
Basis of Marine food webs |
|
Dinoflagellates
|
| |
|
Noctiluca |
|
A bioluminescent dinoflagellate |
| |
|
Zooxanthellae |
|
Dinoflagellate symbiotic with coral polyps-Responsible for CaCO3 capture |
| |
|
Freshwater Dinoflagellate with modifications to slow decent in freshwater |
|
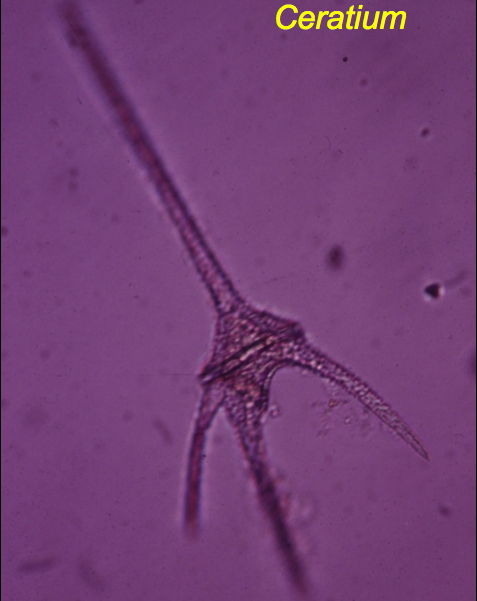
Ceratium |
| |
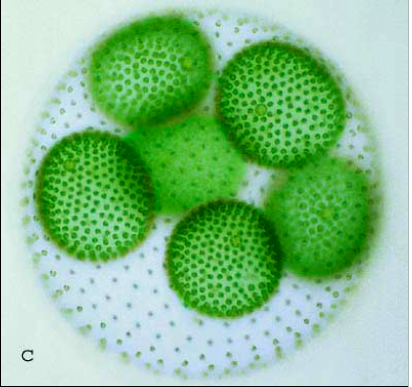
Colonial Chlorophyta, few in numberuses flagellum to move |
|
Volvox |
| |
|
Uses Flagellum to pull itself through water |
|
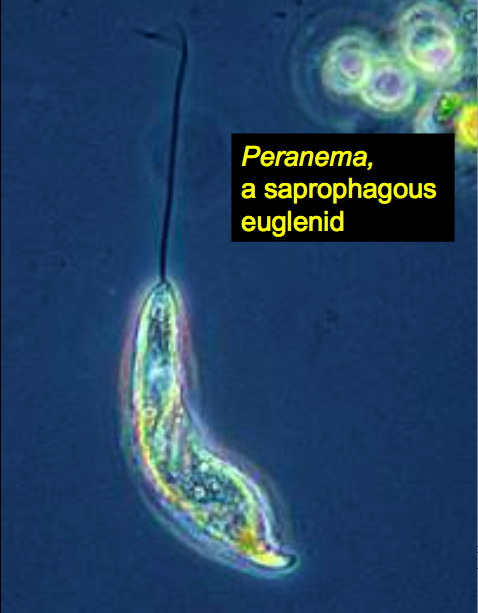
Peranema |
| |
|
Kinetoplastid Life Cycle |
|

Promastigote: flagellatedAmastigotes: cyst |
| |
|
Trypanosoma brucei disease |
|
African Sleeping Sickness |
| |
|
Trypanosoma cruzi |
|
Chaga's Disease |
| |
|
Leishmania vector
|
|

Sand Fly |
| |
|
Diplomondia found in contaminated water supplies. Two nuclei. |
|
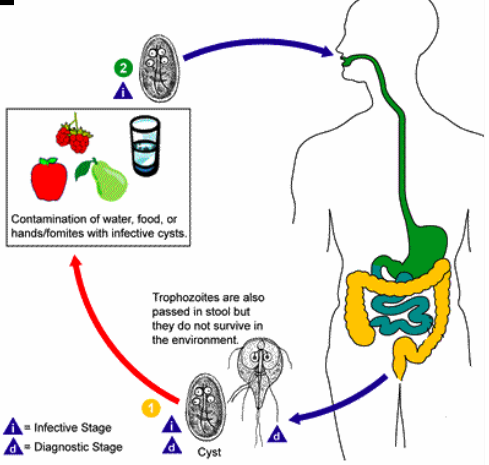
Giardia |
| |

