Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 1st Amendment |
It tells exactly what freedoms we have. The rights listed are freedom of speech, freedom of religion, freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, and freedom of petition.
|
 2nd Amendment |
This ammendment talks about bearing arms. It gives us the right to bear arms.
|
 3rd Amendment |
Quartering of Troops; rights listed: soldiers cannot house with someone during peace or war without consent of the owner under the law.
|
 4th Amendment |
It is about searches and seizures. The rights: police must have a probable cause to search you or your property, police must have a warrant, evidence unlawfully obtained cannot be used against you.
|
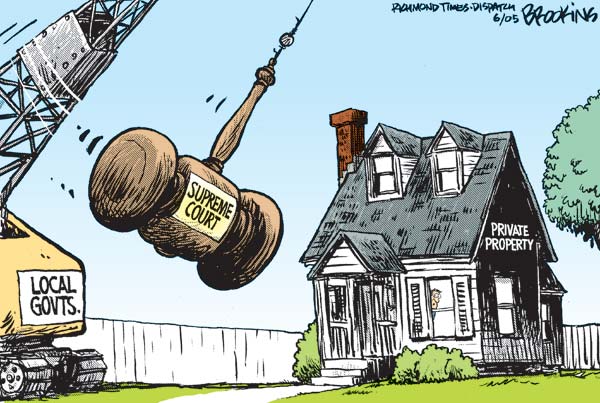 5th Amendment |
Criminal Proceedings; Due Process; Eminent Domain; rights: can only be tried if the person(s) is indicted by a grand jury, double jeopardy, protected against self-incrimination, prohibits unfair actions by the gov., can take property for a legitimate purpose only if the owner recieves fair compensation.
|
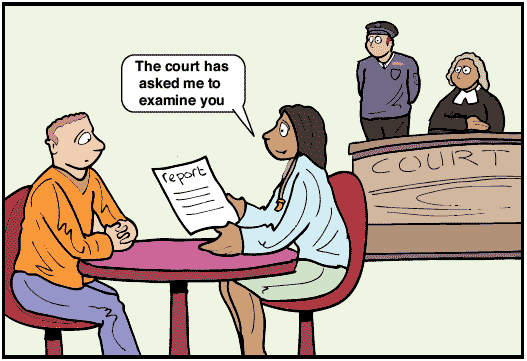 6th Amendment |
Criminal Proceedings; rights: speedy and public trial by an impartial jury, accused informed of the crime, to recieve favorable witnesses, be aware of the witnesses testifying against, right to an attorney.
|
 7th Amendment |
Civil Trials; rights: if the amount of money involved in that case exceeds $20 that right may be waved if both parties agree to bench the trial, right to trial by jury.
|
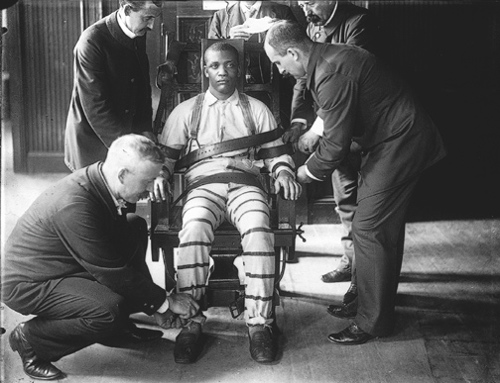 8th Amendment |
Punishment for Crimes; rights: no excessive bails or fines, and no cruel or unusual punishment.
|
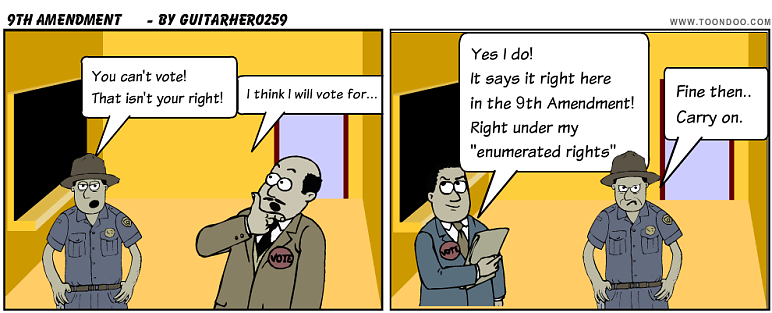 9th Amendment |
Unenumerated Rights; rights: because some rights aren't listed in the Constitution doesn't mean we don't have them
|
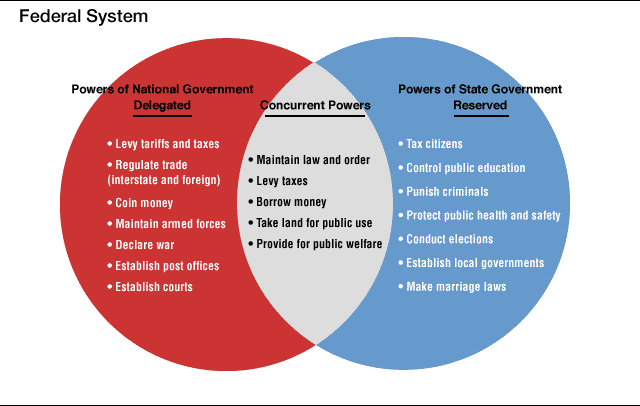 10th Amendment |
Powers Reserved to the States; rights: the powers not granted to the National Government, and at the same time doesn't forbid the States, belongs to the States, or to the people of each State.
|
 11th Amendment |
Suits Against States; rights: no state can be sued by a resident of another state or of a foreign country, state cannot be sued by a foreign country or by its own residents.
|
 12th Amendment |
Election of President and Vice President; rights: the president and the vice president are elected by two different ballots.
|
 13th Amendment |
Slavery and Involuntary Servitude; rights: forbids slavery, forbids other forms of forced labor except punishments for crimes
|
 14th Amendment |
Rights of Citizens; rights: all people born or naturalized in the U.S. are citizens of the U.S. and the State they reside in, States can't make laws taking away citizen rights or immunities, States cannot deprive anyone of life, liberty, or property without due process of law, States can't deny equal protection of the laws to anyone within its jurisdiction
|
 15th Amendment |
Right to Vote-Race, Color, Servitude; rights: the right for citizens to vote can't be denied on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude (slavery).
|






