|
Biconditional |
|
The conjugation of a conditional statement and its converse.
p iff q |
| |
|
Compound Statement |
|
A statement formed by joining two or more statements.
p- Raleigh is a city in N.C.
q- Raleigh is the capital of N.C. |
| |
|
Conclusion |
|
In a conditional statement, the statement that immeadiatly follows then.
If you buy a car, then you get $1,500 back. |
| |
|
Conjecture |
|
An educated guess based on known information.
2+x= 5 x=3 |
| |
|
Contrapositive |
|

The statement formed by negating both the hypothesis and conclusion of the conversion of a conditional statement.
 |
| |
|
Converse |
|
The statement formed by exchanging the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement.
q to p |
| |
|
Counterexample |
|
An example used to show that any given statement is not always true.
2+2= 7 because 2+2= 4 |
| |
|
Deductive Reasoning |
|
A system of reasoning that uses facts, rules, definitions, or properties to reach logical conclusions.
2(9) using the distributive property, you can logically conclude it's 18. |
| |
|
Hypothesis |
|
In a conditional statement, the statement that immeadiatly follows the word if.
If lines m and n never intersect, then they are parallel. |
| |
|
Inverse |
|
The statment formed by negating both the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement |
| |
|
Negation |
|
If a statement is represented by P, then not P is the negation of the statment |
| |
|
Properties |
|
Can be used to justify each step when solving equations |
| |
|
Theorem |
|
A statment or conjecture that can be proven true by undefined terms, definitions, and postualtes |
| |
|
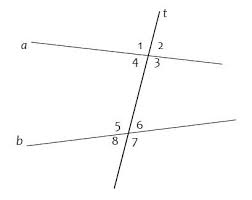
Alternate Exterior Angles |
|

In the figure,<1 and <7 and <2 and <8.
 |
| |
|
Alternate Interior Angles |
|

In the figure, <3 and <4 and <6 and <5.
 |
| |
|
Consecutive Interior Angles |
|

In the figure,< 1 and < 4 and <5 and <8.
 |
| |
|
Corrosponding Angles |
|
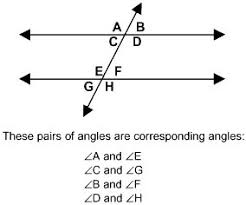
In the figure,< A and |
| |
|
Parallel Lines |
|

Coplanar lines that do not inter
 sect Lines a and b are parallel sect Lines a and b are parallel |
| |
|
Parallel Planes |
|

Planes that do not intersect
 |
| |
|
Skew Lines |
|

Lines that do nto intersect and are not coplanar
Lines RY and SZ.
 |
| |
|
Transversal |
|

A line that intersects 2 or more lines in a plane at different points
Line t is the transversal.
 |
| |
|
Acute Triangles |
|

a triangle in which all of the angles are acute angles
 |
| |
|
Altitude of a traingle |
|
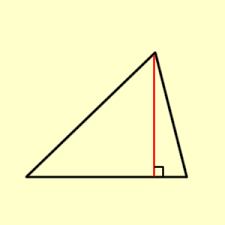
a segment from a vertex of the triangle to the line cointaining oppisite sides and perpendicular to that side
 Red line is altitude. Red line is altitude. |
| |
|
Base Angles |
|

2 angles formed by the base and 1 congruent side
< A and < C are base angles.
 |
| |
|
Centroid |
|

the point of concurrency of the medians of a triangle
G is the centroid.
 |
| |
|
Circumcenter |
|
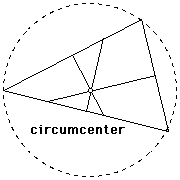
The point of concurrency of the perpendicular bisectors of a triangle
 |
| |
|
Congruence |
|

Slide, turn, or flip a triangle to prove this
 |
| |
|
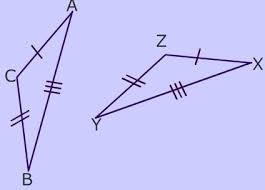
Congruent Triangles |
|
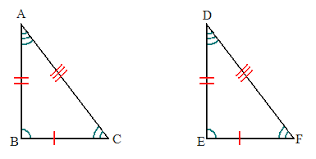
Triangles that have their corrosponding parts congruent
 |
| |
|
Coordinate Proof |
|

A proof that uses figures in the coordinate plane and algebra to prove geometric concepts

