Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Retroperitoneal
|
– Behind the parietal peritoneum
|
|
Erythropoiesis
|
The production of red blood cells (erythrocytes)
|
|
Renal blood flow rate
|
- The rate at which blood flows through the kidneys (1 liter/min)
|
|
Filtrate
|
- Blood plasma without proteins, found in the nephrons of the kidneys
|
|
Glomerular filtration rate
|
- The rate at which filtrate is produced in glomerular filtration
(125 mL/minute)
|
|
Tubular maximum
|
- The maximum rate of reabsorption by active transport through the
nephron tubules
|
|
Buffer system
|
- A mixture of an acid and a base which resists changes in pH
|
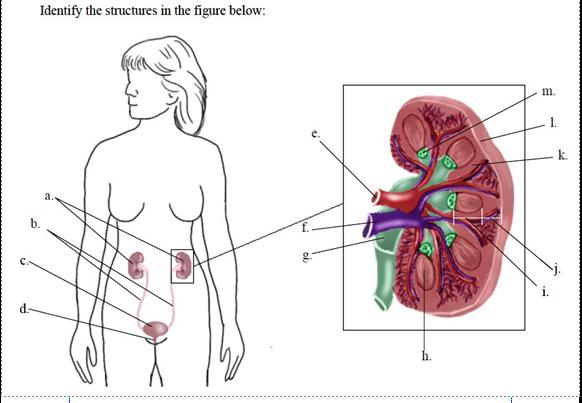 Identify the structures in the figure: |
a. kidneys
b. ureters
c. urinary bladder
d. urethra
e. renal artery
f. renal vein
g. renal pelvis
h. renal pyramid
i. medulla
j. cortex
k. renal column
l. renal capsule
m. minor calyx
|
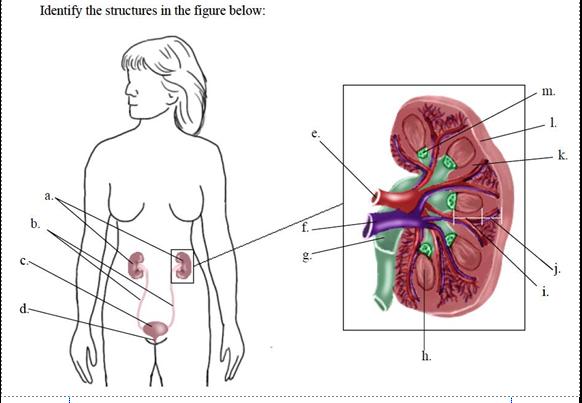 Which structure in the figure contains stratified transitional epithelium? |
The urinary bladder contains stratified transitional epithelium, so that it can stretch.
|
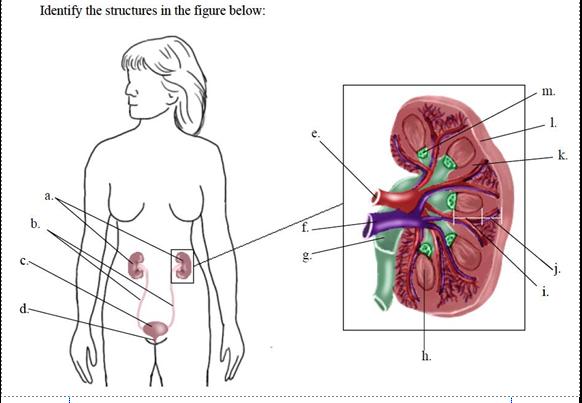 Between (i) and (j), which has the larger concentration of solutes in the interstitial fluid? How much more concentrated do the solutes get compared to normal interstitial fluid? |
The medulla has the higher concentration of solutes in its interstitial fluid. The medulla’s
interstitial fluid is as much as four times more concentrated than normal interstitial fluid.
|
|
List the seven functions of the urinary system.
|
The seven functions of the urinary system are:
1. urine formation,
2. pH control,
3. blood pressure regulation,
4. stimulation of red blood cell formation by the red bone marrow,
5. vitamin D activation,
6. transport of urine,
7. and storage and release of urine.
|
|
Explain the desk drawer analogy and how it relates to urine formation.
|
When cleaning a desk drawer, you can dump everything out of the desk drawer and then start
putting back the things you want to keep. Anything left in the pile at the end is waste. If you
make a mistake and put something in the drawer, you can always take it out again and return it to
the waste pile.
This is like urine formation. The kidney receives all contents of the blood
plasma (except proteins), and then it puts back the things that the blood needs. Anything else is
waste. If something gets back into the blood, it can be put back into the urine before the process
is finished.
|
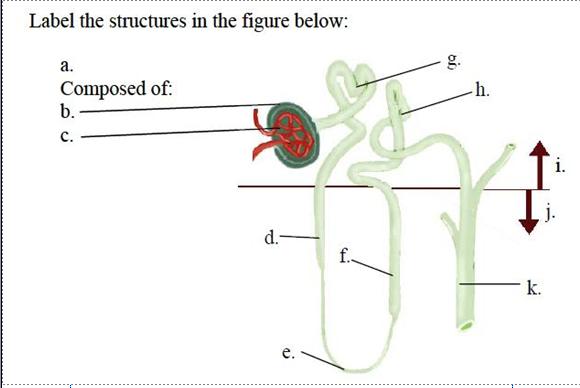 Label the structures in the figure |
a. renal corpuscle
b. Bowman’s capsule
c. glomerulus
d. descending limb of the loop of Henle
e. loop of Henle
f. ascending limb of the loop of Henle
g. proximal tubule
h. distal tubule
i. cortex
j. medulla
k. collecting duct
|
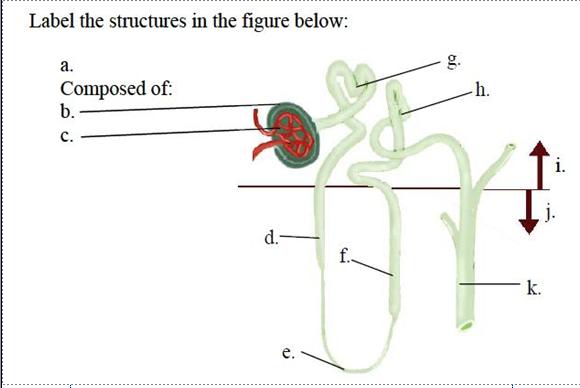 Of the structures pointed out in the figure, which ones are always permeable to water? Which is never permeable to water? Which are permeable to water based on the amount of ADH present? |
The proximal tubule and descending limbs of the loop of Henle are always permeable to
water. The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is never permeable to water. The distal tubule
and collecting duct are permeable to water based on the amount of ADH present.
|
|
What are the four steps of urine formation. Which steps could be grouped together?
|
The four steps are
filtration,
reabsorption,
secretion,
and water reabsorption.
Water reabsorption is often grouped together with reabsorption so that there are only 3 steps to urine
formation.
|