Hypermastigids (Trichomonads) |
|
Parabasalia symbiote of Termites that digest cellulose |
| |
|
Choanoflagellate root words |
|
funnel whips |
| |
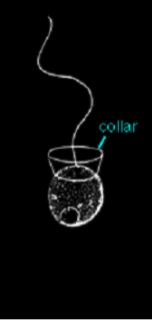
Feeding practice of |
|
flagellum creates current that brings detritus into collar. stationary when feeding |
| |
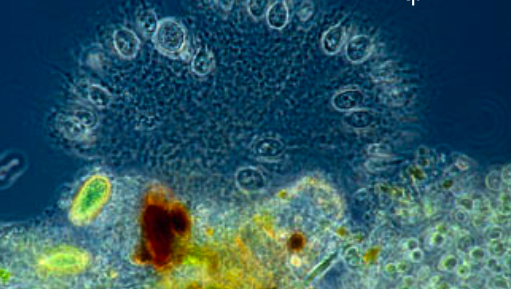
Colonial Choanoflagellate |
|
Spongomonas |
| |
|
Nutrition of Euglena |
|
Autotrophic in lightsaprozoic (dissolved organic and inorganic materials) when dark |
| |
|
Euglenoid Movement |
|
movement of protoplasm in Euglena, usually not involved with locomotion |
| |
|
Name all major parts of Euglena |
|
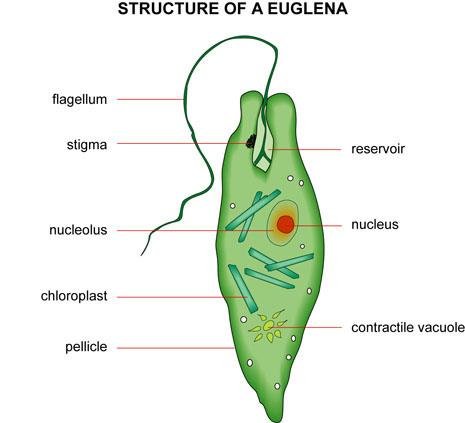
contractile vacuolepelliclestigma (eyespot)chloroplasts
|
| |
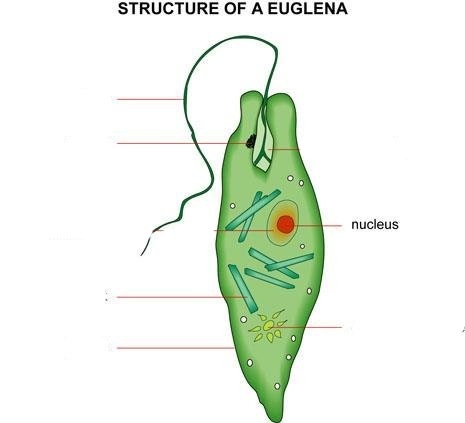
Photoreceptor in Euglena |
|
light sensitive organ or paraflagellar swelling (not pigmented stigma) |
| |

Name and order of: |
|
paramecium (hymenostome)
|
| |

trichocyst |
|
defencive extrusomes that form a fibrous cloud around the paramecium when attacked |
| |
|
describe the differences between fission and conjugation |
|

conjugation is sexual reproduction, individuals line up side to sidefission is asexual reproduction, splitting end to end |
| |
|
are all dinoflagellates photosynthetic? |
|
NO |
| |

What is this protozoan and what is its nutrition? |
|
Stentor: filter feeding heterotrich |
| |
|
Cause of mass fish die offs |
|

Pfiesteria (dinoflagellate) |
| |

Feeding habits of Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
human vaginal parasite |
| |
|
Locomotion of Kinetoplastids |
|
undulating membrane |
| |
|
What defines a sarcodine? |
|
any protist that lacks flagellae and have clearly defined pseudopods. |
| |
|
possible materials for tests |
|

SiO2 in RadiolariansCaCO3 in ForaminiferansChitin in Arcella |
| |

prostomatid (didinium) prey |
|

paramecium (hymenostome) |
| |
|
spirotrich examples |
|

stentor and Spiromstomum |
| |
|
benthic zone |
|
lowest level of a body of watercommon benthic organisms include formaminifermans, nematodes, and just about everything else we studied |
| |
|
(T/F) All coccideans are apicomplexians. |
|
True. Coccidia include toxoplasmosis (cat feces) and plasmodium (malaria) but not Gregarines (gut parasite of insects) which are also in apicomplexia. |
| |
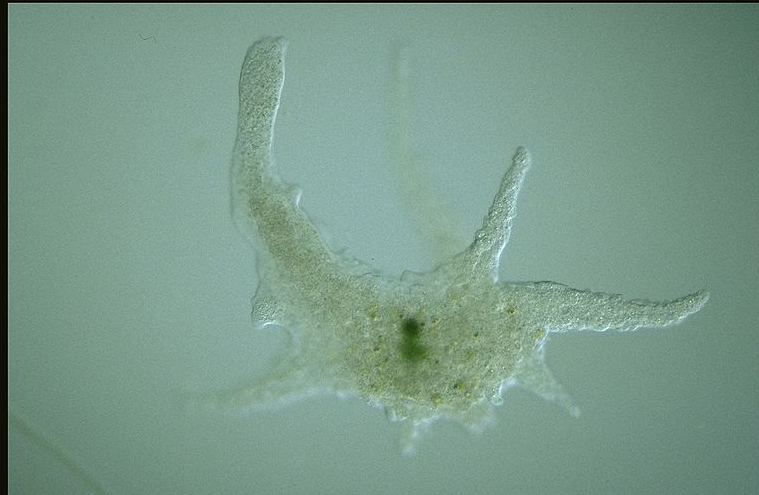
What is this sarcodine? |
|
Chaos |
| |
|
What clear structure is used in phagocytosis? |
|
pseudopod |
| |
|
rhizopodia |
|
thread-like extensions of cytoplasm found in radiolarians |
| |
|
trophozoite |
|
activated, intracellular feeding stage in the apicomplexan life cycle |
| |