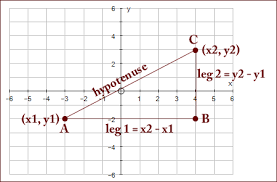 |
| |
|
Corollary |
|
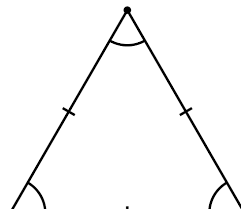
A statment that can be easily proven by using a theorem
This is an equilateral triangle because it has all sides and angles equal.
 |
| |
|
Equiangular triangle |
|
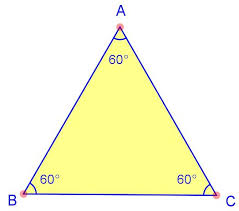
triangle with all angles congruent
All angles are 60 degrees.
 |
| |
|
Equilateral Triangle |
|
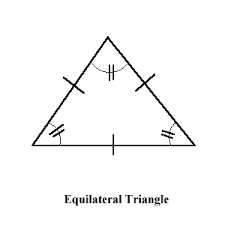
triangle with all sides congruent
All sides are congruent.
 |
| |
|
Exterior angle |
|
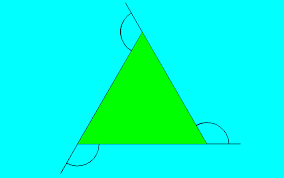
An angle formed by 1 side of the triangle and the extension of the other side
All of the larger 120 degree angles.
 |
| |
|
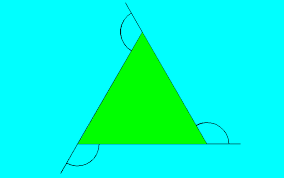
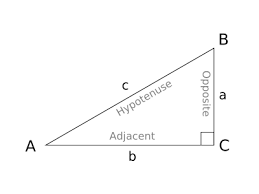
Hypotenuse |
|
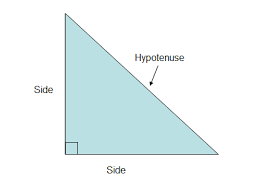
the side opposite of the right angle
The longest part of the triangle.
 |
| |
|
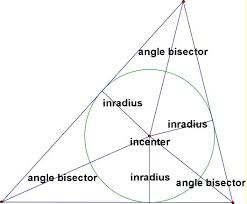
Incenter |
|
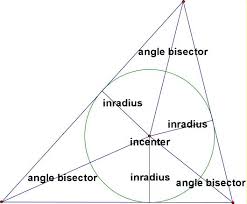
The poitn on coincurrency of the angle bisectors of a triangle
Point in the middle of a circle.
 |
| |
|
Isosceles |
|
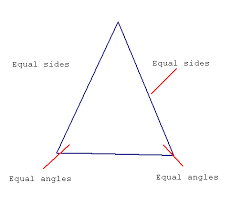
At least 2 sides of the triangle are congruent
The two sides are congruent.
 |
| |
|
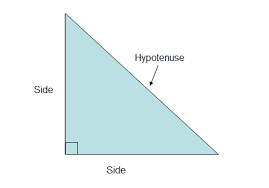
Legs of a right triangle |
|
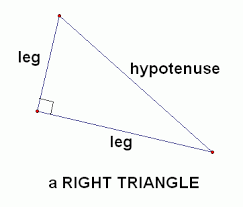
The lines that are part of the right angle
Parts that aren't the hypotenuse.
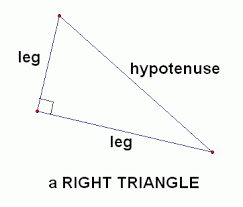 |
| |
|
median of a triangle |
|
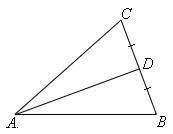
a line segment with endpoints that are a vertex of a triangle and tje midpoint of the side opposite of the vertex. AD is a median of the triangle.
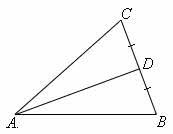
|
| |
|
obtuse triangle |
|
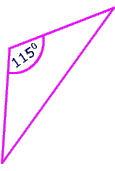
one angle is obtuse
This triangle is obtuse because it has one 115 degree angle in it.
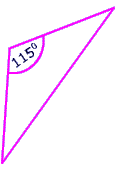 |
| |
|
perpendicular bisector |
|
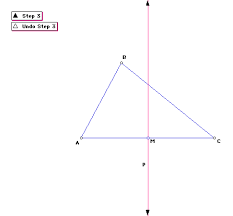
a line, segment, or ray that passes through the midpoint of a side and it perpendicular to that side
.Red line is perpendicular bisector.
 |
| |
|
point of concurrency |
|
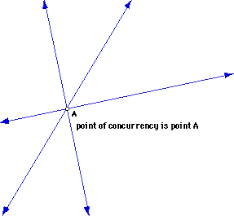
the point of intersection of concurrent lines
 |
| |
|
remote interrior angle |
|
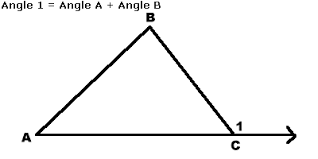
interior angles of the triangle not adjacent to a given exterior angle.A and C are remote interrior angles.

|
| |
|
right triangle |
|

triangle with a right angle
 |
| |
|
scalene |
|
no two sides are congruent
 |
| |
|
vertex angles |
|

the angles formed by the congruent sides
 |
| |
|
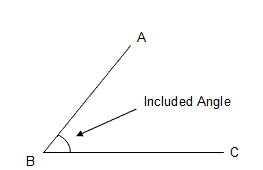
included angle |
|
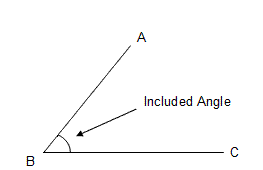
in a triangle, the angle formed by two sides is the included angle for those two sides
 |
| |
|
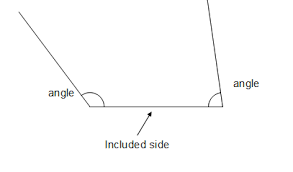
included side |
|
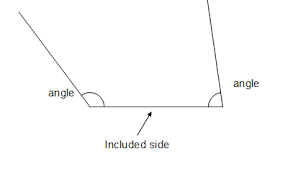
the side of a triangle that is a side of each of the two angles
 |
| |
|
indirect reasoning |
|
reasoning that assumes that the conclusion is false and then shows that this assumption leads to a contradiction of the hypothesis.
ex: -2 +1= 1 because -2 +1= -1 |
| |
|
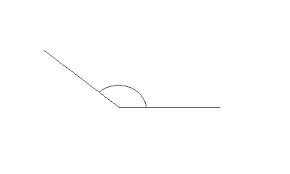
indirect proof |
|
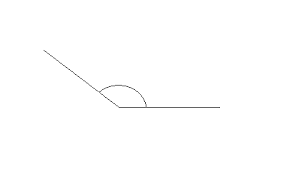
an indirect proof, one assumes that the statement to be proved is false.
True or False: False That isn't an acute angle.
 |
| |
|
concave |
|
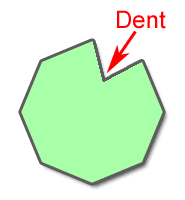
a polygon for which there is a line containing a side of the polygon that also contains a point in the interior of a polygon.
 |
| |
|
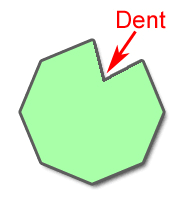
convex |
|
a polygon for which there is no line that contains both a side of the polygon and the point in the interior of a polygon.

