Related Flashcards
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are the types of muscle tissue?
|
Skeletal muscle, Cardiac muscle and Smooth muscle
|
|
What is the function of the muscular system?
|
Allows movememnt of the body and organs; helps circulate blood and move food through the digestive system
|
|
What are the characteristics of sketetal muscle?
|
Most are attached by tendons to bones
Striated (have visible banding) Voluntary - subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded and bundled by sonnective tissue Responsible for all locomotion also maintain posture, stabilize joints and generates heat |
|
Draw a diagram of skeletal muscle showing the connective tissue
|
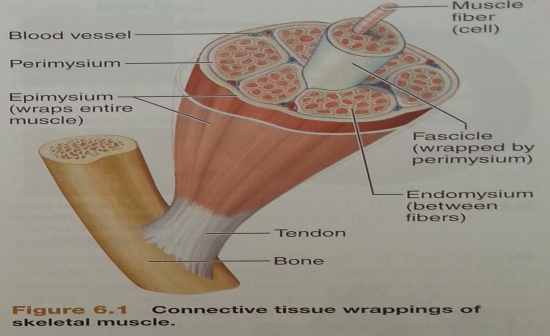 |
|
What are the characteristics of smooth muscle?
|
No striations, involuntary (no consicious control)
Found mainly in the walls of blood vessels and hollow organs e.g. Stomach and Bladder |
|
Draw a smooth muscle cell, transvers cross section and frontal or sagital planar.
|
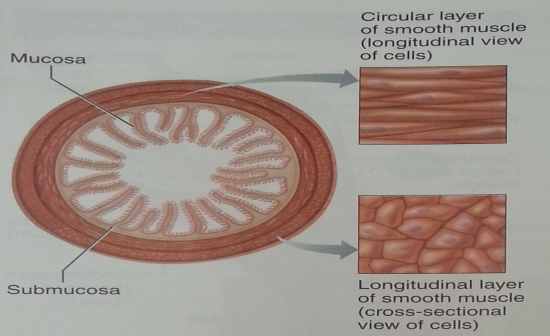 |
|
What are the characteristics of cardiac muscle?
|
Has striations, involuntary - controls itseld with help from the nervous and endocrine system, and only found in the heart
|
|
Draw the different muscle cells
|
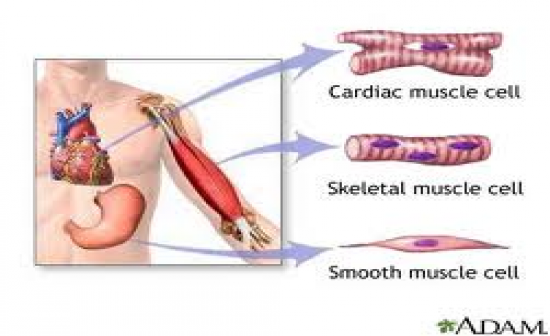 |
|
Draw a cardiac muscle cell
|
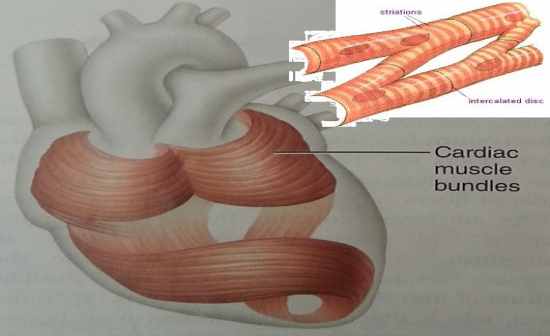 |
|
What are the gross structures of skeletal muscle?
|
Whole muscle
Fascicle Muscle fiber (vell) Myofibrils Myofilaments *actin / myosin |
|
Draw the myofibril and label its sections
|
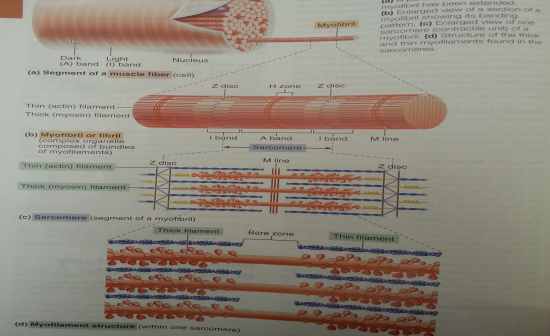 |
|
What is the sacroplasmic reticulum?
|
A specialised endoplasmic reticulium. The major role is to store calcium and to release it on demand when the uscle fiber is stimulated to contract. The unterconnecting tubles and sacs of the SR surround each and every myofibril (like a crocheted sweater around your arm)
|
|
Draw a diagram of the SR around the myofibrils including the coverings and other key features.
|
|
|
What are part of the microscopic anantomy of skeletal muscle?
|
Myofibril - bundles of myofilaments (actin and myosin)
Sarcomere - contractile unit of a muscle fiber * thick filament = myosin filament composed of the protein myosin, which have extensions (heads) and myosin and actin overlap * thin filaments = actin filaments composed of the protein actin, have two addition proteins attacted (regulary or complex proteins) * |
|
What is the myofibril made up of and what does it look like?
|
Bundles of myofilaments (actin and myosin)
Myofibrils are aligned to give distinct bands and are surrounded by sacroplasmic reticulum (SR) which stores calcium |