
"doctor's plot" |
|
Attempted to get rid of Jewish doctors |
| |

de-Stalinization |
|
Movement led by Khrushchev to reduce the influence of Stalin in the Soviet Union |
| |
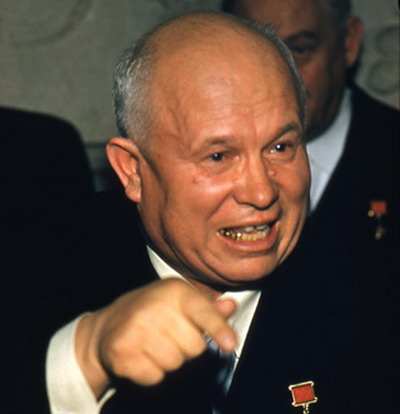

Nikita Khrushchev |
|
Replaced Stalin in 1955, led the "de- Stalinization" movement. Accused Stalin of creating a "cult of Personality" |
| |
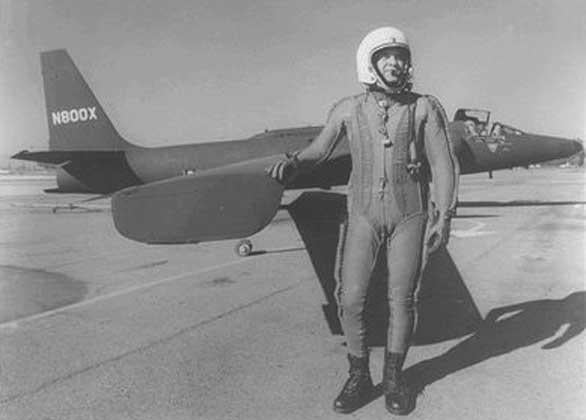

Gary Francis Powers |
|
Pilot of a U-2 spy plane that was shot down on May 1, 1960 despite the "Free Skies" proposal in 1955 |
| |

John F. Kennedy |
|
Elected president in 1961, supported aggressive foreign policy to impress the Soviets. |
| |

Aleksei Kosygin |
|
Soviet Satesman, and Premier of the Soveit Union (1964-1980) |
| |

Leonid Brezhnev |
|
General secretary of the communist party, rose to power by the 1970's, kept power until 1982, reversed the de-Stalinization efforts |
| |

Alexander Solzhenitsyn |
|
Dissident that refused to be quieted. Wrote The Gulag Archipelago,eventually deported to the U.S. |
| |
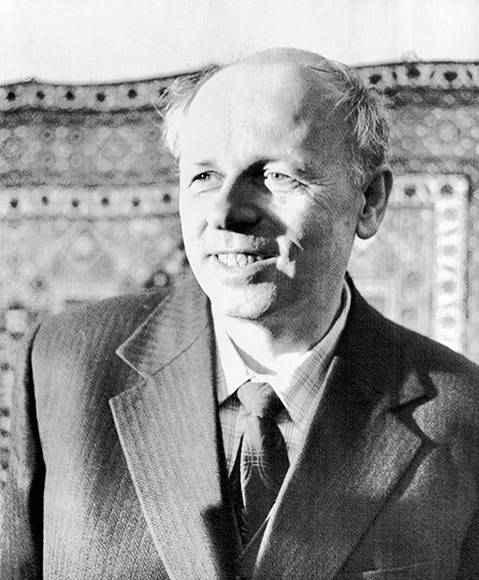

Dr. Andrea Sakharov |
|
Scientist who invented Soviet Hydrogen bomb, denounced arms races and exiled to Gorki |
| |

Eleana Bonner |
|
Wife of Sakharov, claimed to be unable to leave country because of emergency heart surgery |
| |

Richard Nixon |
|
Met with Brezhnev at Moscow Conference in 1972, meeting led to Signing of SALT I |
| |

Josip Broz Tito |
|
Leader of the communist party in Yugoslavia, fought Germans in WWII, wanted to develop own policies, not use Stalin's |
| |

Wladyslaw Gomulka |
|
Became leader of Poland after 1956 workers revolt. Anti-Soviet communist, freed political prisoners, reopened relations with catholic church |
| |

Imre Nagy |
|
elected Prime Minister of Hungary twice, announced Hungary's neutrality and withdrawal from the Warsaw Pact in 1956 |
| |

