Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Sress
|
The subjective experience of a lack of fit between a person and their environment (i.e where the perceieved demands of a situation are greater than a persnon's perceived ability to cope).
|
|
SNS activation on the body - eyes
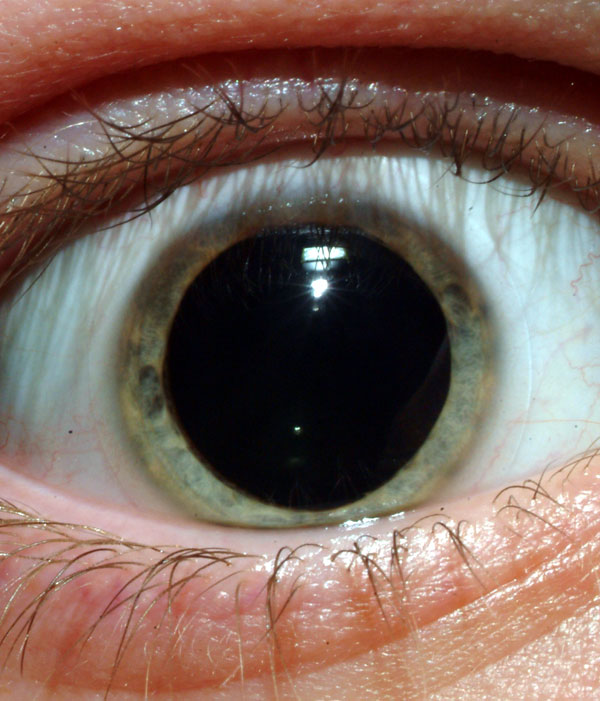 |
Increased pupil size lets in more light for better vision
|
|
SNS activation on the body - lungs
|
Bronchial tubes in lungs dialate for greater oxygen intake.
|
|
SNS activation on the body - heart
|
Increase in heart rate allows for greater blood to flow to skeletal muscles
|
|
SNS activation on the body - sweat glands
|
Stimulated to produce more sweat
|
|
SNS activation on the body - Glycogen
|
Glycogen stored in liver is converted to glucose for energy
|
|
SNS activation on the body - Adrenal medulla
|
Stimulated to release adrenaline
|
|
Acute Stress - Sympathomedullary pathway
|
Arouse autonomic nervous system(ANS)
|
|
ANS
 |
Divided into sympathetic branch (sympathetic nervous system or SNS) and parasympathetic branch.
|
|
SNS
 |
Arouses the animal fro fight or flight
|
|
Parasympathetic branch
 |
Returns the animal to a state to relaxation
|
|
Exposed to acute stressor
|
SNS is activated. Key part of this response is the sympathetic adrenal meduallry system(SAM); SNS + SAM=sympathomedullary pathway
|
|
SNS
 --------> --------> |
Noradrenaline the neurotransmitter released by SNS travel to virtually every organ and gland within the body to activate internal body organs to preapare the body for fight or flight.
|
|
SAM
|
Alerts animal through release of adrenaline(epinephrine) to bloodstream to prepare body for fight or flight. regulated by SNS and adrenal medulla.
|
|
Adrenal medulla
|
Neurons of SNS travel to medulla, so when activated it releases adrenaline to bloodstream. Once in bloostream it effects the body's physiologicalsystems, e.g. boosting supply of oxygen and glucose to brain and muscles and suppressing non-emergency bodily processes such as digestion.
|







