Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is a Case Study?
|
Indepth study of a behaviour or phenomenon of interest in a particular individual, group, situation
Mainly used to study rare/unusual disorders/problems |
|
What are the values and limitations of Case Studies? (p. 100)
|
Value -
a means to study rare or unusual disorders Information derived from case studies are valuable Many details observations can be made Non-invasive The information can lead to new hypotheses or theories about brain/behaviour Limitations - Analysing information can be difficult Time consuming Difficulty with generalising results Hard to ascertain the cause of observed behaviour, |
|
What does ESB stand for, and what does it do?
|
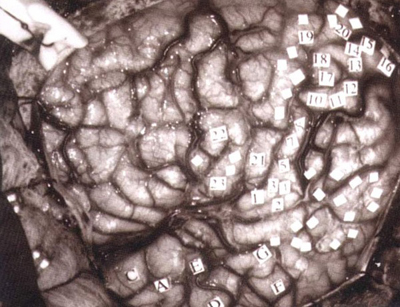 Electrical Stimulation of the Brain (ESB) - Involves the application of an electrode in the form of short pulses to stimulate a specific brain area to initiate a response -The conscious patient can report their experiences, and these reactions are noted and mapped to the stimulated area. |
|
What are the values/limitations of ESB?
|
Values -
Allows us to identify locations and functions of numerous brain areas/structures in conscious patients Results are consistent Able to study localised motor and sensory functions Limitations - Very invasive procedure - patient has no control over their responses to brain stimulation Results are limited Difficulties in generalising results |
|
What does EEG stand for and what does it do?
|
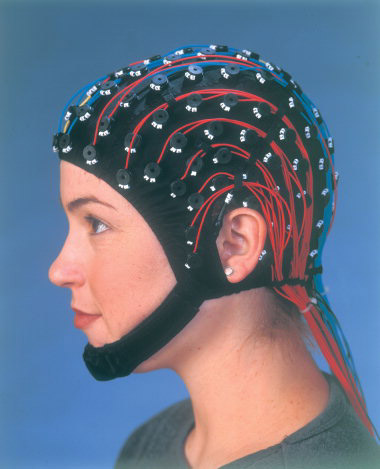 EEG - Electroencephalograph detects, amplifies and records general patterns of electrical activity of the brain. Can be used over a long period of time |
|
Values and limitations of EEG?
|
Values -
Provides general information about brain activity without being invasive Inexpensive - Affordable for hospitals Provides valuable information on levels of brain wave activity Can be used with a wide variety of patients. E.g. infants Limitations - Does not provide info of brain structure Inaccurate as brainwaves must penetrate skull to be measured Time consuming |
|
What does CT stand for and what does it do?
|
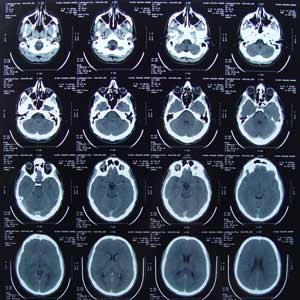 Computerised Tomography or CAT scan X-rays are taken from different angels and then combined by a computer to produce a cross-section image of a brain. It can only be performed with a specialist doctor called a radiologist participant is injected contrast (iodine, non radioactive) which highlights the brain's blood vessels, assisting in the interpretation of CT images. Diagnose tumours, blood cots, locates strokes |
|
What are the values and limitations of CT/CAT scan?
|
Values -
Non-invasive Provides detailed structures of a living brain Useful for identifying precise location or extent of damage to specific structures of the brain Provides great clarity/detail of the brain than a conventional X-ray No health risks Limitations - Only provides information on structure Black and white - MRI are in colour Expensive Needs highly trained staff |
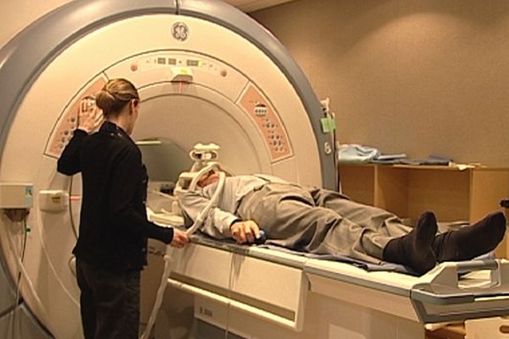 What does MRI stand for, what is it and what is it used for? |
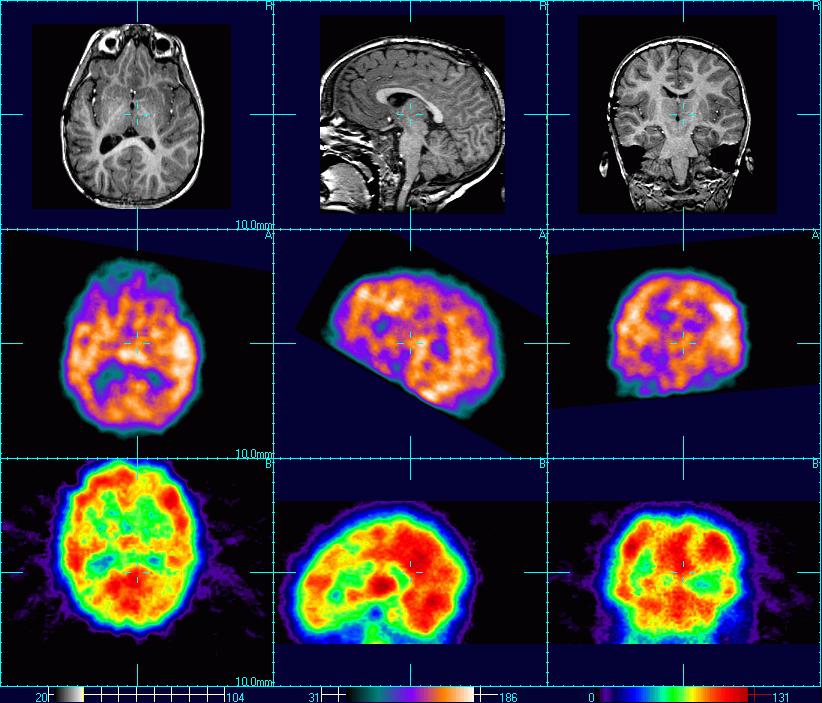 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Patient is surrounded by large electromagnet and exposed to short, powerful bursts of strong magnetic fields to vibrate brain's neurons to produce an image of the brain MRI is more sensitive than CT and provides image much clearer and detailed than a CT scan Computer forms an anatomical image of a slice of the patient's brain Provides greater contrast between normal and abnormal tissue and between grey and white matter Provides side profile and frontal images Used for - Detecting extremely small changes in the brain in children degenerative disease of the CNS involving impaired speech and tremors Brain damage associated with epilepsy Prospagnosia (inability to recognise familiar faces) Akinetopsia (lack of motion perception) |