|
| |
|
mid-segment of a triangle |
|

a segment with endpoints that are midpoints of two sides of a triangle.

|
| |
|
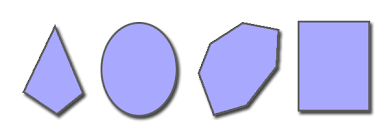
polygon |
|
a closed figure formed by a finite number of coplanar segments.
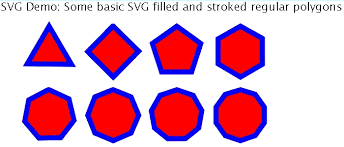 |
| |
|
proportion |
|
an equation of the form a/b = c/d that states two ratios are equal
ex: 5/10 = 1/2 |
| |
|
regular |
|
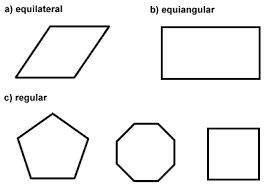
a convex polygon in which all of the sides are congruent and all of the angles are congruent
 |
| |
|
scale factor |
|
the ratio of two lengths of two corresponding sides of two similar polygons or two similar solids
 |
| |
|
similar polygons |
|
two polygons are similar iff their corresponding angles are congruent and the measure of their corresponding sides are proportional
 |
| |
|
angle of depression |
|

the angle between the line of sight and the horizontal when an observer looks downwards
 |
| |
|
angle of elevation |
|

the angle between the line of sight and horizontal when an observer looks upwards
 |
| |
|
altitude of a right triangle |
|

a segment from a vertex of the triangle to the line containing the opposite side and perpendicular of that side
BD is the altitiude of the right triangle.
 |
| |
|
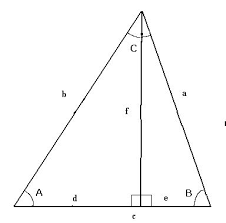
cosine |
|
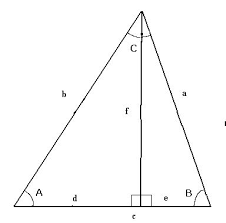
for an acute angle if a right triangle the ratio of the measure of the leg adjacent to the acute angle to the measure of the hypotenuse
 |
| |
|
geometric mean |
|
for any positive numbers, a + b, the positive number such that a/x = x/b
ex. a / x = x / b |
| |
|
Pythagorean triple |
|
a group of whole 3 numbers that satisfies the equation a squared + b squared = c squared
ex: 3 squared + 6 squared = 9 squared |
| |
|
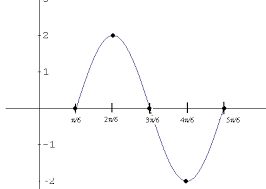
sine |
|
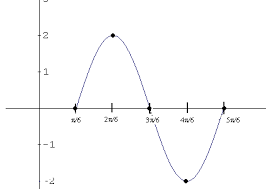
for an acute angle of a right triangle, the ratio of the measure of the leg opposite the acute angle over the hypotenuse
 |
| |
|
solving a triangle |
|

finding the measures of all the angles and sides of a triangle

|
| |
|
tangent |
|
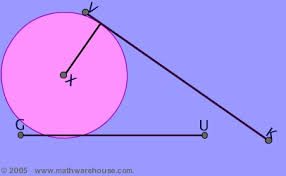
ratio of the legs of a triangle
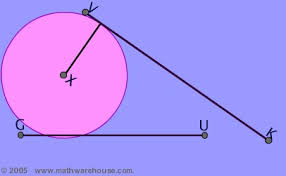 |
| |
|
trigonometry |
|
the study of the properties of triangles and trigonometric functions and their applications
 |
| |
|
arc |
|
a part of a circle that is defined by two endpoints
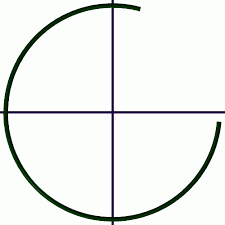 |
| |
|
center |
|
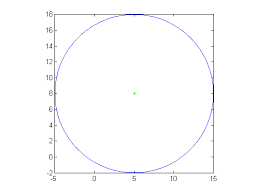
a given point in the middle of a circle
 |
| |
|
central angle |
|
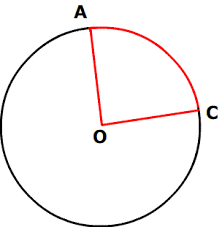
an angle that intersects a circle in two points and its vertex is at the center of a circle
 |
| |
|
chord |
|
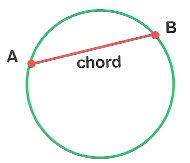
a segment with endpoints that are on the circle

|
| |
|
circle |
|
the locus of all points in a plane equidistant from a given point called the center of a circle

|
| |
|
circumference |
|
distance around a circle
ex: pi r squared |
| |
|
circumscribed |
|
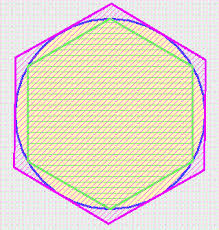
a circle is circumscribed about a polygon if the circle contains all of the verticies of the polygon

|
| |
|
diameter |
|
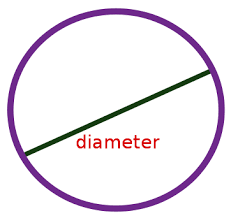
a chord that pssses through the center of a circle
 |
| |
|
inscribed |
|
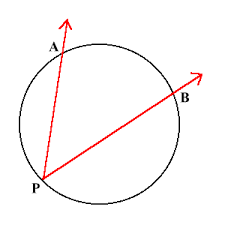
if each of the vertices lie on a circle
 |
| |
|
intercepted |
|

iff the endpoints of the arc lie on the angle
 |
| |
|
major arc |
|

an arc with a measure greater than 180
The blue line is the major arc.
 |
| |
|
minor arc |
|