Janos Kadar |
|
Replaced Nagy after Soviets invaded Hungary |
| |
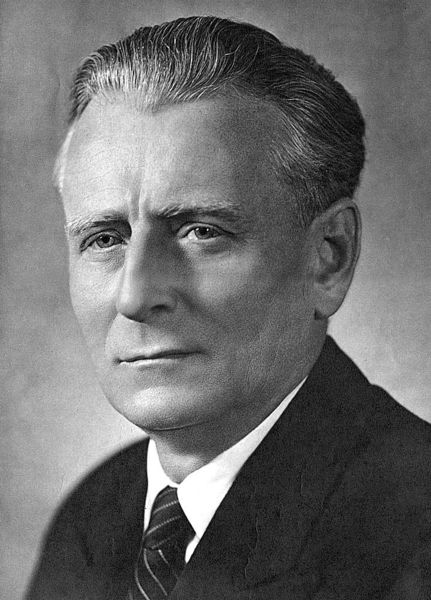

Antonin Novotny |
|
Communist leader in Czechoslavakia, was extremely rigid, De-Satlinization did not being unti the 1960s |
| |

Aexander Dubcek |
|
Liberal communist leader that replaced Novotny in 1968 |
| |

"Cult of Personality" |
|
Boasting his own image at the expensive of the party |
| |

Peaceful Coexsistence |
|
Competing with the United States, but avoiding war and confict |
| |

Sputnik I |
|
First spaceship launched 1957 |
| |

Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles |
|
Long range rockets that were tested by both the US and Soviet Union in the 1950's |
| |

Mutual Assured Destruction |
|
Certain destruction of both nations |
| |
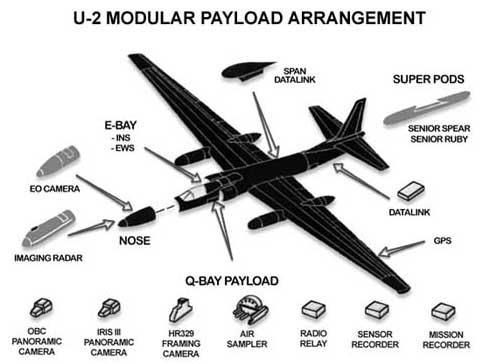
U-2 |
|
Spy planes flown during the Cold War |
| |

Cuban Missile Crisis |
|
Most Significant event of the cold war, US blockaded Soviet Missile bases in Cuba. |
| |

" hot line" |
|
Phone line installed between the Kremlin and the White House in 1963 |
| |

Dissidents |
|
Someone who openly criticizes poicies of his/her government |
| |

The Gulag Archipelago |
|
Written by Sozhenitsyn, an extreme dissident |
| |

Gorki |
|
Nation that Dr. Sakharov was exiled to. |
| |

Detente |
|
The relaxing of tensions between the U.S. and Soviet Unions in the 1970's |
| |

SALT I |
|
Strategic Arms Limitation Agreement Treaty- Bothe sides agreed to limit number of nucs they had. Did not end the arms race. |
| |

Moscow Conference |
|
1972- Nixon met with Brezhnev led to 7 years of Detente and the signing of SALT I |
| |
"Brain Drain" |
|
Nickname fore period in 1953 following the escape of 3 million East Germans by way of West Berlin |
| |

Brezhnev Doctorine |
|
Document telling the west to stay out of Eastern Europe. |
| |

The Berlin Wall |
|
Wall between East and West Berlin constructed in 1961 |
| |
20th Congress od Soviet Communist Party |
|
Held in Moscow (1956) Khrushchev gave controversial speech about Stalin |
| |

"Cold War Thaw" |
|
1950's both sides wanted to reduce tensions |
| |

Paris Summit |
|
Four power meeting planned in Paris during May of 1960 |
| |
|
October 1964 |
|
Khruschev removed from office |
| |

Titoism |
|
Tendency of some communists to place their national interests about that of the Soviet Union |
| |

War Saw Pact |
|
name given to the treaty between Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and the Soviets |
| |

Camp David |
|
Town in Massachusettes where a summit meeting was held in 1959 |
| |

Afghanistan |
|
The Soviet's Vietnam, they invaded and could not win. |
| |

Yugoslavia |
|
Only large European communist state to resis soviet control |
| |

East Berlin |
|
Area on the east side of The Berlin Wall |
| |

West Berlin |
|
Area on the west side of The Berlin Wall |
| |

Poland |
|
Industrialized under communist rule, poles resented Soviet ruling |
| |

Hungary |
|
Agricultural nation, experienced harsh communist rule after 1947 |
| |
Czechoslavakia |
|
Last eastern European country to become communist |
| |
