Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
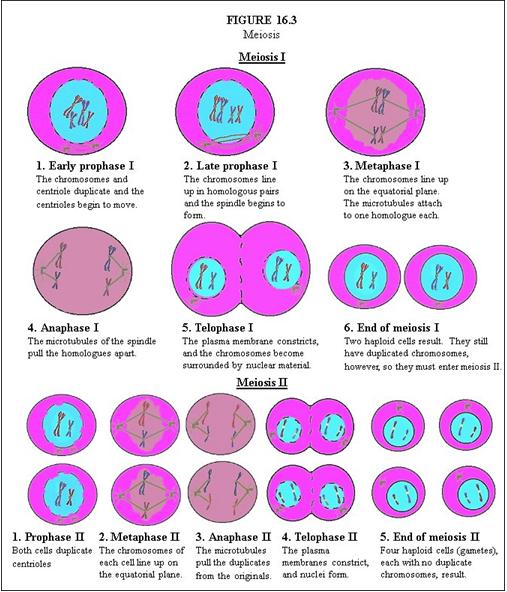
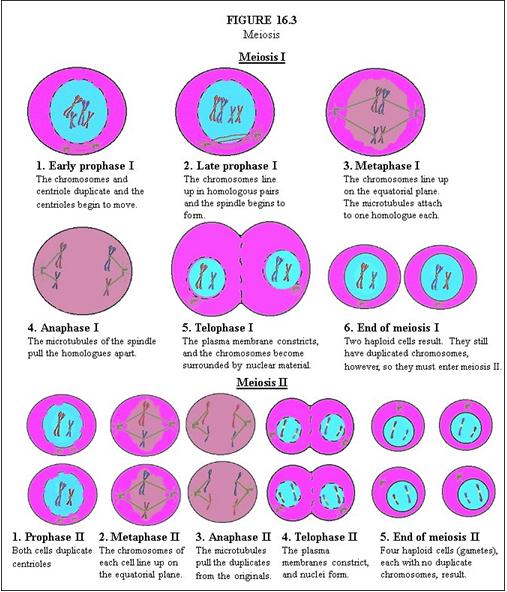 In Meiosis I, describe Early Prophase I. |
The chromosomes and centriole duplicate and the centrioles begin to move.
|
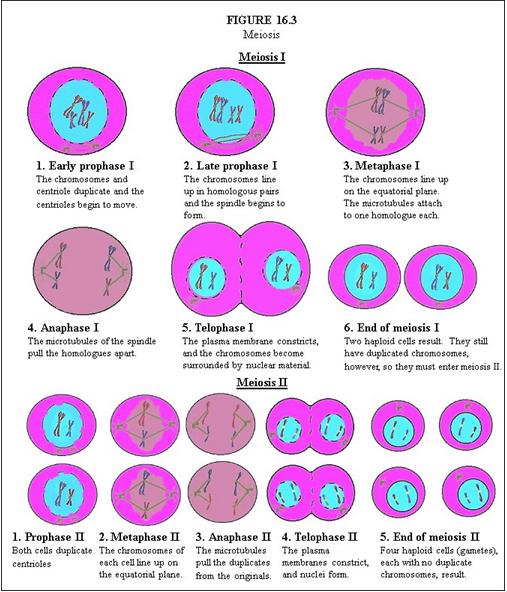 In Meiosis I, describe Late Prophase I. |
The chromosomes line up in homologous pairs and the spindle begins to form.
|
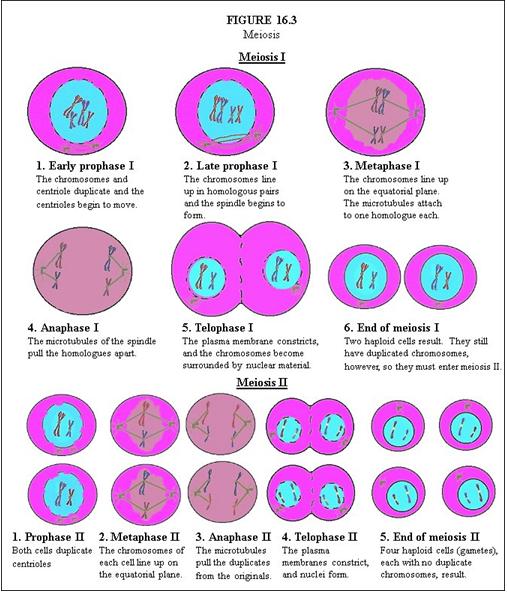 In Meiosis I, describe Metaphase I. |
The chromosomes line up on the equatorial plane. The microtubules attach to one homologue each.
