|
Mucocele |
|
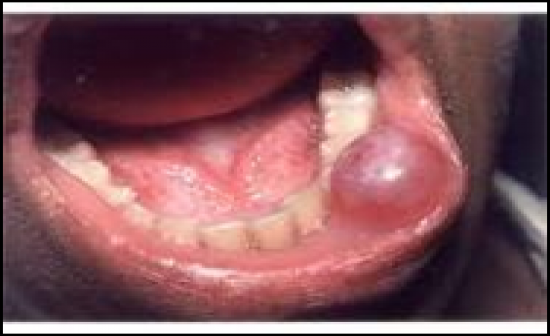
-Tissue swelling composed of pooled mucus that escaped into the connective tissue from a severed excretory duct
-Ranula- mucocele in the floor of the mouth
-Most often occur on the mucosal surface of the lower lip in children and young adults
|
| |
|
Mucus Retention Cyst |
|
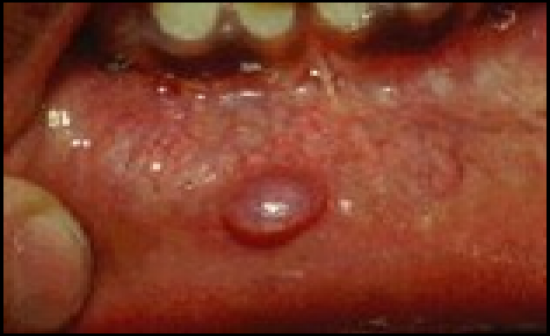
-Swelling caused by and obstruction of a salivary gland excertoryduct resulting in an epithelial lined cavity containing mucus
-Most often occur in minor salivary glands of adults and may be uni- or multilocular
-Can not be discerned from a mucoceleclinically and may resemble a mucoepidermoidcarcinoma |
| |
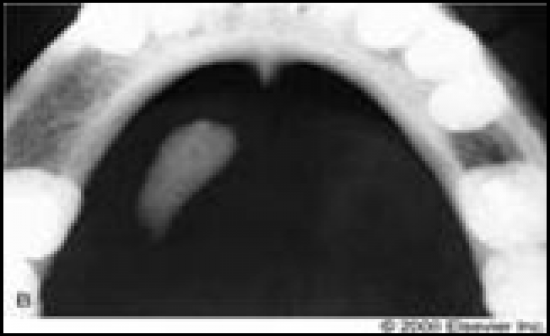
Sialolithiasis |
|
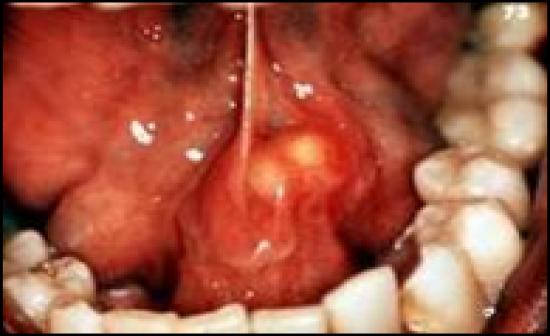
-The presence of one or more oval or round calcified structures (salivary stones) in a duct of a major or minor salivary gland
-In major salivary glands, bacterial infection can cause sever pain in glands that are completely blocked
-treatment- manual removal through manipulation or surgical removal |
| |
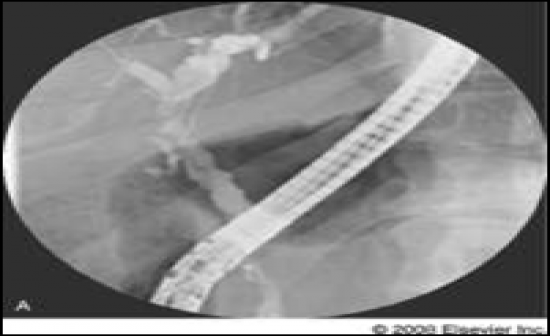
Chronic SclerosingSiliadentitis |
|
-Chronic inflammation of salivary gland tissue resulting in replacement of aciniby fibrous tissues, but sparing much of the ductalarchitecture
-Results from duct blockage, trauma or compression of the gland and radiation treatment(siliadentitis) |
| |
|
Parotitis |
|
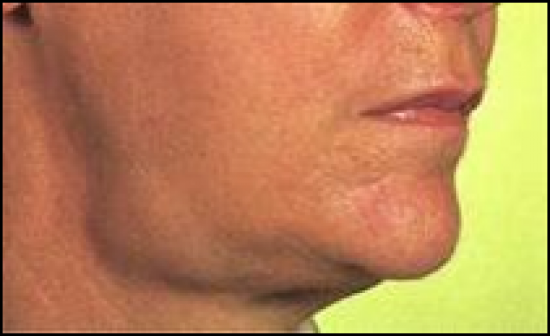
-Acute infection of the salivary glands
-Viral Endemic Parotitis(Mumps) |
| |
|
Bacterial Sialadenitis |
|
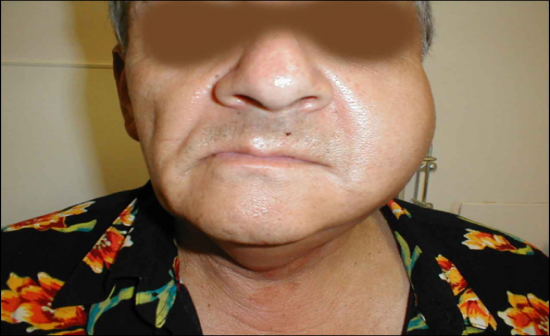
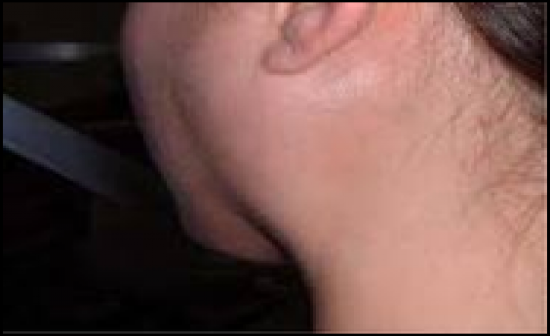
-Can occur following abdominal surgery, possibly due to lack of salivary flow due to atropine sulfate used in general anesthesia |
| |
|
Lymphoepithelial Sialadenitis |
|
-A progressive autoimmune chronic inflammatory process, primarily of the parotid glands, in which dense infiltrates of T lymphocytes replace the aciniand residual ductaltissue undergoes hyperplasia, forming irregular shaped islands of
squamousepithelium
-Precursor to Sjogrensyndrome |
| |
|
SjogrenSyndrome |
|
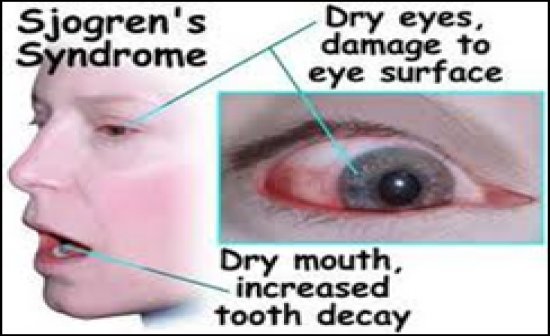
-A groups of autoimmune conditions with a marked predilection for women; it has an intense T lymphocyte- mediated autoimmune process in the salivary and lacrimalglands as one of its most prominent components
-Salivary ducts undergo hyperplasia causing xerostomiaand xeropthamia
-Other autoimmune diseases may be present
-No treatment exists |
| |