an arc with a measure less than 180
Red arc is a minor arc because its less than 90 degrees.
 |
| |
|
pi |
|

an irrational number represented by the ratio of the circumference of a circle to the diameter of a circle
 |
| |
|
point of tangency |
|
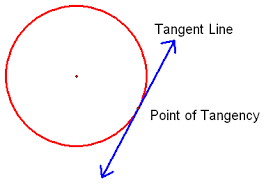
for a line that intersects a circle in only one point, the point at which they intersect
 |
| |
|
radius |
|

any segment with endpoints that are in the center of the circle
 |
| |
|
secant |
|

any line that intersects a circle at exactly two points
 |
| |
|
semicircle |
|

an arc that measures 180 degrees
 |
| |
|
tangent |
|
a line in the plane of a circle that intersects the circle in exactly one point
 |
| |
|
apothem |
|
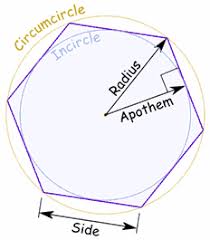
a segment that is drawn from the center of a regular polygon perpendicular to a side of the polygon
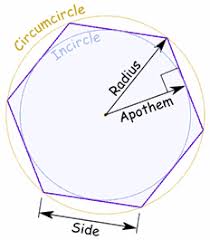 |
| |
|
geometric probability |
|
using the principles of length and area to find the probability of an event
 |
| |
|
irregular figure |
|

a figure that can't be classified as a regular polygon
 |
| |
|
irregular polygon |
|

a polygon thats not regular
 |
| |
|
sector of a circle |
|

a region of a circle bounded by a central angle and its intercepted arc

|
| |
|
segment of a circle |
|
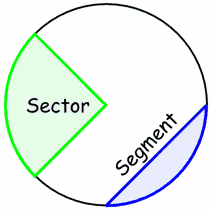
the region of a chord bounded by an arc and a chord
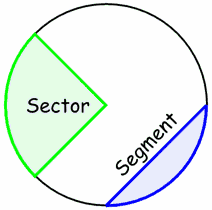 |
| |
|
consecutive angles of a quadrilateral |
|
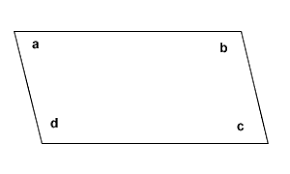
any two angles whose vertices are the endpoints of the same side
A and C are consecutive angles.
 |
| |
|
decagon |
|
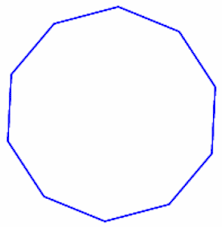
10 sided figure
 |
| |
|
diagonal |
|

a segment that connects any two nonconsecutive vertices
 |
| |
|
dodecagon |
|
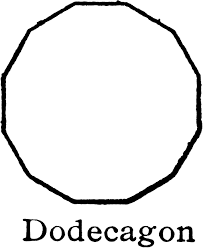
12 sided figure
 |
| |
|
exterior angles of a polygon |
|
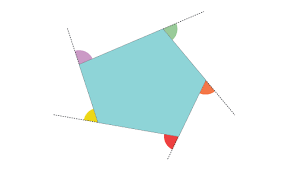
add up to 360 degrees
 |
| |
|
hexagon |
|
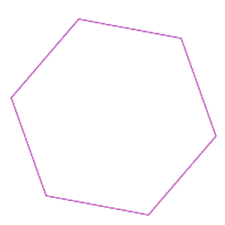
6 sided figure
 |
| |
|
heptagon |
|
7 sided figure
 |
| |
|
interior angles of a polygon |
|
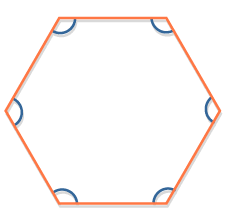
add up to 360 degrees on the outside
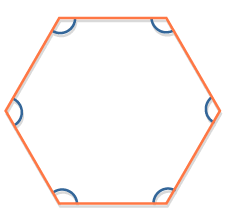 |
| |
|
isoceles trapezoid |
|

if the legs are congruent
 |
| |
|
kite |
|
quadrilateral with two disjointed pairs of congruent adjacent sides
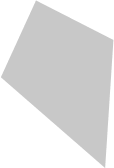 |
| |
|
median of a trapezoid |
|
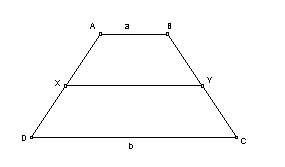
the segment that joins midpoints of the legs of a trapezoid
 |
| |
|
n-gon |
|
polygon with n- sides
 |
| |
|
nonagon |
|
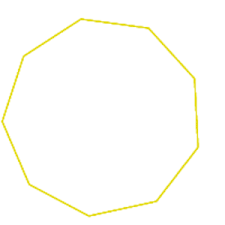
9 sided figure
 |
| |
|
octagon |
|
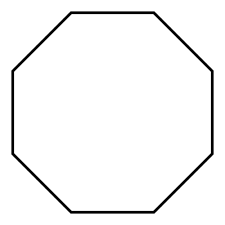
8 sided figure
 |
| |
|
opposite angles of a quadrilateral |
|

any two angles that are not consecutive
 |
| |
|
opposite sides of a quadrilateral |
|

