|
Paleolithic |
|

second part of the Stone Age beginning about 750,00 to 500,000 years BC and lasting until the end of the last ice age about 8,500 years BC |
| |
|
Mesolithic |
|

Belonging to the period of human culture from about 15,000 years ago to about 7000 BCE characterized by complex stone tools and greater social organization - "middle stone age" |
| |
|
Neolithic |
|

the New Stone Age between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; period in which adaptation of sedentary agriculture occurred; domestication of plants and animals accomplished. |
| |
|
Findspot |
|

Place where an artifact was found, or provenance. |
| |
|
Burin |
|

A pointed tool used for engraving or incising. |
| |
|
Relief Sculpture |
|

A sculpture that projects from a flat background. |
| |
|
Freestanding Sculpture |
|
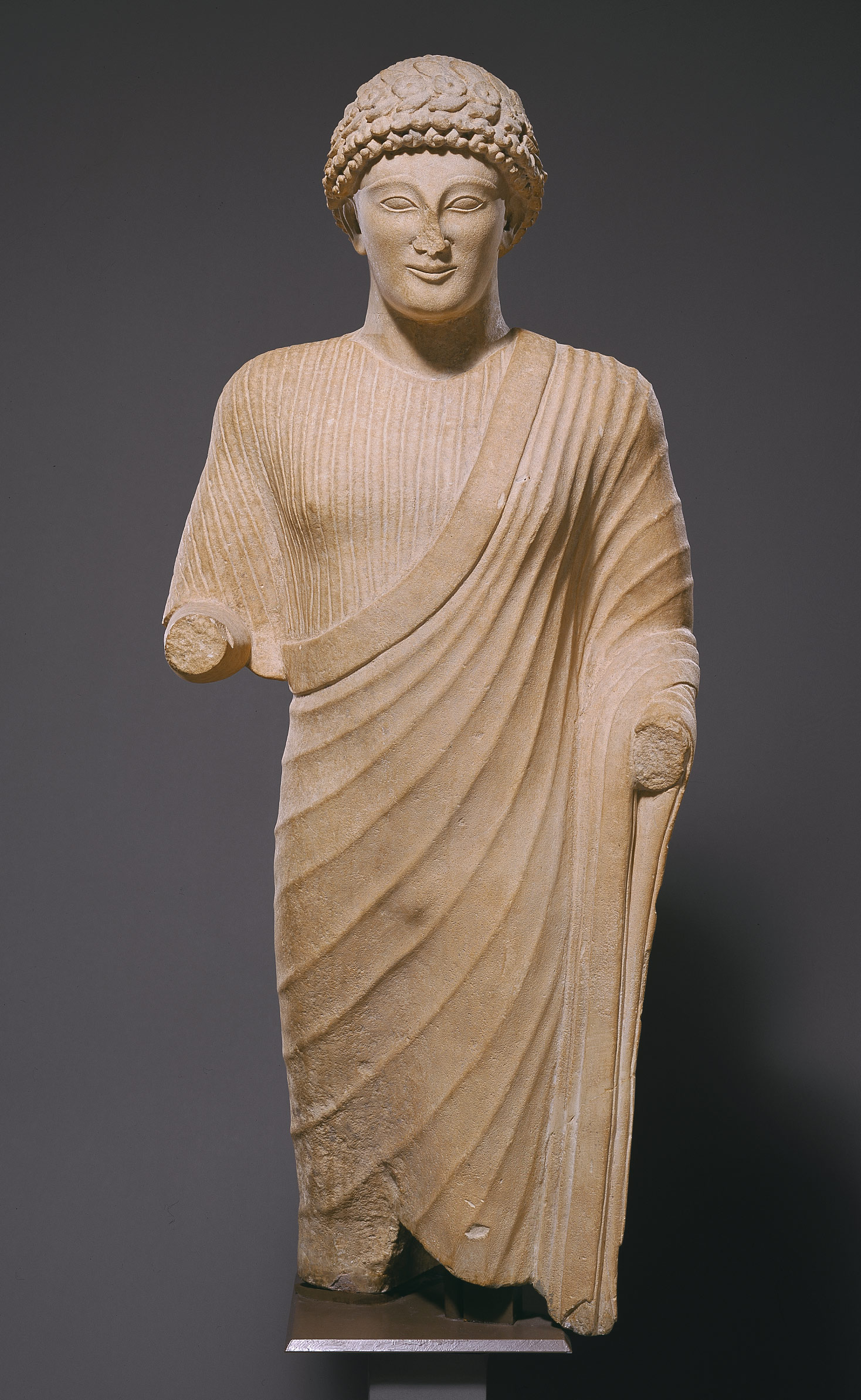

A sculpture that is self-supporting and is designed to be viewed from all sides. |
| |
|
Chisel |
|

An edge tool with a flat steel blade with a cutting edge. |
| |
|
Ground Line |
|

the line where the picture plane and the ground meet |
| |
|
Mural |
|

a large painting applied directly to a wall or ceiling surface |
| |
|
Composite View |
|

A convention of representation in which part of a figure is shown in profile and another part of the same figure is shown frontally; also called twisted perspective. |
| |
|
Corbeled Vault |
|

