|
Which one of the following
aquifers would be best for purifying groundwater that is contaminated with
harmful sewage bacteria? |
|
a. clay
b. coarse gravel
c. sand
d. cavernous limestone
|
| |
|
Which of the following
rock materials would be least permeable? |
|
a. coarse sand
b. clay-rich, fine‑grained sand
c. gravel
d. cavernous limestone
|
| |
|
The major cause of most low‑latitude
dry climates is: |
|
a. their positions in the deep interiors
of continents
b. the presence of high mountains that
separate these areas from moist
maritime air masses
c. zones of high atmospheric pressure
and dry descending air
d. none of the above
|
| |
|
An open ocean wave has a
wavelength of 20 meters, a wave height of 4 meters,
and a period of 6
seconds. At what depth will this
wave begin to "feel
bottom"? |
|
a. 1 meter
b. 2 meters
c. 10 meters
d. 15 meters
e. impossible to
determine from the information given
because the wave moves half of the wavelength below the surface. therefore that is where the wave would begin to feel the ground. |
| |
|
A steep‑sided
amphitheater‑shaped bowl, excavated by frost action
and glacial erosion, at the head of a
glacial valley is called
a(n) |
|
a. horn
b. arete
c. cirque
d. fjord
|
| |
|
The dominant erosional
force on Mercury is: |
|
a. meteorite
cratering
b. heat expansion
c. solar radiation
d. moonquakes
|
| |
|
Which of the following is
NOT found on Venus |
|
a. prominent plateaus
and basins
b. volcanoes
c. two-step
topography
d. atmosphere
|
| |
|
At a bend in a river,
the main point of deposition is: |
|
a. on the outside of the
bend
b. on the inside of
the bend
c. both outside and
inside the bend
d. in the center of the
channel
|
| |
|
The downhill tilting of
fences and telephone poles, and the presence of trees with curved trunks
(convex downslope) are indications of what geologic process? |
|
a. Debris avalanche
b. Slump
c. Soil creep
d. Gliding
e. Mudflow
|
| |
|
Which of the following
types of mass wasting is generally the slowest? |
|
a. mudflow
b. creep
c. slump
d. they are all about the same
|
| |
|
mass wasting events are caused by |
|
1) Over-steepening of slope,
2) Too much water, and
3) Unusual rock/soil conditions.
|
| |
|
ways to mitigate mass wasting dangers? |
|
-Steep slopes can be covered or
sprayed with concrete covered with a wire mesh to prevent rock falls.
-Retaining
walls could be built to stabilize a slope.
-If
the slope is made of highly fractured rock, rock bolts may be emplaced to hold the slope together and prevent
failure.
-Drainage
pipes could be inserted into the slope to more easily allow water to get out
and avoid increases in fluid pressure, the possibility of liquefaction, or
increased weight due to the addition of water.
-Oversteepened
slopes could be graded to reduce the slope to the natural angle of repose.
