Related Flashcards
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Most of the earth's residents are _______. The most ancient and abundant are the _________.
|
Unicellular, bacteria
|
|
What are the 3 main types of microscopes?
|
Light, transmission electron, scanning electron
|
|
What is the cell theory?
|
New cells are formed from other existing cells, and that the cell is a
fundamental unit of structure, function and organization in all living
organisms.
|
|
Cellular activity is both individual and ________
|
Collective
|
|
Cell activity is dictated by _______________
|
Sub-cellular structures
|
|
Continuity of life has _________ basis.
|
Cellular
|
|
Humans are composed of about __________ cells.
|
70 trillion
|
|
Know the fluid mosaic model.
|
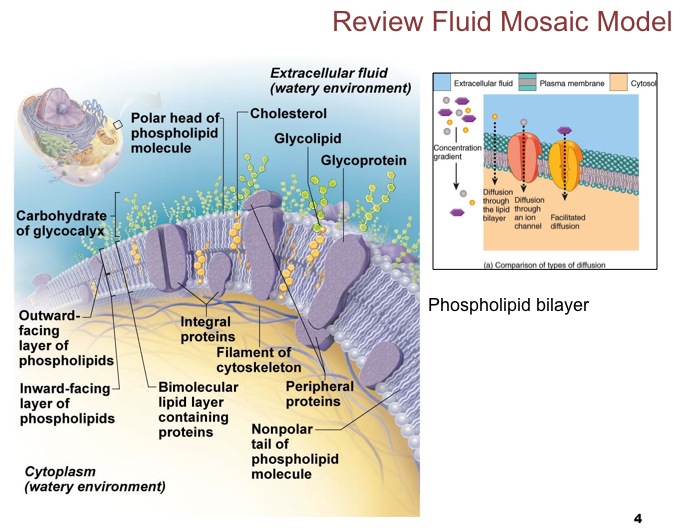 Fluid Mosaic Model |
|
Review membrane proteins
|
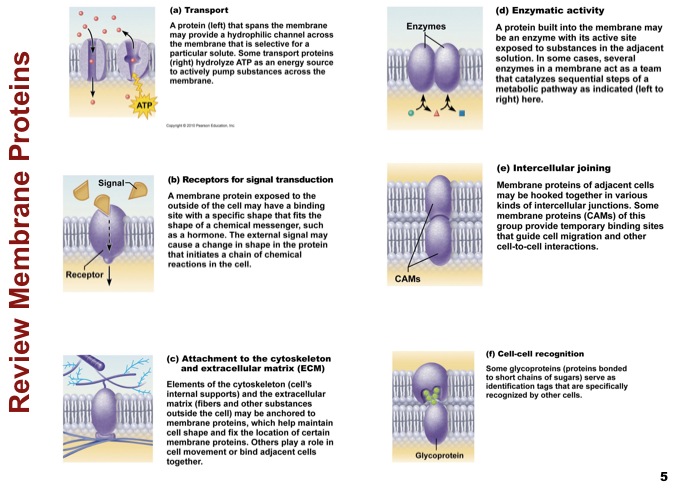 Membrane Proteins |
|
Know the membrane junctions
|
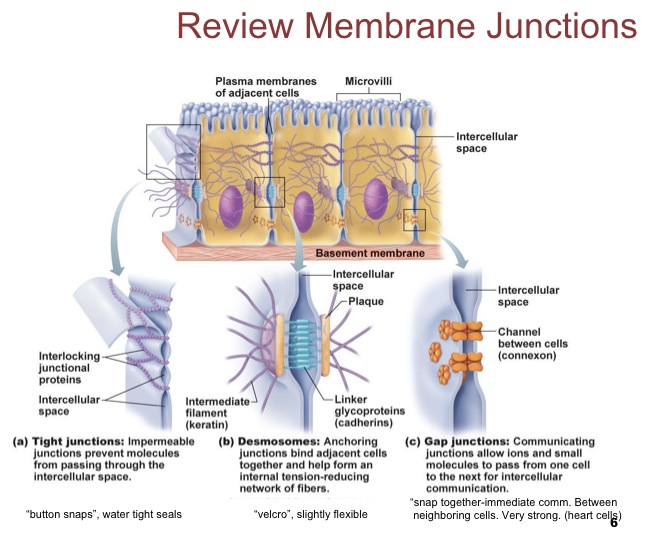 Membrane Junctions |
|
How does membrane transport work?
|
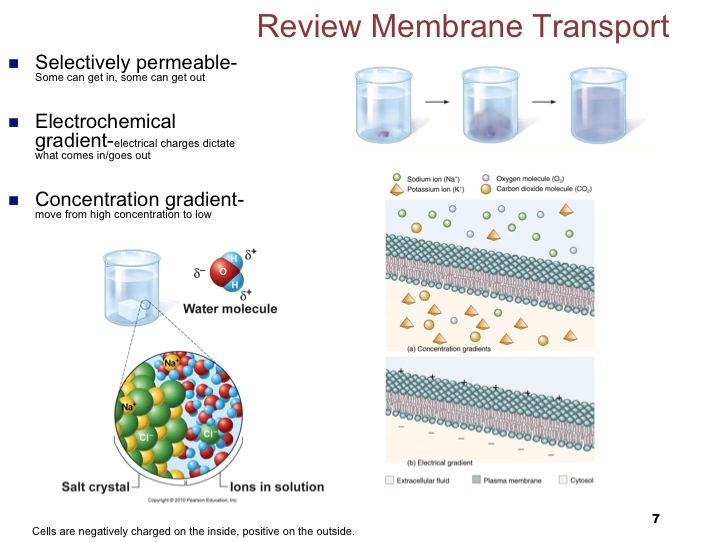 Membrane Transport |
|
Passive transport means
|
Moving biochemicals
and atomic or molecular substances across the cell membrane.
|
|
What are the 4 main types of passive transport?
|
1) osmosis
2) simple diffusion 3) facilitated diffusion 4) filtration |
|
What is osmosis?
|
It is the movement of water across a partially permeable membrane from
an area of low solute
concentration to an area of high solute
concentration. It is a physical process in which a solvent moves,
without input of energy, across a semipermeable membrane (permeable to
the solvent,
but not the solute) separating two solutions of different
concentrations.
Water follows "stuff", usually salt. |
|
What is simple diffusion?
|
The net movement of substances from a region of high concentration to a
region of low concentration so its overall net movement is along the
concentration gradient. Substances are diffused across the membrane between the phospholipids
|