Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
12.1.1
Describe the inducing of an emf by relative
motion between a conductor and a magnetic field
|
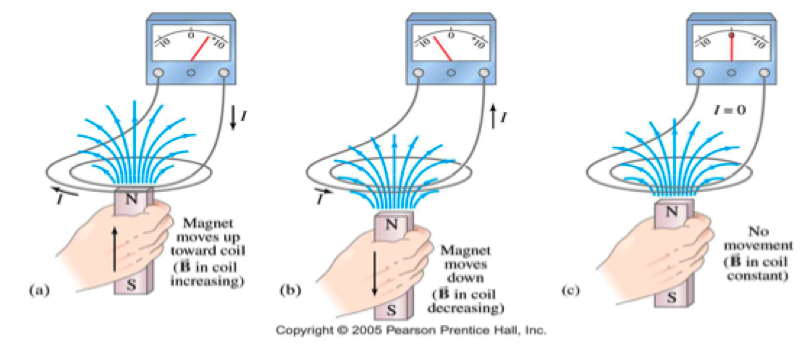 A changing magnetic field induces an emf — current within a conductor. Such a current is called an induced current. Motion or change is required to induce an emf. If does not matter whether the magnet or the coil moves. |
|
12.1.2
Derive the formula for the emf induced in a
straight conductor moving in a magnetic field
|
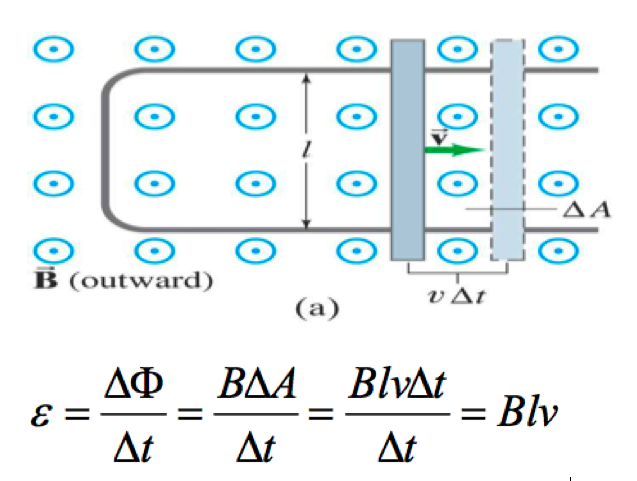 If the rod is made to move at a speed v, it travels a distance of ∆x = v∆t. Therefore the area of the loop increases by an amount ∆A = l ∆x = lv∆t. |
|
12.1.3
Define Magnetic Flux and Magnetic Flux
Linkage
|
•Magnetic Flux is the product of the flux
density normal to the surface and the area of the surface. Φ=BAcosθ
•Magnetic Flux Linkage is the magnetic flux multiplied
by the number of coils. Φ=NBAcosθ
|
|
12.1.4
Describe the production of an induced emf by
a time changing magnetic flux
|
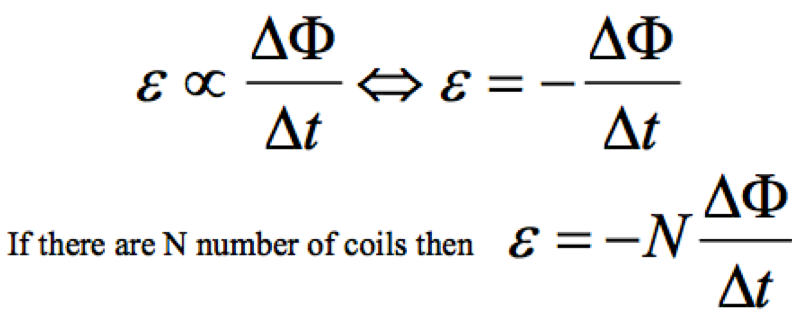 Refer to image |
|
12.1.5
State Faraday’s and Lenz’s Law
|
Faraday’s Law
The magnitude of the induced emf in a circuit
is directly proportional to rate of change of magnetic flux or flux- linkage.
Lenz’s Law
The direction of the induced emf is such that
the current it causes to flow opposes the change producing it.
