|
ventral |
|
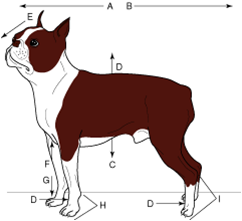
the belly or underside of a body |
| |
|
cranial |
|
toward the head |
| |
|
anterior |
|
front of the body |
| |
|
rostral |
|
nose end of the head |
| |
|
cephalic |
|
pertaining to the head |
| |
|
medial |
|
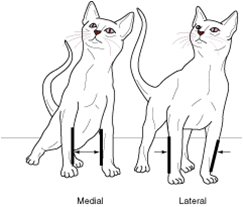
toward the midline |
| |
|
superior |
|
uppermost, above, or toward the head |
| |
|
proximal |
|
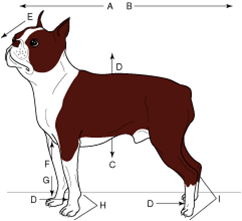
nearest the midline or nearest the beginning of a structure |
| |
|
superficial |
|
near the surface; also called external |
| |
|
palmar |
|
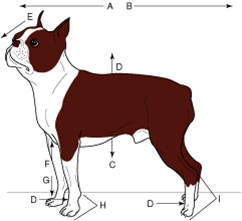
the caudal surface of the manus (front paw) including the carpus (from the antebrachial joint distally) |
| |
|
dorsal |
|
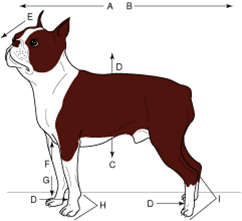
to the back |
| |
|
caudal |
|
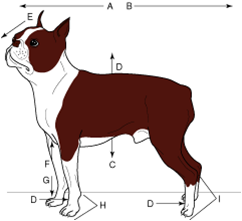
towards the tail |
| |
|
posterior |
|
rear end of the body |
| |
|
caudal |
|
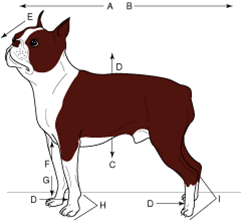
toward the tail |
| |
|
lateral |
|
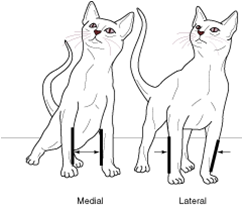
away from the midline |
| |
|
inferior |
|
lowermost, below, or toward the tail |
| |
|
distal |
|
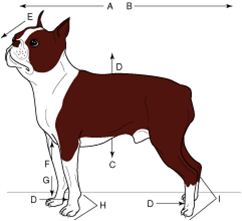
farthest from the midline or farthest from the beginning of a structure |
| |
|
deep |
|
away from the surface; also called internal |
| |
|
plantar |
|
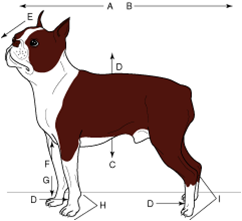
means the caudal surface of the pes (rear paw) including the tarsus (from the tibiotarsal joint distally) |
| |
|
midsagittal plane |
|
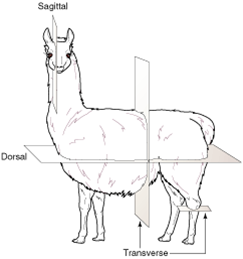
plane that divides the body into equal right and left halves; also called median; it is also called midline |
| |
|
sagittal plane |
|
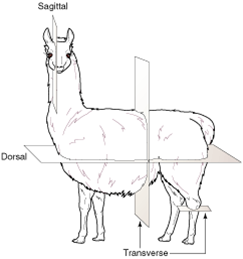
plane that divides the body into unequal right and left parts |
| |
|
dorsal plane |
|
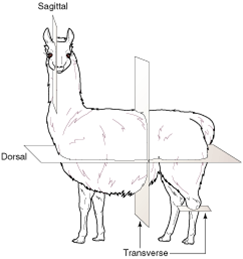
the plane that divides the body into dorsal (back) and ventral (belly) parts; also called frontal plane or coronal plane |
| |
|
transverse plane |
|
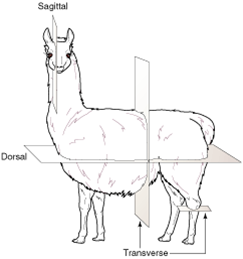
the plane that divides the body into cranial and caudal parts; also called horizontal plane or cross-sectional plane |
| |
|
anatomy |
|
the study of body structure |
| |
|
physiology |
|
the study of the body function(s) |
| |
|
pathophysiology |
|
the study of changes in function caused by disease |
| |
|
etiology |
|
the study of disease |
| |
|
arcade |
|
term used to describe how teeth are arranged in the mouth |
| |
|
lingual surface |
|
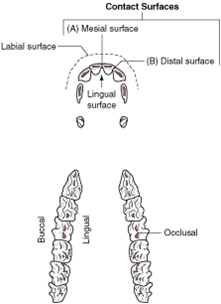
the aspect of the tooth that faces the tongue |
| |
|
palatal surface |