|
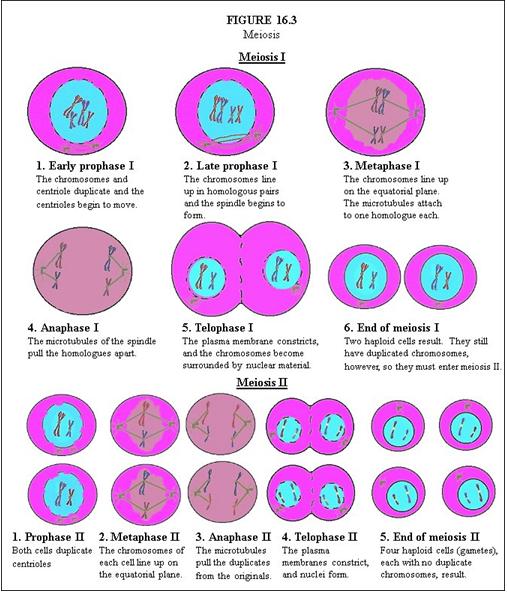 In Meiosis I, describe Anaphase I. |
The microtubules of the spindle pull the homologues apart.
|
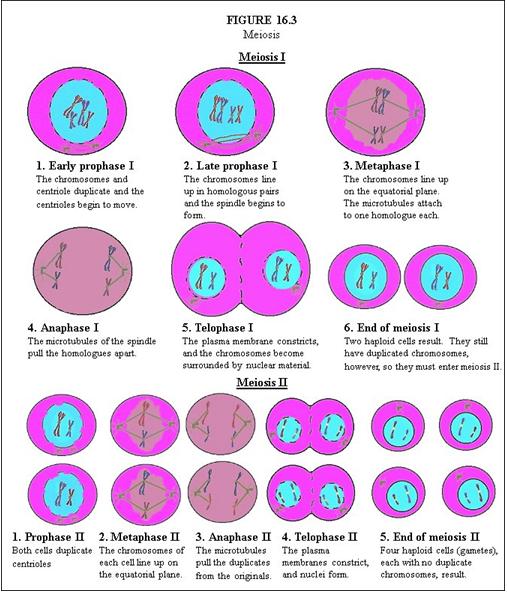 In Meiosis I, describe Telophase I. |
The plasma membrane constricts, and the chromosomes become surrounded by nuclear material.
|
 In Meiosis I, describe End of Meiosis I. |
Two haploid cells result. They still have duplicated chromosomes, however, so they must enter meiosis II.
|
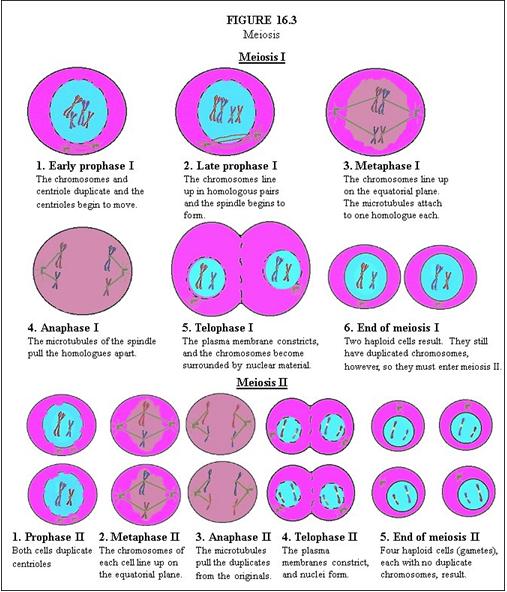
 In Meiosis II, describe Prophase II. |
Both cells duplicate centrioles.
|
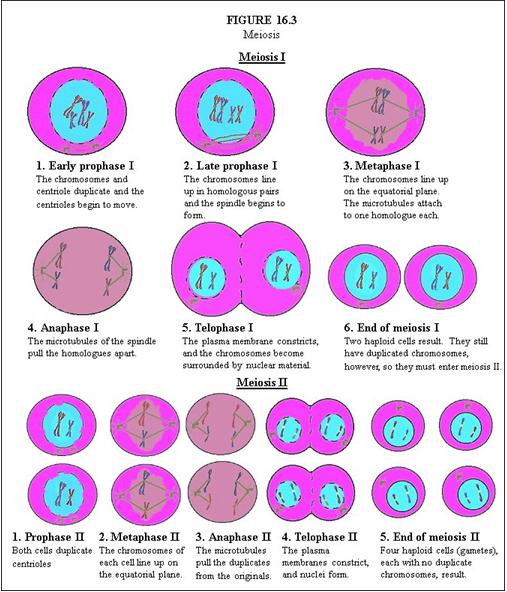 In Meiosis II, describe Metaphase II. |
The chromosomes of each cell line up on the equatorial plane.