|
Values and limitations of MRI?
|
Values -
Provides very detailed knowledge about structure 3D imaging - provides detailed view of the brain than a CT scan Safe, painless, non-invasive - prevents the need for exploratory surgery - no x-rays or radioactive material - no special preparation required by patient Limitations - Expensive Susceptible to ghosting from movement, head placements, cavities. Cannot be used by claustrophobic patients who dislike loud noises No ferromagnetic materials allowed. e.g. Patients with a pacemaker, steel pins in bones cannot use the MRI scanner Shows brain structure, not function |
|
What does PET stand for, what is it and its function?
|
PET - Positron Emission Tomography Produces a computer-generated colour coded image - provides info about brain function and activity during various tasks. records brain activity of different areas of the brain while the patient is involved in a cognitive task. This is tracked by measuring the use of radioactive glucose prior injected into the blood stream. This radioactive substance emits radioactive signals which are detected, recorded and compiled into images. Adjacent slices can be combined to form 3D images that reveal blood flow and metabolic and chemical activity of brain tissue |
|
What does fMRI stand for, what is it and its function?
|
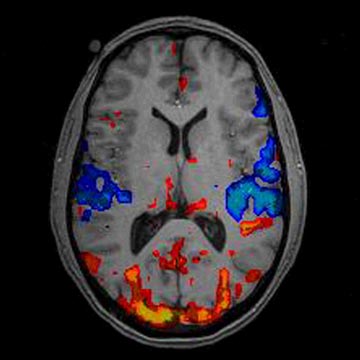 FMRI -Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Subject required to carry out cognitive tasks while the brain is repeatedly scanned for changes in brain activity measured by changes in blood-oxygen levels |
|
What are the values and limitations of fMRI?
|
Values -
Can take number pictures of the brain in rapid succession, detecting changes that occur moment to moment Does not require exposure to radiation Detailed images of the functioning brain and colours make it easy for interpretation Limitations - Observed differences in brain activity showing up may be due to associated tasks and not specifically the task being studied VERY expensive Non-subject friendly Poor temporal resolution - Images appear about 5-8 seconds behind real time change |
|
Values and limitations of a PET scan?
|
Values
- Provides easily interpreted colour-coded images on the function and activity of the brain -sensitive in detecting brain damage -Provides detailed information on neural activity (Blood flow, metabolic activity) -Used for research with healthy patients Limits - Mildly invasive as it requires the injection of radioactive substance -Use of radioactive substance means the number of scans performed is limited per patient -VERY EXPENSIVE! Does not show brain structure Patient is injected with a radioactive substance beforehand |
|
Professor Edwards is interested in conducting brain research. To do so he must always follow ethical guidelines, including getting informed consent from his participants. What information does that participant need to have in order to give informed consent?
|
An explanation of the tasks to be performed in the study
Explanation of any risks associated with participation in the study Details of participant's rights to: withdraw, confidentiality of results, debriefing after study, beneficence of study |