|
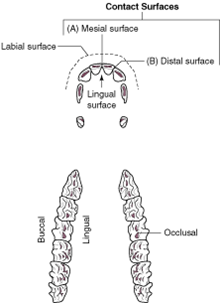
the tooth surface of the maxilla that faces the tongue on both the maxilla (upper jaw) and mandible (lower jaw) |
| |
|
buccal surface |
|
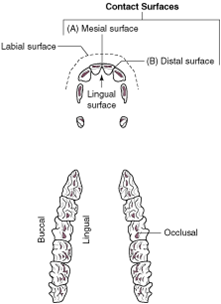
the aspect of the tooth that faces the cheek; also called vestibular surface |
| |
|
occlusal surfaces |
|
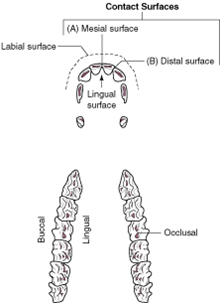
the aspects of the teeth that meet when you chew |
| |
|
labial surface |
|
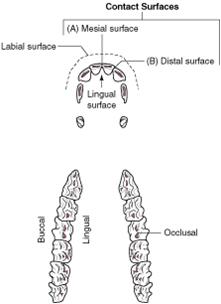
the tooth surface facing the lips |
| |
|
contact surfaces |
|
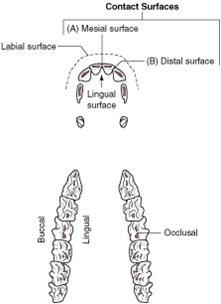
the aspects of the tooth that touch other teeth |
| |
|
mesial surface |
|
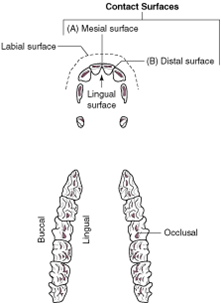
the contact surface closest to the midline of the dental arcade or arch |
| |
|
distal surface |
|
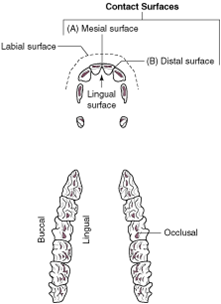
the contact surface is the one that is furthest from the midline of the dental arcade |
| |
|
cranial cavity |
|
hollow space that contains the brain in the skull |
| |
|
spinal cavity |
|
hollow space that contains the spinal cord within the spinal column |
| |
|
thoracic cavity |
|
also called chest cavity; hollow space that contains the heart and lungs within the ribs between the neck and diaphragm |
| |
|
abdominal cavity |
|
hollow space that contains the major organs of digestion between the diaphragm and pelvic cavity |
| |
|
peritoneal cavity |
|
hollow space within the abdominal cavity between the parietal peritoneum and the visceral peritoneum |
| |
|
pelvic cavity |
|
hollow space that contains the reproductive and some excretory system organs formed by the pelvic bones |
| |
|
abdomen |
|
the portion of the body between the thorax and the pelvis containing the abdominal cavity |
| |
|
thorax |
|
chest region located between the neck and diaphragm |
| |
|
groin |
|
lower region of the abdomen adjacent to the thigh; also known as the inguinal area |
| |
|
membranes |
|
thin layers of tissue that cover a surface, line a cavity, or divide a space or organ |
| |
|
peritoneum |
|
the membrane lining the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers some organs in this area |
| |
|
parietal peritoneum |
|
the outer layer of the peritoneum that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities |
| |
|
visceral peritoneum |
|
inner layer of the peritoneum that surrounds the abdominal organs |
| |
|
umbilicus |
|
the pit in the abdominal wall marking the point where the umbilical cord entered the fetus; also called the navel |
| |
|
mesentery |
|
the layer of the peritoneum that suspends parts of the intestine in the abdominal cavity |