-In
mountain valleys subject to mudflows, plans could be made to rapidly lower
levels of water in human-made reservoirs to catch and trap the mudflows. |
| |
|
slump |
|
A form of mass wasting
event that occurs when loosely consolidated materials or rock layers move a
short distance down a slope. |
| |
|
slide |
|
Rocks moving rapidly along
a surface parallel to slope. |
| |
|
flow |
|
Material moves as fluid. |
| |
|
collecting phase |
|
The upper part has numerous
tributaries, is actively down-cutting the land (eroding), and tends to have
V-shaped channels. |
| |
|
transporting phase |
|
is highly meandering, has
fewer tributaries and is not down-cutting and eroding sediment but moving it
like a conveyor belt. The river in
this phase may be either braided (with a broad flat channel) or meandering
(with a semicircular channel). |
| |
|
dispersing phase |
|
is the delta where the
rivers sediment is dumped into a body of water and gradually extends the river
and eventually (if you wait long enough) fills the bay. |
| |
|
oxbow lake |
|
Because rivers erode at the
outside of the bend, they are constantly changing shape and cutting off loops
creating oxbow lakes. |
| |
|
braided river |
|
is one of a number of
channel types and has a channel that consists of a network of small channels
separated by small and often temporary islands called braid bars |
| |
|
flood plain |
|
Is flat or nearly flat land
adjacent to a stream or river that experiences occasional or periodic flooding. |
| |
|
types of mass wasting: PHOTO |
|
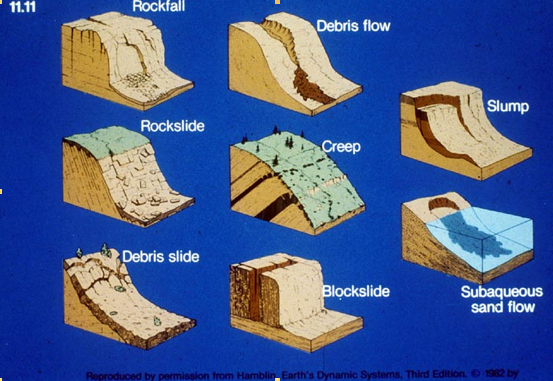
photo |
| |
|
Stream: PHOTO |
|
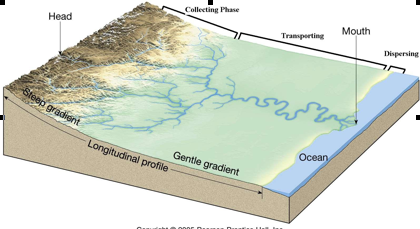
photo |
| |
|
dependance on ground water? |
|
It provides about 40% of
our water nationally. However, it takes many years to replenish itself |
| |
|
how much of worlds water is fresh? |
|
2% |
| |
|
problem when wells are over pumped? |
|
Pumping a well in an
unconfined aquifer will produce a cone of depression around the well. (
Occurs in an aquifer when
groundwater is pumped from a well. In an unconfined (water table) aquifer, this
is an actual depression of the water levels. In confined (artesian) aquifers,
the cone of depression is a reduction in the pressure head surrounding the
pumped well.) |
| |
|
zone of aeration |
|
The subsurface sediment
above the water table containing air and water. |
| |
|
recharge |
|
hydrologic process where
water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. This process usually
occurs in the vadose zone below plant roots and is often expressed as a flux to
the water table surface. |
| |
|
sinkhole |
|
A natural depression or
hole in the surface topography caused by the removal of soil or bedrock, often
both, by water. |
| |
|
how do glaciers erode? |
|
They erode because they
carry rocks and grit in their bases and their great weight grinds these rocks
into the underlying bedrock. |
| |
|
features caused by glaciers |
|
They are tremendous eroders
and will straighten, deepen and round out V-shaped valleys which were
originally carved by rivers |
| |
|
firn |
|
It is ice that is at an
intermediate stage between snow and glacial ice. Firn has the appearance of wet
sugar, but has a hardness that makes it extremely resistant to shovelling. |
| |
|
zone of accumulation |
|
Above the snowline where
accumulation of snow exceeds evaporation and melting. |
| |
|
zone of ablation |
|
Below the snowline where
evaporation and melting exceed accumulation, has crevasses. |
| |
|
terminus |
|
The end of the glacier. |
| |
|
erratic |
|
A piece of rock that
differs from the size and type of rock native to the area in which it rests. |
| |
|
striations |
|
Scratches or gouges cut
into bedrock by process of glacial abrasion. |
| |
|
alpine glacier |
|
Tongue shaped glaciers in mountains.