any two sides that intersect
 |
| |
|
parallelogram |
|
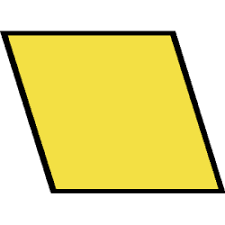
a quadrilateral with parallel opposite sides
 |
| |
|
pentagon |
|
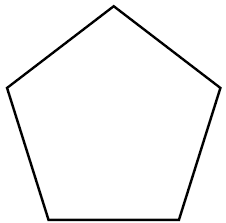
5 sided figure
 |
| |
|
perimeter |
|
length of a boundary:
ex: a rectangle 2 by 2 , the perimeter is 8
|
| |
|
quadrilateral |
|
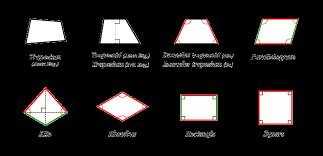
having 4 sides
 |
| |
|
rectangle |
|
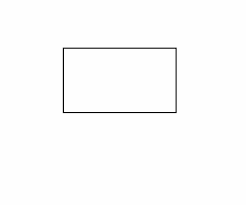
 a quadrilateral with 4 right angles a quadrilateral with 4 right angles
 |
| |
|
rhombus |
|

a quadrilateral with all 4 sides are congruent
 |
| |
|
square |
|

if a quadrilateral is both a rhombus and a rectangle
 |
| |
|
trapezoid |
|

a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides
 |
| |
|
bases of a trapezoid |
|
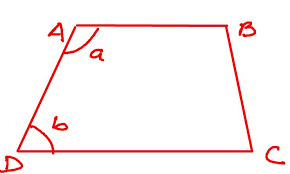
the parallel sides
AB and DC are bases of the trapezoid.
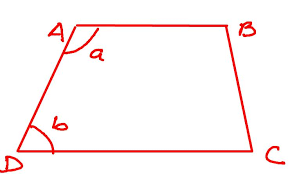 |
| |
|
height of a trapezoid |
|
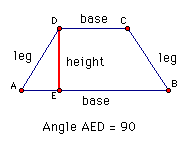
sides that aren't parallel
 |
| |
|
altitude of a 3D figure |
|
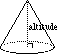
a segment perpendicular to the bases with endpoints in each plane
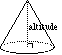 |
| |
|
bases |
|
bottom of a figure
This figure has a square base.
 |
| |
|
congruent solids |
|

2 solids are congruent if all of the following conditions are met, plane as the base, and a lateral surface area composed of all points in the segments connecting the vertex to the edge of the base
 |
| |
|
cylinder |
|

a figure with bases that are formed by congruent circles in parallel planes
 |
| |
|
edges |
|
a line or border at which a surface terminates
 |
| |
|
face |
|

a face of the polygon that make up its boundaries
 |
| |
|
great circle |
|

the intersection of the sphere and a plane that contains the center of the sphere
 |
| |
|
height |
|

the distance between the highest and lowest point of a figure
 |
| |
|
acute angle |
|
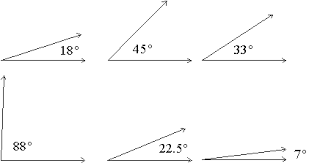
an angle with a measure less than 90 degrees
 |
| |
|
obtuse angle |
|

an angle with a measure greater than 90 degrees
 |
| |
|
hemisphere |
|
one of the two congruent parts into which a great circle seperates a sphere

|
| |
|
lateral area |
|
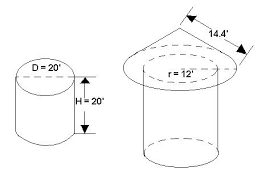
the area of the figure not including the bases
 |
| |
|
lateral faces |
|
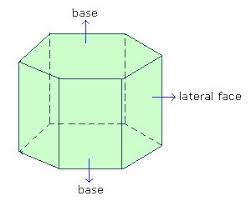
faces that aren't bases
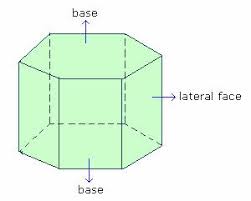 |
| |
|
nets |
|

a 2-dimensional figure that when folded forms the surface of a 3-dimensional object

|
| |
|
oblique cone |
|
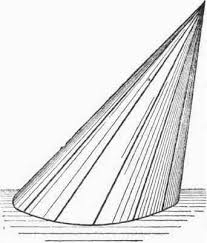
a cone that isn't a right cone
 |
| |
|
oblique cylinder |
|
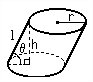
a cylinder that is not right
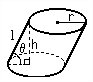 |
| |
|
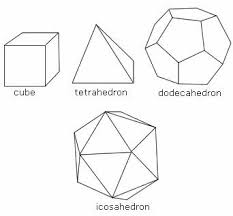
platonic solids |
|
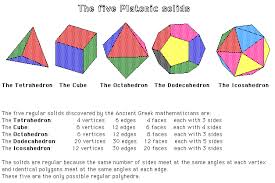
5 regular polyhedra
 |
| |
|
dodecahedron |
|
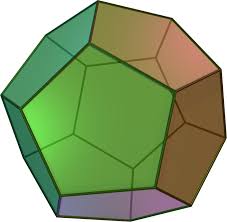
a solid figure having 12 faces

 |
| |
|
hexahedron |
|
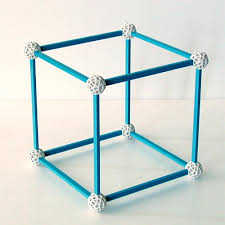
a solid having 6 faces
|
| |
|
icosahedron |
|

a solid having 20 faces
 |
| |
|
octahedron |
|
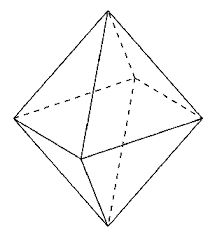
a solid having 8 faces
 |
| |
|
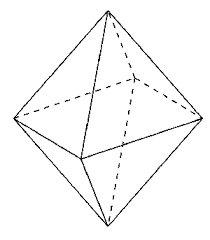
tetrahedron |
|
a solid having 4 sides

