Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Describe direct receptor activaion (ionotropic).
|
-Let ions through, binding to a receptor causes it to form a channel. Fast time frame signaling.
|
|
Describes the metabotropic or indirect recptor activation.
|
-Binding of a activates a G-protein and the protein binds intracellularly activating a channel. Slower acting than ionotropic (1sec up to minutes depending on signaling pathway)
-depends on lots of biochemical reactions.
|
|
Describe the discovery of chemical synapses in cardiac muscles.(Otto Lewi)
|
Came up with a dream in an experiment, A frog heart in a chamber was shocked (vagus nerve), the aplitude and the frequency go down. The profuse dripped into the sencond chamber. Upon stimulation of the first heart dripped into second chamber and slowed the beat of the heart rate.
|
|
What did this explain?
|
That chemicals mediate synaptic tranmission.
|
|
Electrical.
|
-direct current flow from one cell to another. AP invades terminal and currents flow. Class of proteins, virtually forming gap junctions or conexus. The proteins are called connexus in the vertebrates. (invertebrates have a class of protein called innexus). WHen current flows you get instantaneous activation of that cells.
|
|
How is the junction formed?
|
The connexus is formed and inserted into the membrane, they line up forming the connexons.
|
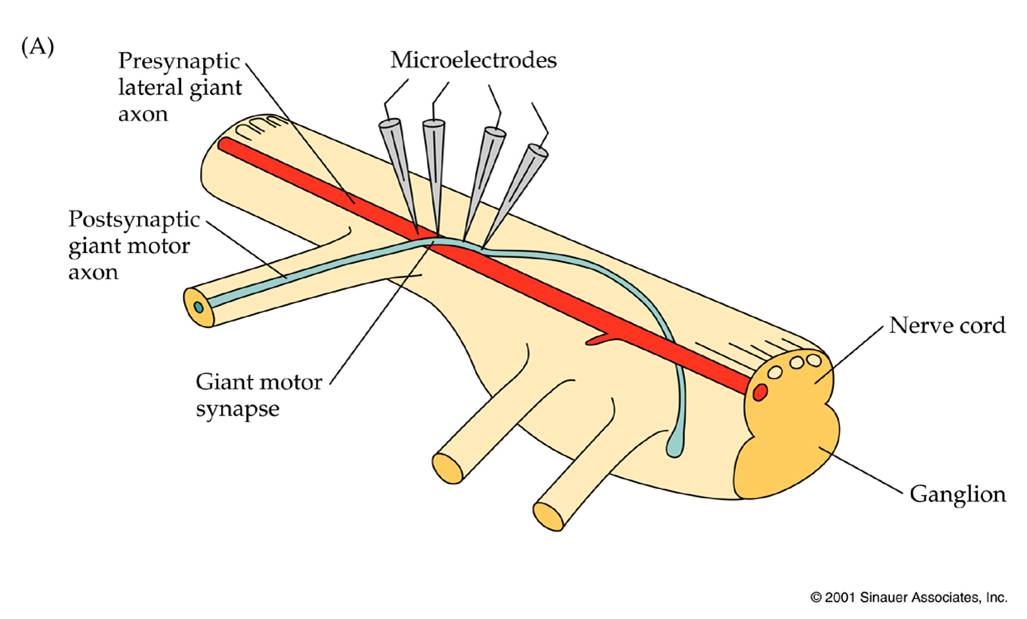 Describe the stimulation of the crayfish axxon? |
Electrodes were inserted in the electrical crayfish axon. It was shown there there was no synaptic delay upon stimulation, the activation in across the synapse was instantaneous.
|
|
What happens if the postsynptic axon was activated?
|
No transmission, this showed that it was a rectified synapse.
|
|
What determines that electrical synapses are rectified?
|
Its determeined by second messanger properties, voltage properties, and many other factors.
|
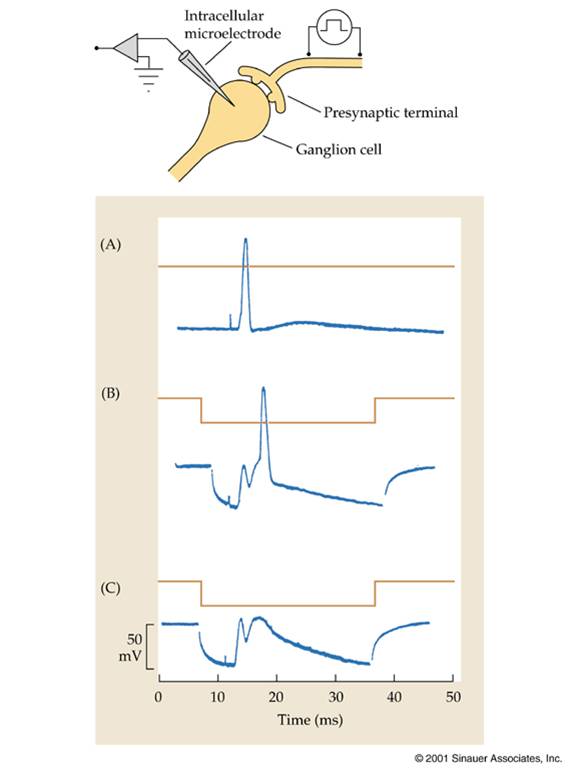 Describe the duel electrical/chemical synpase in a chick ganglion cell. |
-Stimulate presynaptic fiber, and record postsynaptically. A blip is created by stimulus, transmitter is released and there is an electrical junction as well and you get AP.