|
|
12.2.1
Describe the emf induced in a coil rotating within a uniform magnetic field
|
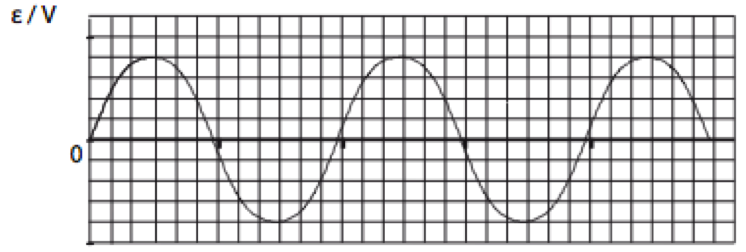 •The emf is alternating or sinusoidal. |
|
12.2.2
Explain the operation of a basic alternating current (ac) generator
|
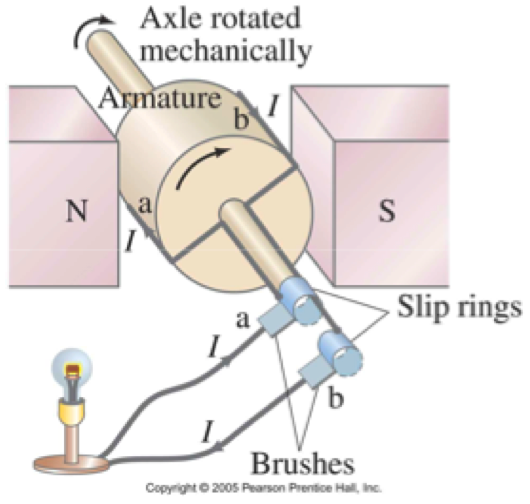 A generator consists of many loops of wire wound on an armature that can rotate in a magnetic field. The axle is turned by some mechanical means and an emf is induced in the coil. |
|
12.2.3
Describe the effect on the induced emf of changing the generator frequency
|
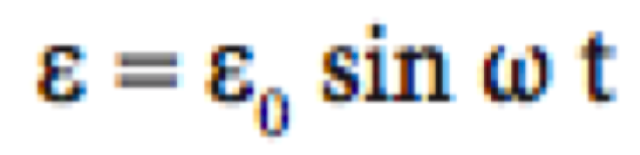 Refer to image |
|
12.2.4
Discuss what is meant by the root mean squared (rms) value of an
alternating current or voltage
|
Rms values are used to find the average voltage as they are sinusoidal
|
|
12.2.5State the relation between peak and rms values for sinusoidal voltage and currents
|
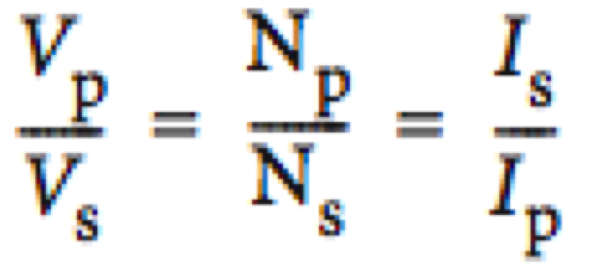 Peak value = rms value x ,-2. Vpeak = Vrms x,-2.Ipeak = Irms x ,-2. |
|
12.2.8Describe the operation of an ideal transformer
|
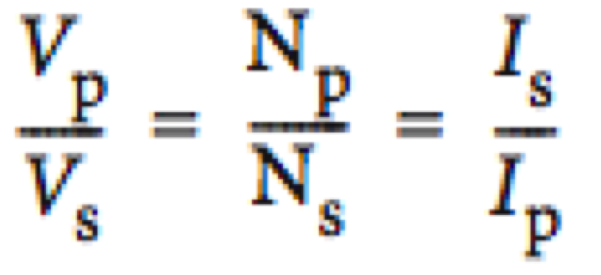 A useful device that makes use of electromagnetic induction is the ac transformer as it can be used for increasing or decreasing ac voltages and currents. |
|
12.3.1
Outline the reasons for power losses in
transmission line and real transformers
|
Power loss in
transmission line
·
Heat
loss due to current
·
Resistance
of the metal used
·
Dielectric
losses
·
Self-inductance
Power loss in real
transformers
·
Eddy
currents
·
Resistance
of the wire in the winding
·
Hysteresis
·
Physical
Vibration
·
Dielectric
losses
·
Electromagnetic
radiation
·
Flux
leakage
|
|
12.3.2
Explain the use of high-voltage step-up and
step-down transformers in the transmission of electrical power.
|
The voltage is
step-up from the power plant to have a higher power output due to power
dissipating. The voltage is then step-down when the power has reached its
consumer source (where the power is being consumed). There is no ideal valve of
step-up voltage due to economic reason.
From the power
plant, a step-up transformer is used to increase voltage (so that current is
decreased) from 11,000 V to 250,000 V. from the transmission line to city
storage, a step-down transformer reduces voltage from 250,000 to 4500 V. then
in front of a house, a step-down transformer reduces that to 200-240V.
|
|
12.3.4
Suggest how extra-low-frequency electromagnetic fields such as those
created by electrical appliances and power lines induce currents within a body
|
A human body is a
conducting medium, so when it is moving in an alternating magnetic field at
extra-low-frequency, then electric field is induced, hence inducing current in
human body.
|
|
12.3.5
Discuss some of the possible risks involved in living and working near
high-voltage power lines
|
Current experimental
evidence suggests that low-frequency fields don’t harm genetic material. There has
been evidence that this may lead to infant cancer and infant leukemia. These
risks are likely to be dependent on current (density) frequency, and length of
exposure.
|