|
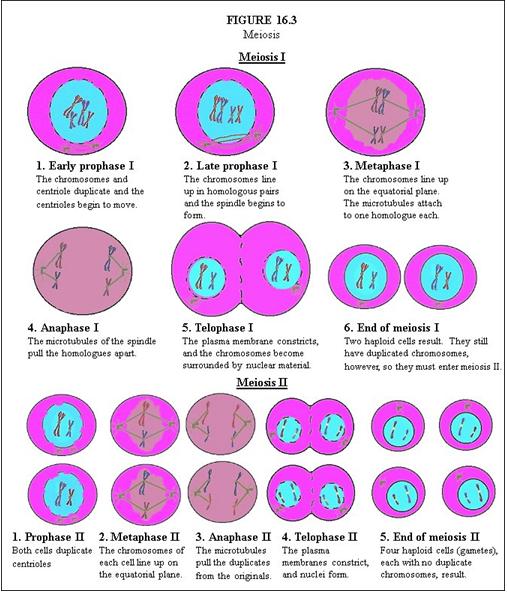 In Meiosis II, describe Anaphase II. |
The microtubules pull the duplicates from the originals.
|
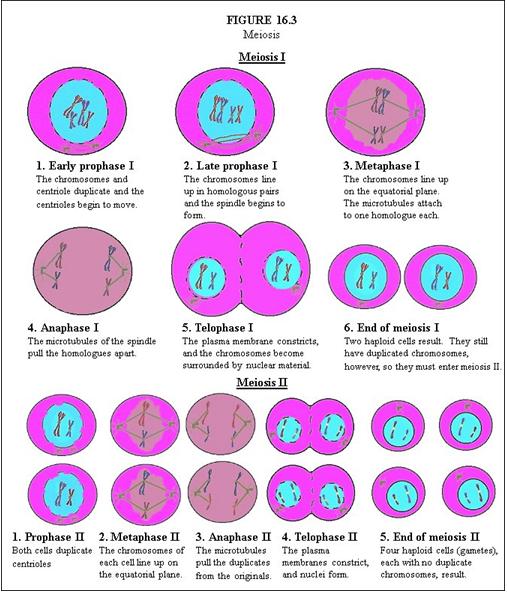 In Meiosis II, describe Telophase II. |
The plasma membranes constrict, and nuclei form.
|
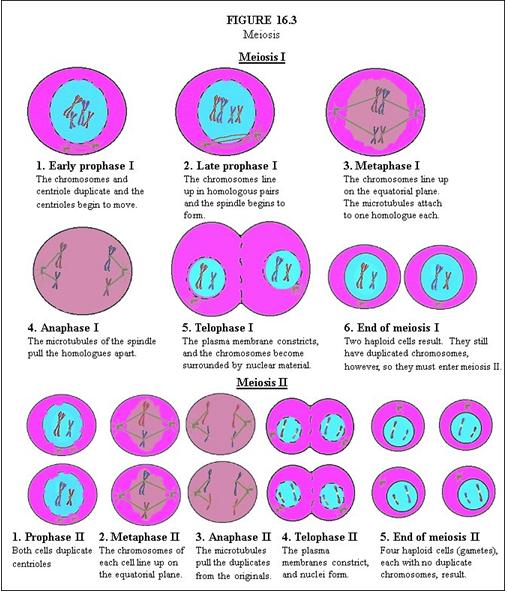 In Meiosis II, describe End of Meiosis II. |
Four haploid cells (gametes), each with no duplicate chromosomes, result.
|
|
How many homologous pairs of chromosomes are in a normal human cell?
|
23.........This means there are a total of 46 chromosomes.
|
|
haploid number
|
The number of homologous pairs is called the haploid number of the cell, thus the haploid number of human cells is 23
|
|
The total number of chromosomes in the cell is called the _______.
|
diploid number
the diploid number of human cells is 46
|
|
haploid cells
|
Meiosis produces cells which have only one chromosome from each homologous pair. Thus, it produces cells with only the haploid number. These are called haploid cells
|






