Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
3.1.1:
Describe the arrangement of
elements in the periodic table in
order of increasing atomic number.
|
Names and symbols of the elements are given
in the Chemistry data booklet. The history of the
periodic table will not be assessed.
|
|
3.1.2:
Distinguish between the terms group
and period.
|
|
|
3.1.3:
Apply the relationship between the
electron arrangement of elements
and their position in the periodic
table up to Z = 20.
|
|
|
3.1.4:
Apply the relationship between the
number of electrons in the highest
occupied energy level for an element
and its position in the periodic table.
|
The number of valence electrons is the same for a group, but increases across a period.
|
|
3.2.1:
Define the terms first ionization energy
and electronegativity.
|
Electronegativity: The tendency for the atoms of the element to attract electrons when they are
chemically combined with another element.
Ionisation energy: The energy that is required (or given out) to overcome the attraction of the nuclear charge and remove an electron from a gaseous atom. Removing 1 electron results in a +1 charge. |
|
3.2.2:
Describe and explain the trends in
atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization
energies, electronegativities and
melting points for the alkali metals and the halogens.
|
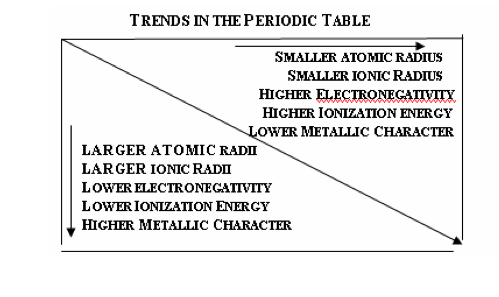 Data for all these properties is listed in the Chemistry data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of the balance between the attraction of the nucleus for the electrons and the repulsion between electrons. Explanations based on effective nuclear charge are not required. |
|
3.2.3:
Describe and explain the trends in
atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization
energies and electronegativities for
elements across period 3.
|
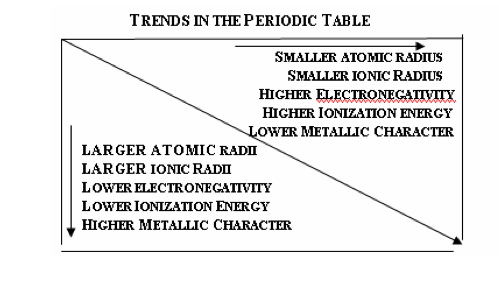 See image. |
|
3.2.4: Compare the relative
electronegativity values of two
or more elements based on their
positions in the periodic table.
|
Compare.
|
|
3.3.1:
Discuss the similarities and
differences in the chemical properties
of elements in the same group.
|
The following reactions should be covered.
|
|
3.3.2:
Discuss the changes in nature, from
ionic to covalent and from basic to
acidic, of the oxides across period 3.
|
 Equations are required for the reactions of Na2O, MgO, P4O10 and SO3 with water. |