|
| |
|
polyhedron |
|
closed 8 dimensional figures made up of flat polygonal regions
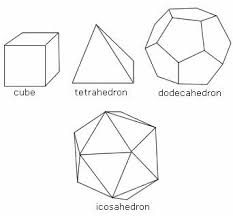 |
| |
|
prism |
|
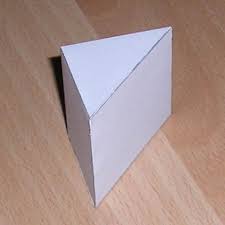
a solid with 2 bases, 2 lateral faces, and lateral edges
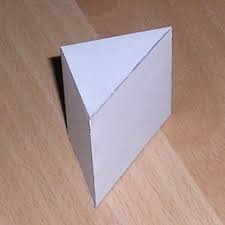 |
| |

pyramid
 |
|

a solid with all faces intersecting at a vertex, a base, and lateral face
 |
| |
|
regular cone |
|
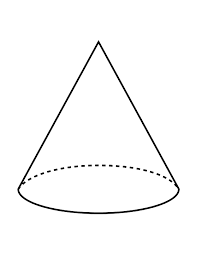
right cone with bases that are regular polygons

|
| |
|
regular prism |
|

right prism with bases that are regular polygons
 |
| |
|
regular cylinder |
|
.png)
a cylinder with an altitude thats also an axis
.png) |
| |
|
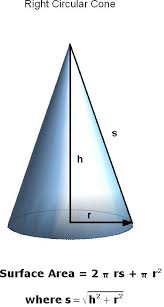
right cone |
|
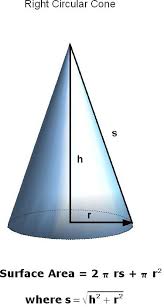
a cone with an axis thats also an altitude
|
| |
|
right cylinder |
|
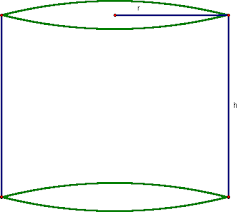
a cylinder with an altitude thats also an axis

|
| |
|
right prism |
|
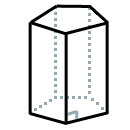
a prism with lateral edges that are also altitudes
 |
| |
|
similar solids |
|

solids that have the exactly the same shape, but not necessarily the same size
 |
| |
|
slant height |
|

the altitude of the side of a regular pyramid
 |
| |
|
sphere |
|

the set of all points that are given distance from a given point
 |
| |
|
surface area |
|

the sum of the areas of all faces and side surfaces of a 3-dimensional figure
 |
| |
|
volume |
|
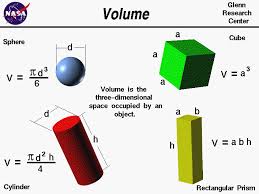
a measure of the amount of space enclosed by a 3- dimensional figure
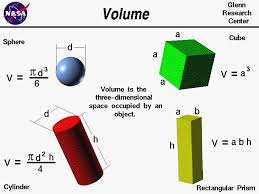 |
| |
|
vertices of a 3D object |
|

the points on a graph
 |
| |
|
center of dilation |
|

the fixed point in the plane about whuch all points are expanded or contracted
 |
| |
|
center of rotation |
|
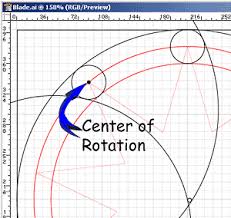
a point or line around which all other points in a body move
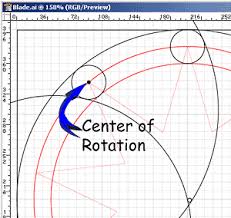 |
| |
|
column matrix |
|
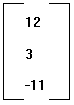
In linear algebra, a column vector or column matrix is an m × 1 matrix, i.e. a matrix consisting of a single column of elements.

|
| |
|
columns of a matrix |
|
line up to form points on an object
 |
| |
|
composition |
|

the act of combining parts and elements to form a whole
 |
| |
|
dilation |
|

the act or process of expanding
 |
| |
|
identity matrix |
|
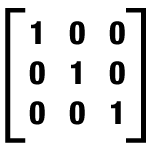
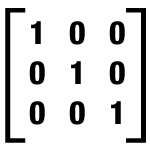
 |
| |
|
image |
|
to resemble
 |
| |
|
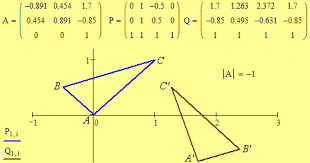
isometry |
|
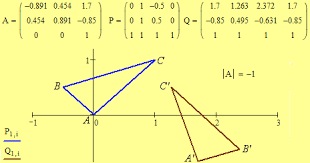
a function from one metric space onto a second metric space having the property that the distance between two points in the first space is equal to the distance between the image points in the second space
 |
| |
|
mapping |
|

function
 |
| |
|
pre-image |
|

the point or set of points in the range corresponding to a designated point in the domain of a given function
 |
| |
|
reflection |
|
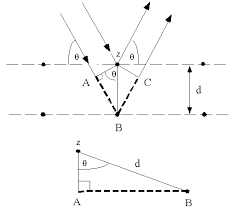
the replacement of each point on one side of a line by the point place symmetrically on the other line
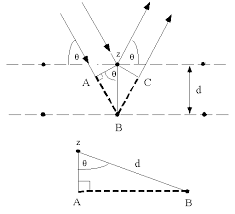 |
| |
|
reflection matrix |
|

 |
| |
|
rotation |
|

an operation that rotates an object around a fixed point
 |
| |
|
rotation matrix |
|

 |
| |
|
row matrix |
|

a matrix with only one row
 |
| |
|
scalar |
|
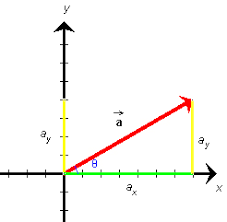
a number , numerical quantity , or elment in a field
 |
| |
|
standard matrix |
|

 |
| |
|
translation |
|
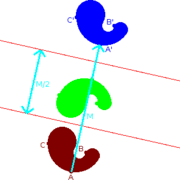
moving every point a constant distance in a specified direction
 |
| |
|
translation matrix |
|

