Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
State that thermal energy may be
completely converted to work in a
single process, but that continuous
conversion of this energy into work
requires a cyclical process and the
transfer of some energy from the
system.
|
Thermal energy may be
completely converted to work in a
single process, but that continuous
conversion of this energy into work
requires a cyclical process (thermodynamic cycle) and the
transfer of some energy from the
system (degraded energy).
|
|
Explain what is meant by degraded
energy.
|
Useless energy is that is transfered from a system
|
|
Coal fired power station energy flow diagram
|
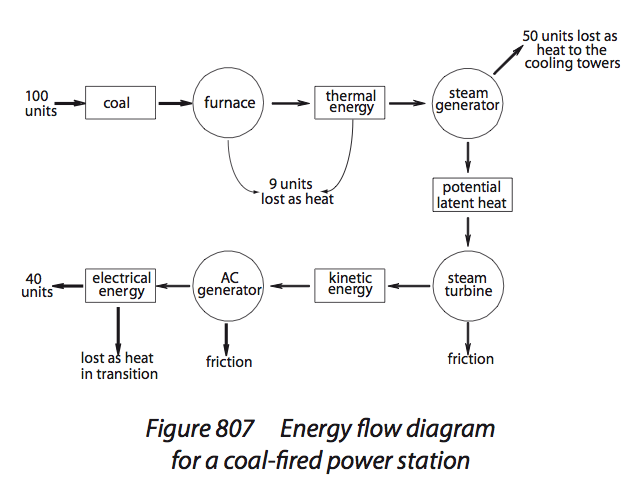 Pic, |
|
Outline the principal mechanisms
involved in the production of
electrical power.
|
(thermal, gravitational potential or wind) converting some kind of energy to kinetic energy, used to rotate a turbine. this turbine rotates the shaft of a generator to make electricity.Nuclear power stations - nuclear - chemical - kineticknow transformationsGravitational potential --> kinetic --> electric
|
|
Construct and analyse energy
flow diagrams (Sankey diagrams)
and identify where the energy is
degraded.
|
The forward arrow is the useful energy, the spliting arrows are the degraded energy, The thickness of the arrows are proportional to the scale of the energy transformation
|
|
Coal fired power station skanky diagram
|
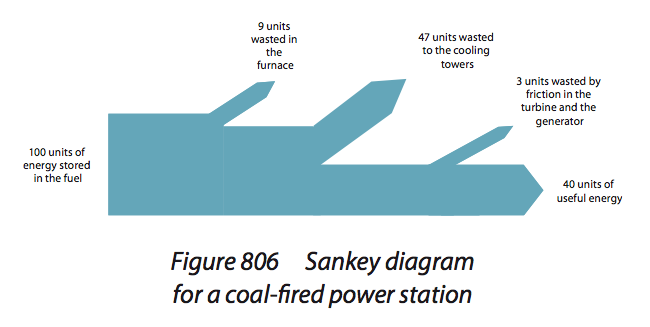 Pic 9, 47, 3, 40 |
|
Identify the different world energy sources
|
Fossil fuels - peat, coal, crude oil, oil shale, oil tar, natural gasnuclear energy, Geothermal, tidal, chemical energySun - primary source of world energy, directly or indirectly, due to radiant energy --> wind, ocean currents, wave action, water evaporation, precipitation, food, wood, biomass, fossil fuels (aka alternative energy source)Moon - tidesChemical energy - battery, fuel cellsNuclear energy - nuclear fission/fussion(only some) reactors
|
|
Outline and distinguish between renewable and non renewable energy sources
|
Renewable - a source of energy that could not be depleted with use, replenishes faster than you use itnon-renewable - a source of energy that could be depleted someday with use, using more of it faster than it is replenished
Coal - peat, sub-bituminous, bituminous, anthracite |
|
Coal (water, carbon, volatile)
|
Table
|
|
Oil shade and Oil Tar 2%
|
Oil shade - kerogen found in Marl, expensiveoil tar - bitumen pyrolysed...
|
|
Define energy density of a fuel
|
Amount of potential energy stored in a fuel per unit mass or per unit volume, chemical potential energy/mass, measured in J g-1
|
|
Energy density of fuels table
|
Table
|
|
Discuss how choice of fuel is influenced by its energy density
|
- cost for production of electricity per kwh- energy density- political, social, econ issues- use and storage of the fuel (natural gas)- heating capability, rank (peat-anthracite)
|
|
State the relative proportion of world use of hte different energy sources availabe
|
Graph, oil, natural gass and coal at the top
|
|
Outline the historical and geographical widespread use of fossil fuels
|
Historical - Industrial Revolution- increase in population demands more fuel- inventions that requires fossil fuel use
Geographical - oil in Mid East and South America- lots of oil and coal reserves in every continent |