| |
|
retroperitoneal |
|
superficial to the peritoneum |
| |
|
recumbent |
|
lying down |
| |
|
dorsal recumbency |
|
lying on the back |
| |
|
ventral recumbency or sternal recumbency |
|
lying on the belly |
| |
|
left lateral recumbency |
|
lying on the left side |
| |
|
right lateral recumbency |
|
lying on the right side |
| |
|
adduction |
|
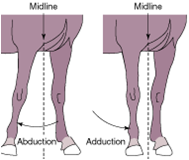
movement toward the midline |
| |
|
abduction |
|
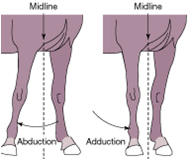
movement away from the midline |
| |
|
flexion |
|
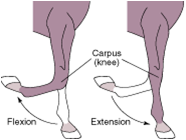
closure of a joint angle, or reduction of the angel between two bones |
| |
|
extension |
|
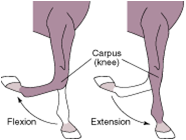
straightening of a joint or an increase in the angle between two bones |
| |
|
hyperflexion |
|
palmar or plantar movement of the joint angles |
| |
|
hyperextension |
|
occurs when the joint is flexed or extended too far |
| |
|
supination |
|
the act of rotating the limb or body part so that the palmar surface is turned upward |
| |
|
pronation |
|
the act of rotating the limb or body part so that the palmar surface is turned townward |
| |
|
rotation |
|
circular movement around an axis |
| |
|
cytology |
|
the study of cells |
| |
|
protoplasm |
|
the cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus |
| |
|
cytoplasm |
|
the material located within the cell membrane that is not part of the nucleus |
| |
|
nucleus |
|
structure of a cell that contains nucleoplasm, chromosomes, and the surrounding membrane |
| |
|
nucleoplasm |
|
the material in the nucleus |
| |
|
chromosomes |
|
the structures in the nucleus composed of DNA, which transmits genetic information |
| |
|
genetic disorder |
|
any disease or condition caused by defective genes and is inherited |
| |
|
congenital |
|
something that is present at birth |
| |
|
anomaly |
|
a deviation from what is regarded as normal |
| |
|
tissue |
|
a group of specialized cells that are similar in structure and function |
| |
|
histology |
|
the study of the structure, composition, and function of tissue |
| |
|
epithelial tissue |
|
tissue that covers internal and external body surfaces and is made up of tightly packed cells in a variety of arrangements |
| |
|
epithelium |
|
the cellular covering that forms the outer layer of the skin and covers the external surfaces of the body |
| |
|
endothelium |
|
the cellular covering that forms the lining of the internal organs including the blood vessels |
| |
|
mesothelium |
|
the cellular covering that forms the lining of serous membranes such as the peritoneum |
| |