a matrix represnting a translated figure
 |
| |
|
vertex matrix |
|
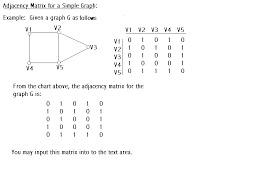
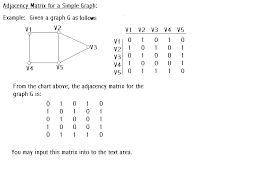 If a graph has If a graph has
 vertices, we may associate an vertices, we may associate an
 matrix matrix
 |
| |
|
distance |
|
 the greatest lower bound of differences from one point to another the greatest lower bound of differences from one point to another
 |
| |
|
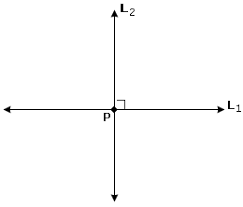
perpindicular lines |
|
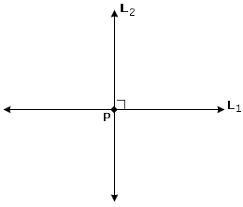
forms four 90 degree angles
acute triangle
 |
| |
|
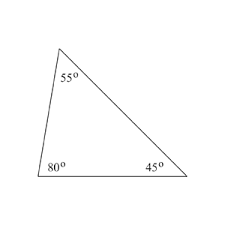
acute triangle |
|
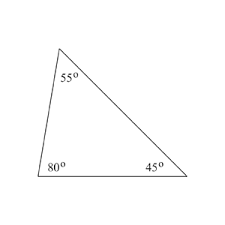
a triangle that has all angles less than 90 degrees
exterior
 |
| |
|
exterior |
|
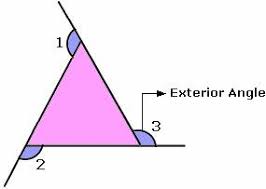
outer ;external
 |
| |
|
plane |
|
a flat surface extending indefinately in all directions
|
| |
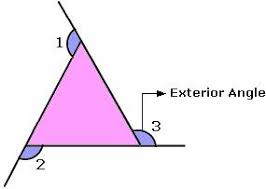
|
interior |
|
on the inside
 |
| |
|
point |
|
a geometric element that has position but no extension
 |
| |
|
angle |
|
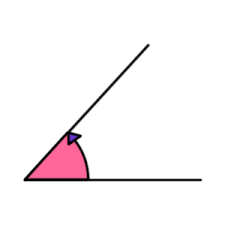
the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint
 |
| |
|
line |
|
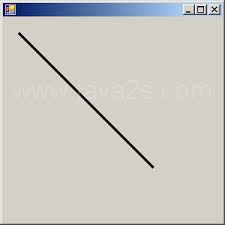
a series of points
 |
| |
|
postulate |
|
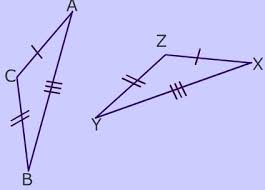
a declaration of something self-evident
angle bisector
 |
| |
|
angle bisector |
|

divides the angle into two equal or congruent parts
 |
| |
|
line segment |
|
a line that is bounded by 2 endpoints
 |
| |
|
ray |
|

a line that extends indefinately in one direction
colr

|
| |
|
collinear |
|
lying on the same line
linear pair add up to 180 degrees
 |
| |
|
linear pair |
|
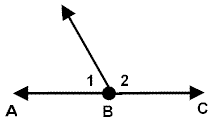
add up to 180 degrees
 |
| |
|
right angle |
|

adds up to 90 degrees

|
| |
|
complementary angles |
|

are angles next to each other that form 90 degrees
 |
| |
|
midpoint |
|
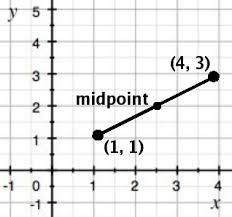
a point equidistant from the ends of a line
 |
| |
|
segment bisector |
|
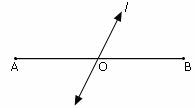
any line, segment, or ray that intersects a segment at its midpoint
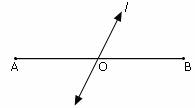 |
| |
|
congruent |
|
same shape and same size
 |
| |
|
space |
|
the set of all points
 |
| |
|
coplanar |
|
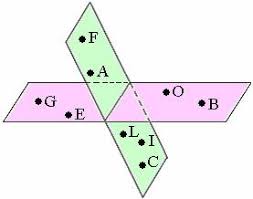
lying in the same plane
Q and B are coplanar .
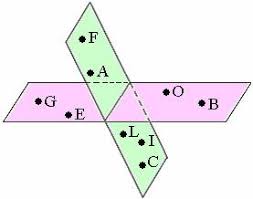 |
| |
|
opposite rays |
|
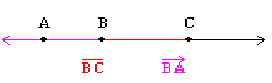
form a line
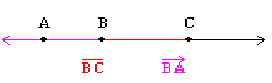 |
| |
|
supplementary angles |
|
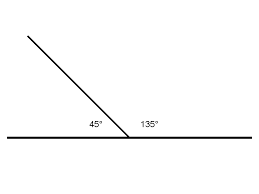
add up to 180 degrees
 |
| |
|
degree |
|

used to measure angles
 |
| |
|
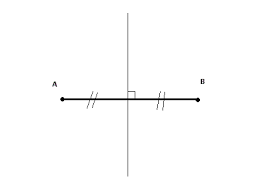
perpendicular bisector |
|
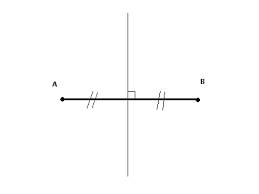
makes 4 right angles
 |
| |
|
undefined terms |
|

