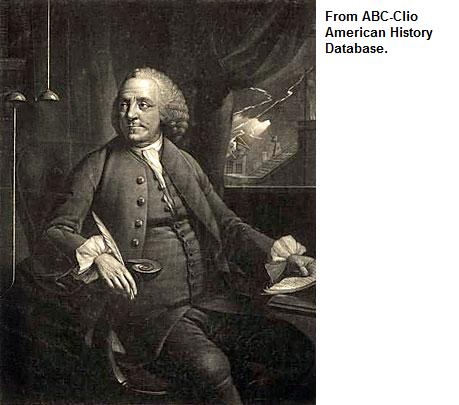

During the Revolutionary War, he went to France to create an alliance that helped the American colonists win the war
- In 1783, he helped with the Treaty of Paris, which ended the Revolutionary War |
| |

King George III of England |
|

Wanted to keep control of the American colonies by fighting against their attempts at independence
- the colonial greviances against him are listed in the 2nd part of the Declaration of Independence |
| |

Thomas Jefferson |
|

A leader of the American Revolution
- Wrote the Declaration of Independence |
| |
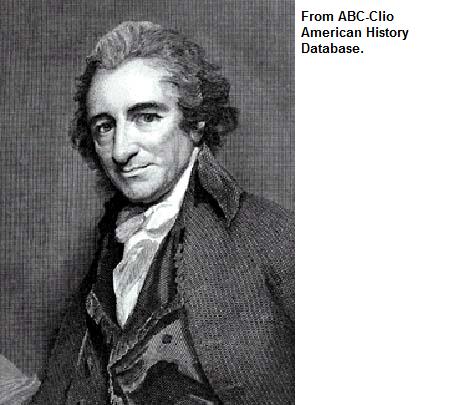

Thomas Paine |
|
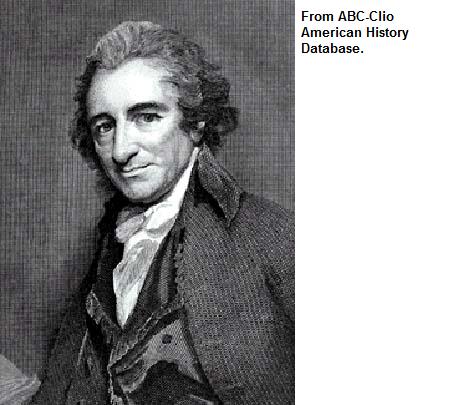

Wrote an article (Common Sense) that told the American colonists to revolt against England & declare independence |
| |

George Washington |
|

Commander-in-chief of the Contential (colonists') Army
- 1st President of the United States |
| |
|
delegate |
|
a person who represents a group of people
(also known as a representative) |
| |
|
Battles of Lexington & Concord (1775) |
|
The first battles of the Revolutionary War |
| |
|
amendment |
|
change or correction |
| |

impose |
|

force (as in taxes) |
| |
|
Battle of Saratoga (1777) |
|
the Americans defeat the British
- this is the major turning point in the Revolutionary War |
| |
|
Battle of Yorktown (1781) |
|
The final battle of the Revolutionary War
- the Americans (with help from France) defeat the British |
| |

U.S. Constitution |
|

Formed the government of the United States
|
| |

trial by jury |
|

having a jury (12 people) decide if the person on trial is innocent or guilty
(this is a right promised in the Bill of Rights) |
| |
|
negotiate |
|
agree to (as in treaties or terms of surrender) |
| |
|
pardon |
|
excuse |
| |
|
guarantee |
|
promise |
| |
|
inalienable rights |
|
rights that can not be taken away from a person
(such as life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness) |
| |
|
Republicanism |
|
government by elected representatives of the people |
| |