|
| |
|
continental glacier |
|
Large ice sheets covering
large areas. They are more or less round or elliptical in shape and have a
central zone of accumulation surrounded by the zone of ablation kind of like a
large sunny side up egg. |
| |
|
crevasse |
|
A crack in an ice sheet or
glacier. |
| |
|
cirque |
|
Bowl-shaped depressions on
the side of mountains. |
| |
|
horn |
|
A mountaintop that has been
modified by the action of ice during glaciation and frost weathering. |
| |
|
glacial trough (u-shaped valley) |
|
A deep U-shaped valley with
steep sides that leads down from a cirque and was excavated by a glacier. |
| |
|
hanging valley |
|
A tributary valley with the
floor at a higher relief than the main channel into which it flows. |
| |
|
Arete |
|
A thin, almost knife-like,
ridge of rock which is typically formed when two glaciers erode parallel
U-shaped valleys. |
| |
|
fjord |
|
If you fill the glacial
trough above with water you get a fjord. |
| |
|
till |
|
Unsorted glacial sediment. |
| |
|
moraine |
|
Any glacially formed
accumulation of unconsolidated glacial debris (soil and rock) which can occur
in currently glaciated and formerly glaciated regions, such as those areas
acted upon by a past ice age. |
| |
|
why deserts form where they do |
|
Deserts occur in two
parallel bands centered at around 25 degrees latitude. This distribution is because of
atmospheric cells that create a dry high pressure system over these areas
pretty much permanently. |
| |
|
why deserts are windy |
|
There is a lot of wind in
deserts because they tend to have very hot temperatures in the day and cool
temperature at night. This usually
causes lots of air to move and blow things around. Most wind erosion is causing by wind moving silt and fine
sand grains in zone about a meter above the ground. |
| |
|
effects of wind erosion |
|
Wind erosion causes a
typical desert feature known as desert pavement. This is caused when wind removes fine grains and leaves a
residual rock pavement. This
process is called deflation. |
| |
|
barchan dune |
|
Arc shaped sand dune with
two downward pointing ends. |
| |
|
barchanoid dune |
|
Where there is more sand
and the barchans coalesce into something like a line. |
| |
|
transverse dune |
|
A transverse dune is
perpendicular to the prevailing wind, probably caused by a steady build-up of
sand on an already existing minuscule mound. |
| |
|
star dune |
|
A dune that has slip faces
on three or more sides, which is formed by multiple wind directions. |
| |
|
ventifact |
|
Rocks that have been
abraded, pitted, etched, grooved, or polished by wind-driven sand or ice
crystals. |
| |
|
flash flood |
|
A rapid flooding of
geomorphic low-lying areas - washes, rivers, dry lakes and basins. It is caused
by heavy rain associated with a storm, hurricane, or tropical storm. |
| |
|
alluvial fan |
|
Formed where a fast flowing
stream flattens, slows, and spreads typically at the exit of a canyon onto a
flatter plain. |
| |
|
breakwater |
|
structures constructed on
coasts as part of coastal defence or to protect an anchorage from the effects
of weather and longshore drift. |
| |
|
groin |
|
A structure that juts out into a body of water perpendicular
to the shoreline and is built to restore an eroding beach by intercepting
longshore drift and trapping sand.
|
| |
|
drowned coast |
|
A shoreline transformed
from a hilly land surface to an archipelago of small islands by inundation by
the sea. |
| |
|
wave refraction |
|
When waves approach an
irregular shoreline, those approaching headlands (parts of the coast that stick
out) feel bottom and slow before those that are heading towards indentations in
the shore. This causes the waves
to wrap around coastal features. |
| |
|
tsunami |
|
which are usually generated by earthquakes, are odd in that
they have very long wavelengths and low wave heights and very high speed. In the open ocean they have very low
heights (a foot or so) and are usually not even noticed by boats. But their wavelengths are so large that
they feel bottom in fairly deep water, far offshore and they therefore have a
long way in which to build a tremendous wave height. Under the right conditions a tsunami can reach a hundred
feet or more.
|
| |
|
wave of oscillation |
|
open ocean wave |
| |
|
wave of translation |
|
waves that are breaking |
| |