points, lines, and planes
 |
| |
|
vertex |
|
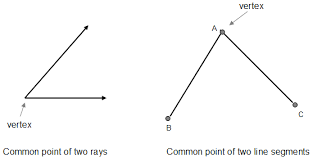
the point of intersection of lines or points opposite the base of the figure
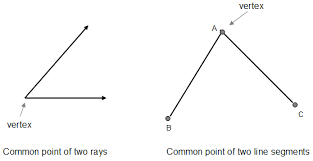 |
| |
|
vertical angles |
|

the pair of angles that are directly across from each other when two straight lines intersect
 |
| |
|
flow proof |
|

putting the statements in boxes then putting arrows showing the most logical way to prove the proof
 |
| |
|
if-then statement |
|
the words that follow the if are the if statement and the words that follow the then statement are the then statement
ex: If all squares are rectangles then all rectangles aren't squares. |
| |
|
inductive reasoning |
|
reasoning from detailed facts to general principles
 |
| |
|
paragraph proof |
|

explaning the proof using sentences and paragraphs
 |
| |
|
proof |
|

any factual evidence to establish the truth of something
 |
| |
|
properties |
|
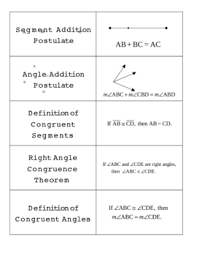
something a shape or any figure can have
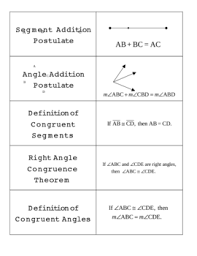 |
| |
|
statement |
|

a message that is stated or declared
 |
| |
|
two-column proof |
|

two columns explaining why you did what you did to solve the proof
 |
| |
|
equidistant |
|
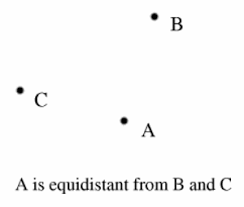
the same amount of space apart
 |
| |
|
included angle |
|

angle made by two sides with a common vertex
 |
| |
|
included side |
|

the common leg of two angles
 |
| |
|
hypotenuse leg |
|

theorem proving right triangles similar or congruent
 |
| |
|
CPCTC |
|

theorem proving that congruent parts of congruent triangles are congruent
 |
| |
|
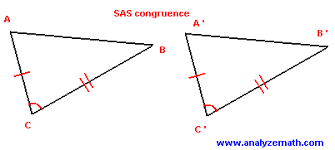
SAS |
|
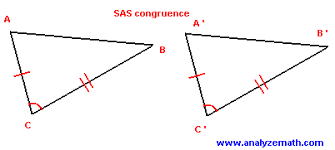
theorem proving triangles congruent by side angles side
 |
| |
|
SSS |
|

theorem proving triangles congruent by side side side

|
| |
|
ASA |
|
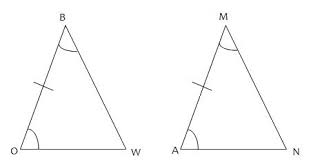
postulate proving triangles congruent by angle side angle
 |
| |
|
AAS |
|
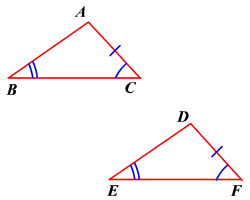
postulate proving triangles congruent by angle angle side
 |
| |
|
indirect proof |
|

a proof in which one false assumption is made
 |
| |
|
indirect reasoning |
|

reasoning using the law of Contrapositive, and negating
 |
| |
|
overlapping triangles |
|

triangles that are on top of each other
 |
| |
|
extremes |
|

the greatest degree of intensity or extent
 |
| |
|
means |
|

the averages
 |
| |
|
ratio |
|

the relative magnitude of 2 quantities
 |
| |
|
Law of Sines |
|
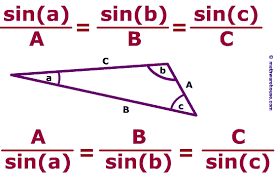
used to find angles of a general triangle
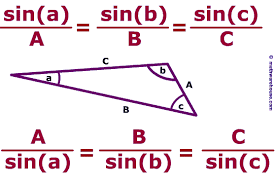 |
| |
|
Law of Cosines |
|

used to find one side of a triangle when an angle and the other side is known
 |
| |
|
Unit Circle |
|
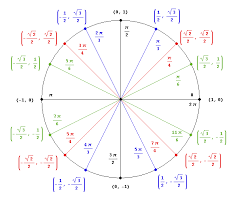
a circle with a radius of one
 |
| |
|
undecagon |
|
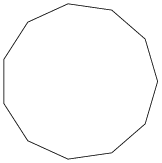
an eleven sided polygon
 |
| |
|
common external tangent |
|
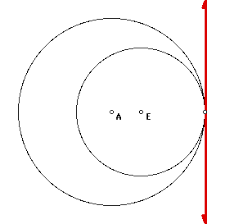
a common tangent that is common in two circles and doesn't intersect the center of the two circles
 |
| |
|
common internal tangent |
|

a line that is common in two circles and intersects the center of the two circles
 |
| |
|
concentric circles |
|

two or more circles that have the same center and different radii
 |
| |
|
externally tangent circles |
|

two circles that aren't inside of each other
 |
| |
|
inscribed angles |
|

angles whose vertex is on the circle and whose sides are chords of the circle
 |
| |
|
inscribed figure |
|
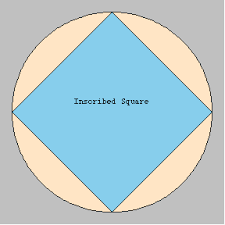
an inscribed shape inside of the circle
 |
| |
|
internally tangent circles |
|
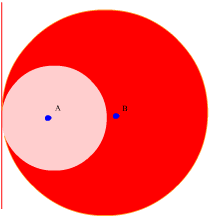
two circles, one of which is inside the other
 |
| |
|
The end |
|
:) |
| |