A vault formed by the piling of stone blocks in horizontal courses, cantilevered inward until the two walls meet in an arch. |
| |
|
Post-lintel system |
|

a type of architectural construction in which two vertical members (posts) support horizontal members (lintels) |
| |
|
Mesopotamia |
|

first civilization located between the Tigris & Eurphrates Rivers in present day Iraq; term means "land between the rivers;" Sumerian culture |
| |
|
Sumerian |
|

a culture that flourished in southern Mesopotamia (contemporary south Iraq) from about 3200 BCE until about 1790 BCE and is credited with the development of significant early city states and the invention of cuneiform writing |
| |
|
Akkadian |
|
2332BCE - when the loosely linked group of cities, known as Sumer, became dominated by the Sargon of Akkad |
| |
|
Neo-Sumerian |
|

Around 2100 BCE - culture that arose after the Guti control, under King Urnammu of Ur |
| |
|
Babylonian |
|
Conquered Akkads. Were first the Amorites, but when they took over, they named their capital Babylon, and were known as such. They were led by Hammurabi, who made the famous code of laws. |
| |
|
Neo-Babylonian |
|

a new Babylonian empire who restored Babylon to its former greatness., An empire ruled by Nebuchadnezzar, that restored Babylon to it's former glory and reigned Mesopotamia from 627 B.C. to 539 B.C. |
| |
|
Ziggurat |
|

a tiered, pyramid-shaped structure that formed part of a Sumerian temple |
| |
|
City-States |
|

Different sections of land owned by the same country but ruled by different rulers |
| |
|
Cuneiform |
|

a system of writing with wedge-shaped symbols, invented by the Sumerians around 3000 B.C. |
| |
|
Cylinder Seals |
|

Sumer's most famous works of art; they were stone cylinders engraved with designs that when rolled over clay, the designs would leave behind their imprint and each seal left its own distinct imprint showing a person's ownership; it was a way to "sign" documents or decorate other objects. |
| |
|
Pictographs |
|

pictures that stand for words or ideas; picture writing |
| |
|
Bent Axis Plan |
|

A plan that incorporates two or more angular changes of direction, characteristic of Sumerian architecture. |
| |
|
Cella |
|

the chamber at the center of an ancient temple; in a classical temple, the room (greek, naos) in which the cult statue usually stood |
| |
|
Votive |
|

an offering given to fulfill a vow |
| |
|
Hierarchy of Scale |
|

a system of representation that expresses a person's importance by the size of his or her representation in a work of art |
| |
|
Registers |
|

also known as bands, one of a series of super imposed bands/friezes in a pictorial narrative, or the particular levels on which motifs are placed |
| |
|
Stele |
|

a monument, vertical in style, small or large, that contained writing or pictures to commemorate or record something |
| |
|
Venus of Willendorf |
|

limestone, Paleolithic, Austria, ca. 28,000-25,000 BCE |
| |
|
Bisons in cave at Altamira |
|

natural pigments, Paleolithic, Spain, ca. 12,000-11,000 BCE |
| |
|
Hall of the Bulls |
|

natural pigments, Paleolithic, Lascaux, France, ca. 15,000-13,000 BCE |
| |
|
Stonehenge |
|

sarsen and bluestones, Neolithic, England, ca. 2550-1600 BCE |
| |
|
White Temple at Uruk |
|

mud bricks, Sumerian, Iraq, ca. 3200-3000 BCE |
| |
|
Statuettes of two worshippers |
|
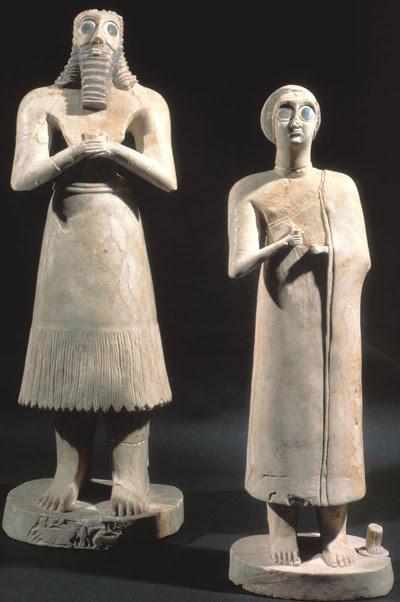

gypsum inlaid with shell and black limestone, Sumerian, Iraq, ca. 2700 BCE |
| |
|
Standard of Ur, from Royal Cemetery at Ur |
|

wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli and red limestone, Sumerian, Iraq, ca. 2600 BCE |
| |
|
Cylinder seal, from Royal Cemetery at Ur |
|

lapis lazuli, Sumerian, Iraq, ca. 2600 BCE |
| |
|
Victory Stele of Naram-Sin |
|

pink sandstone, Akkadian, Iraq, 2250-2218 BCE |
| |
|
Lamassu, from the citadel of Sargon II |
|

limestone, Assyrian, Iraq, ca. 720-705 BCE |
| |
|
Assyrian archers pursuing enemies from the Palace of Ashurnasirpal II |
|

ypsum, Assyrian, Iraq, ca. 875-860 BCE |
| |
|
Gates of Ishtar |
|

glazed bricks, Neo-Babylonian, Iraq, 575 BCE |
| |
