Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is a Marketing Channel?
|
Set of interdependent organizations involve in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by the consumer or business user.
|
|
Why Are Channels Important?
|
- Channel choices affect other decisions in the marketing mix - A strong distribution system can be a competitive advantage - Channel decisions involve long-term commitments to other firms
--> Depending where you sell, your price will vary--> When you are making a decision about a channel, you are making a long term commitment |
|
What is the difference between a company that has a channel vs. a company that does not have one?
|
If you do not have a distributor, a channel, you have to directly sell to customers. Each company would have to contact different groups of clients themselves, however, when there is a channel in the middle, all they have to deal with is selling their products to the distributor and the channel can organize/manage everything (they have contact and records regarding their customers and the product)
|
|
What are the three channels for consumer marketing? / define them
|
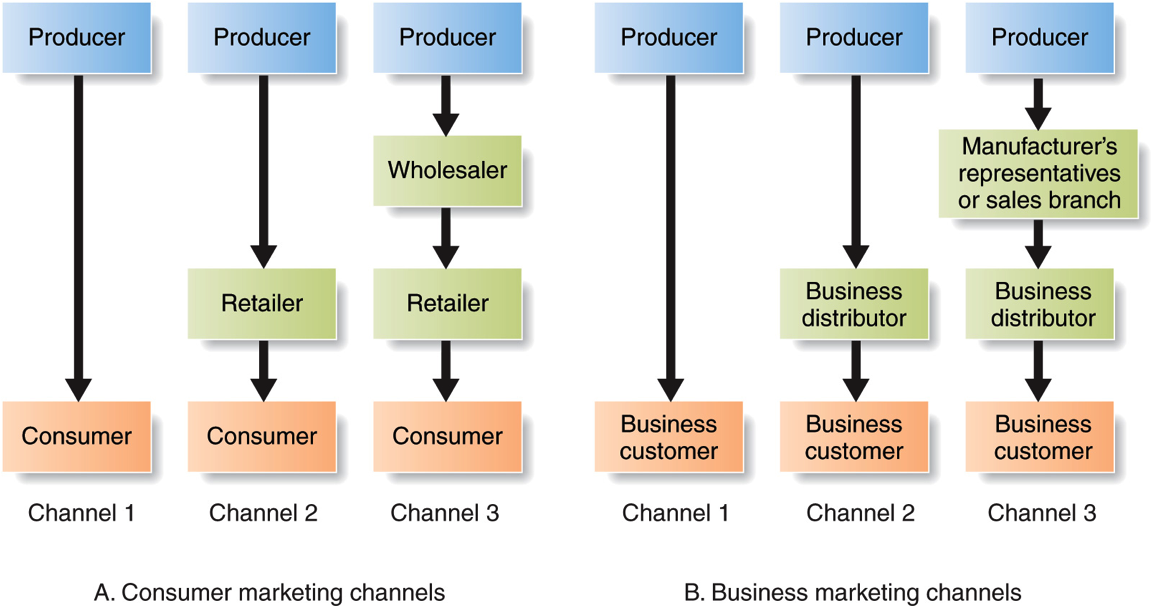 Channel 1: Single channel, two members are involved, there is a producer that directly sells to the consumer (example: online shopping) -> there are no intermediaries here Channel 2: There is one element in the middle, a retailer. Here the producer doesn't sell directly to the consumer, they sell to the retailer and the retailer takes care of selling to the consumer. (This is good for companies who have numerous customers) Channel 3: In additional to the retailer, you may the wholesaler. There may be numerous retailers. So producers sell to wholesalers and retailers buy products from wholesalers. |
|
What are some disadvantages and advantages when you have a channel?
|
Advantage: you do not have to deal with each individual customer
Disadvantage: you loose control and there will be complexity |
|
How much control do you have for each channel?
|
Channel 1: full controlChannel 2&3: no control(example: you sell your tickets to a travel agency, they promote other tickets)
|
|
What is Conventional Channel?
|
Producer-->Wholesaler-->Retailer-->Consumer
-Each channel is seeking to maximize its own profit and often results in poor performance because price is valued higher than it should be and customers are not happy (and decide to go buy products from competitors instead) |
|
What is Vertical Marketing Channel?
|
Producer+wholesaler+retailer --> consumer-- all three get together, as a unified system, and discuss a reasonable profit that suites each and everyone of them --> try to come with a price that they all will benefit from as well as their customers
|
|
What is the multichannel distribution systems?
|
The producer could reach the consumers in two different methods: 1) Single Channel Method- the producer uses only one way to reach the consumers: sell directly --> Internet, telephone, cataloguese.g. selling tickets only through one website - you have full control / understand what your customers want2) Multi-Channel Method - the producer uses several ways to reach out to their consumers, they use multiple methods to sell to the consumer- if you sell through different ways, you will get different groups of consumers - the more flexibility you have, the more variations you will get
|
|
What is an example of a channel conflict?
|
You are selling your
tickets through travel agencies, suddenly you decide to sell tickets on the
Internet as well. Travel agencies are not happy with this and tell your company
that if they choose to do this, then they could sell their tickets online however,
they would want nothing to do with them if this is done.
|
|
What are the four steps for channel design decisions?
|
Step 1: Analyzing Consumer NeedsStep 2: Setting Channel ObjectivesStep 3: Identifying Major AlternativesStep 4: Evaluating Major Alternatives
|
|
Define: Step 1: Analyzing Consumer Needs
|
- Cost and feasibility of meeting needs must be considered - You
must analyze your consumer needs --> depending on where
people buy, they might have different needs (e.g. people who go online to do
their banking online want to save time. However, people who go to bank
branches, go there to get personalize services, feel safer etc.)
|
|
Define: Step 2: Setting Channel Objectives
|
- Set channel objectives in terms of targeted level of customer service- Objectives
must be set after choosing your channel (e.g. if you are a bank, and one of
your branches are your distributive channel, you must set objectives for them. à working hours)
|
|
Define: Step 3: Identifying Major Alternatives
|
Intensive
distribution : when you try to sell in any possible place, as many places as
possible, every corner people can find your product (sell to every grocery
store, depanneur etc.)…everybody can buy your product.
Selective:
sometimes companies sell only in a few places.
Exclusive:
in one or two places
Many
companies remain selective because of brand personality --> if you sell intensively, your brand personality will be in
danger. The personality of the brand, image of the brand, will become ordinary,
normal etc.
|
|
Define: Step 4: Evaluating Major Alternatives
|
- Economic Criteria- Control Issues - Adaptive Criteria e.g.
manufacturer of food --> you want to evaluate
major alternatives (which one is easier to control etc.)
|