|
|
What happens if you inject negative current into postsynaptic neuron?
|
You hyperpolarize the postsynaptic cell, then you shock the nerve.
|
|
What happens if you shock the nerve after the negative current is injected into postsynaptic cell?
|
There are two responses, The elctrical component is instantaneous, then there is a chemical EPSP sometime later.
|
|
What happens if you inject more negative current sometime later?
|
It causes the AP to fail because makes it even more negative.
|
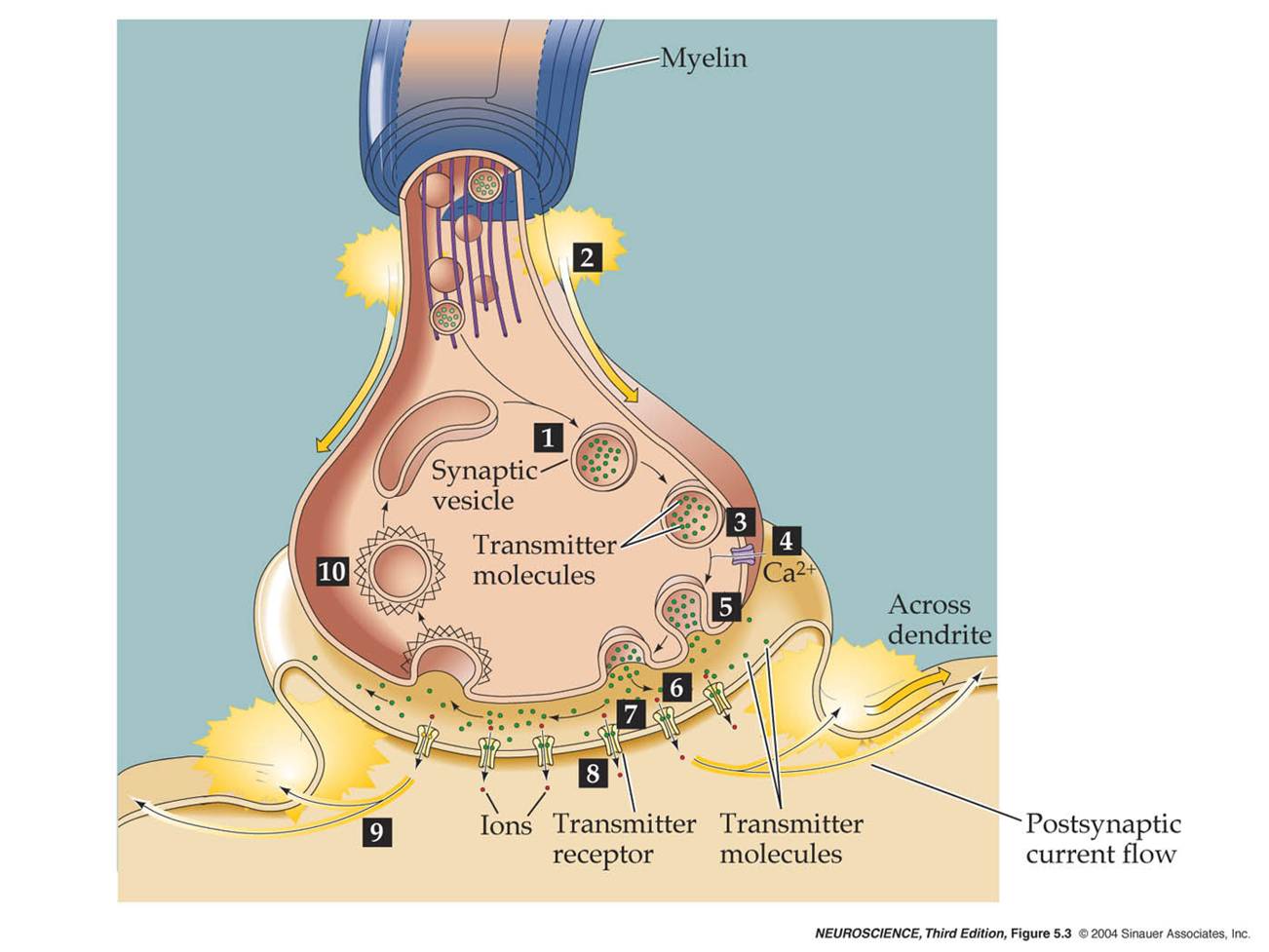 Describe the steps involved in chemical synaptic transmission. |
AP invades terminal---> vesicale docks--> it then merges membrane with plasma membane.
|
|
How does the vesicle merge with the presynaptic membrane?
|
The depolarization activates voltage gated CA2+ channels that are more densely packed near the synaptic gap next to the dock vesicles.
|








